ABBREVIATIONS
VCAM-1
ICAM-1
LPS
HUVEC
NF-κB
MAPK
PI3-kinase
MEK/ERK
JNK
IκBα
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Materials
Cell culture
Western blot analysis
Cell adhesion assay
Data analysis
RESULTS
Effect of ginsenoside Rg2 on LPS-induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression from endothelial cells
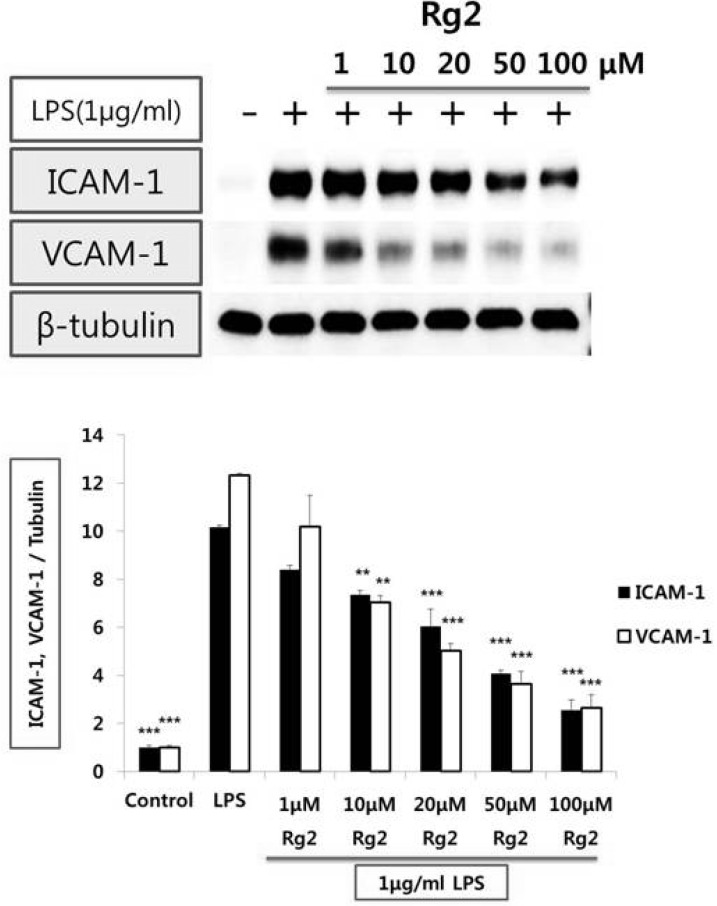 | Fig. 1Effect of Rg2 on the protein expression levels of adhesion molecules in HUVEC stimulated with LPS. Endothelial cell was treated with 1, 10, 20, 50 and 100µmol/l of Rg2 for 1 hr prior to LPS (1µg/ml) stimulation for 8 hr. Cell extracts were resolved on 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and Western blot analysis with the respective primary antibody against VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. β-tubulin was used as an internal control. The bar graph represents the amount of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 estimated by image scanning and is expressed in arbitrary units. Values are means±SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (**p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs LPS). |
The signaling mechanism(s) by which LPS induces VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression from endothelial cells
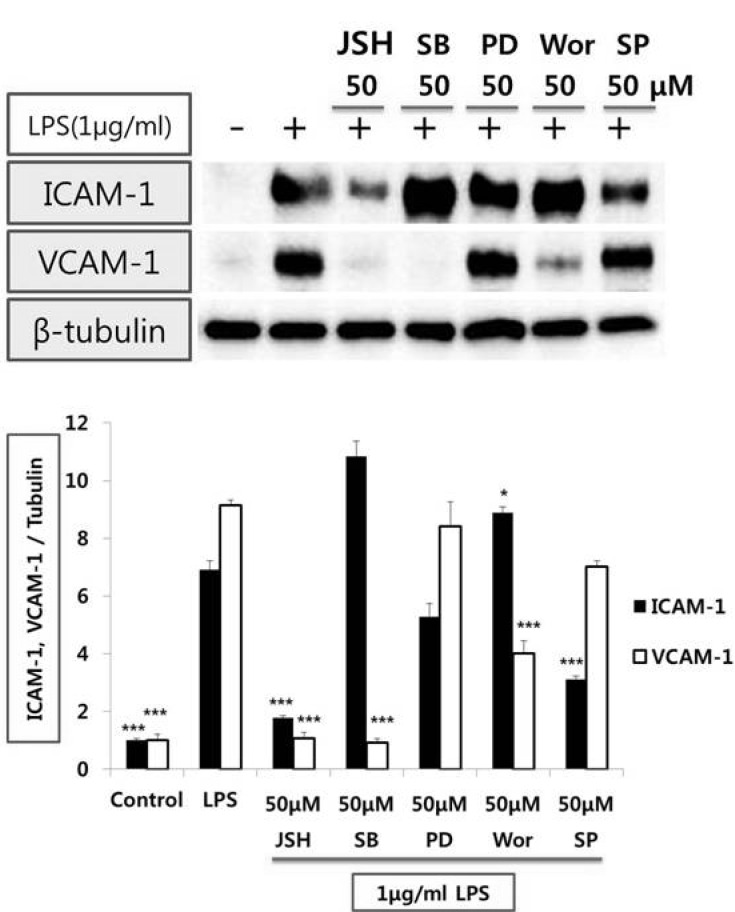 | Fig. 2Effect of inhibitors of signal transduction pathway on the protein expression levels of adhesion molecules in HUVEC stimulated with LPS. Endothelial cell was treated with 50µmol/l of JSH (NF-κB inhibitor), SB202190 (p38 MAPK inhibitor), PD98059 (MEK/ERK inhibitor), wortmannin (PI3-K inhibitor), and SP600125 (JNK inhibitor) for 1hr prior to LPS (1µg/ml) stimulation for 8 hr. Cell extracts were resolved on 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and Western blot analysis with the respective primary antibody against VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. β-tubulin was used as an internal control. The bar graph represents the amount of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 estimated by image scanning and is expressed in arbitrary units. Values are means±SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001 vs LPS). |
Effect of ginsenoside Rg2 on IκBα expression from endothelial cells
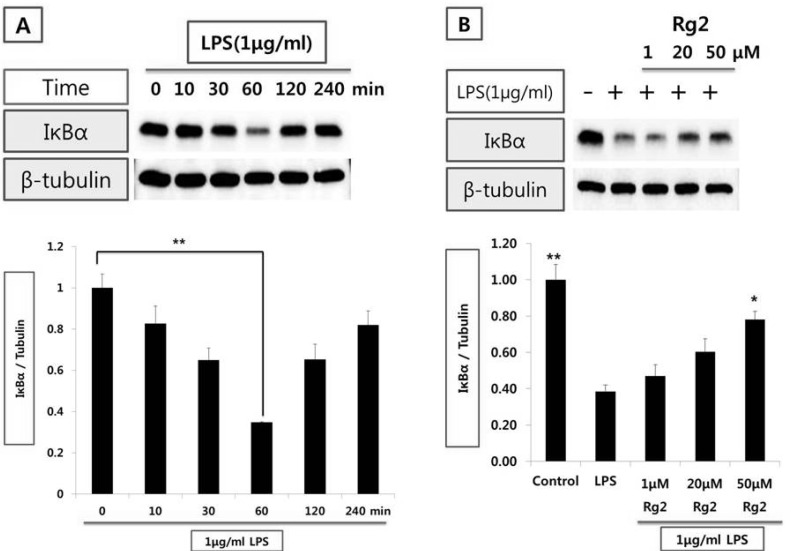 | Fig. 3Effect of Rg2 on IκBα expression in HUVEC stimulated with LPS. (A) Time-course of IκBα expression in HUVECs stimulated with LPS (1µg/ml). (B) Effect of Rg2 on time-course of IκBα expression in HUVEC stimulated with LPS. Endothelial cell was treated with 1, 20, and 50µmol/l of Rg2 prior to LPS (1µg/ml) stimulation for 1 hr. Cell extracts were resolved on 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and Western blot analysis with the respective primary antibody against IκBα. β-tubulin was used as an internal control. The bar graph represents the amount of IκBα estimated by image scanning and is expressed in arbitrary units. Values are means±SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (A: **p<0.05 vs control; B: *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs LPS). |
Effect of ginsenoside Rg2 on THP-1 cell adhesion from endothelial cells
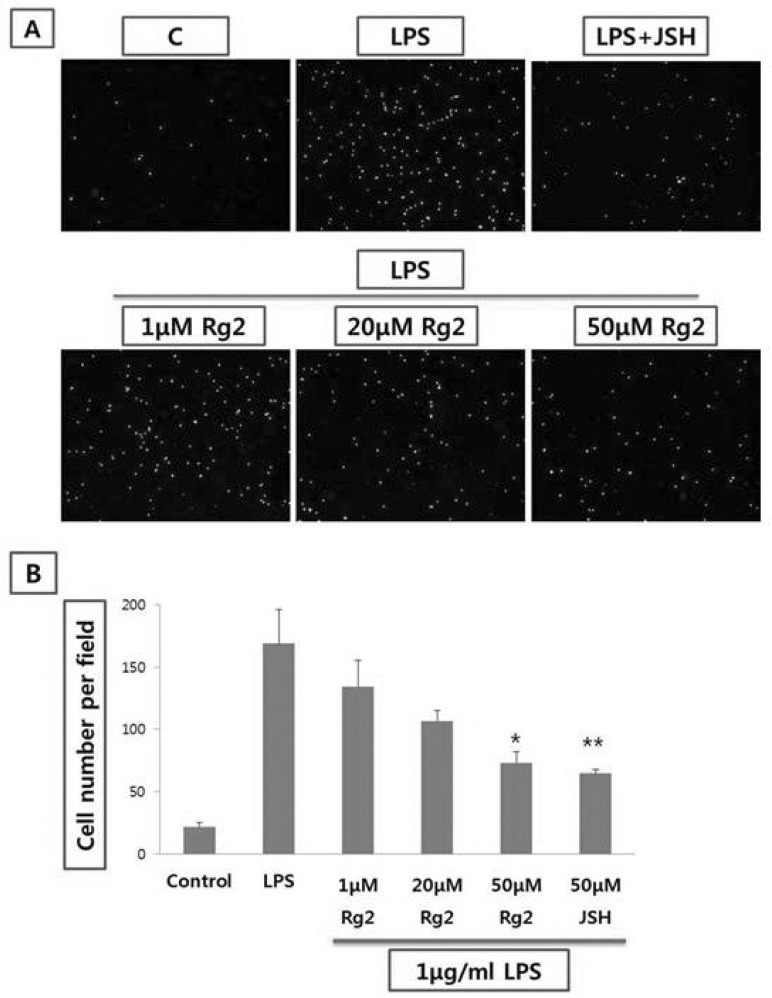 | Fig. 4Effect of Rg2 on THP-1 monocyte adhesion to LPS in HUVEC stimulated with LPS. (A) Endothelial cell was treated with 1, 20, and 50µmol/l of Rg2 prior to LPS (1µg/ml) stimulation for 8 hr. THP-1 cells were labeled with Calcein-AM (5µmol/l) for 30 min. The labeled THP-1 cells were seeded at a density of 5.0×105 cells/well onto endothelial cells treated with the Rg2 and/or LPS and then incubated for 1 hr. Microphotographs (four independent experiments) were obtained using fluorescence microscopy. Magnification ×100. (B) The bar graph represents the cell number of THP-1 monocyte. Values are means±SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by Scheffe post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (*p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs LPS). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download