INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Animals
Induction of chronic constriction injury (CCI)
Drugs
Behavioral assessments
Immunohistochemistry and imaging analysis for pNR1 (ser897)
Rota-rod test
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Antinociceptive effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) on neuropathic pain
 | Fig. 1Effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced mechanical allodynia (MA) and thermal hyperalgesia (TH). CR at a dose of 30 mg/kg significantly reduced mechanical allodynia (A, B) when it was treated in the induction and maintenance phases. In a thermal hyperalgesia test, CR at doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg increased the paw withdrawal latency in the maintenance phase (D), but not induction phase (C). Pregabalin (30 mg/kg) was used as a positive control drug. Lines in each panel indicate the treatment period of CR or pregabalin. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 control vs CR. #p<0.05 and ##p<0.01 control vs pregabalin. |
Antinociceptive effect of Corydalis tuber (CT) on neuropathic pain
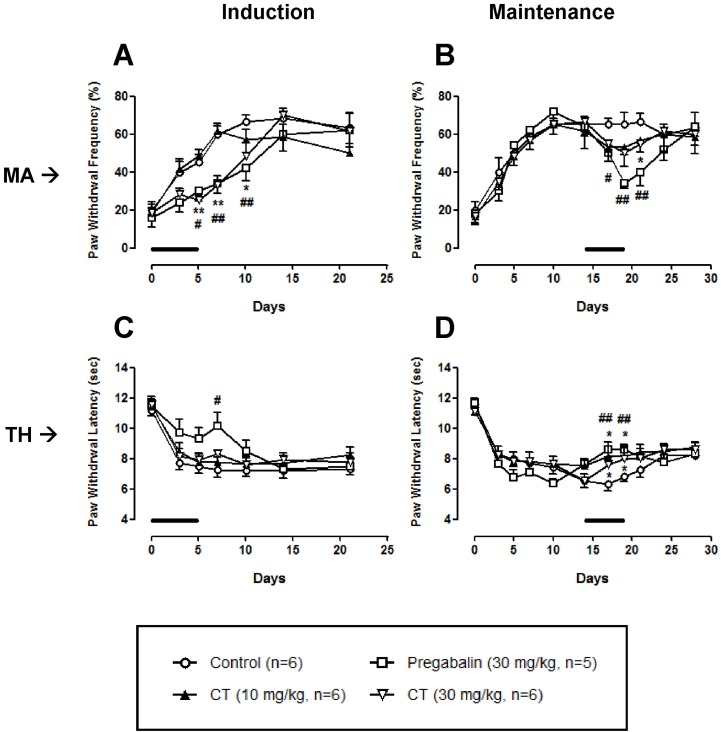 | Fig. 2Effect of Corydalis tuber (CT) on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced mechanical allodynia (MA) and thermal hyperalgesia (TH). CT at a dose of 30 mg/kg significantly reduced mechanical allodynia when it was treated in the induction and maintenance phases (A, B). In a thermal hyperalgesia test, CT at doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg increased the paw withdrawal latency in the maintenance phase (D), but not induction phase (C). Pregabalin (30 mg/kg) was used as a positive control drug. Lines in each panel indicate the treatment period of CT or pregabalin. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 control vs CR. #p<0.05 and ##p<0.01 control vs pregabalin. |
Inhibitory effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) and Corydalis tuber (CT) on chronic constriction injury-induced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit (pNR1)
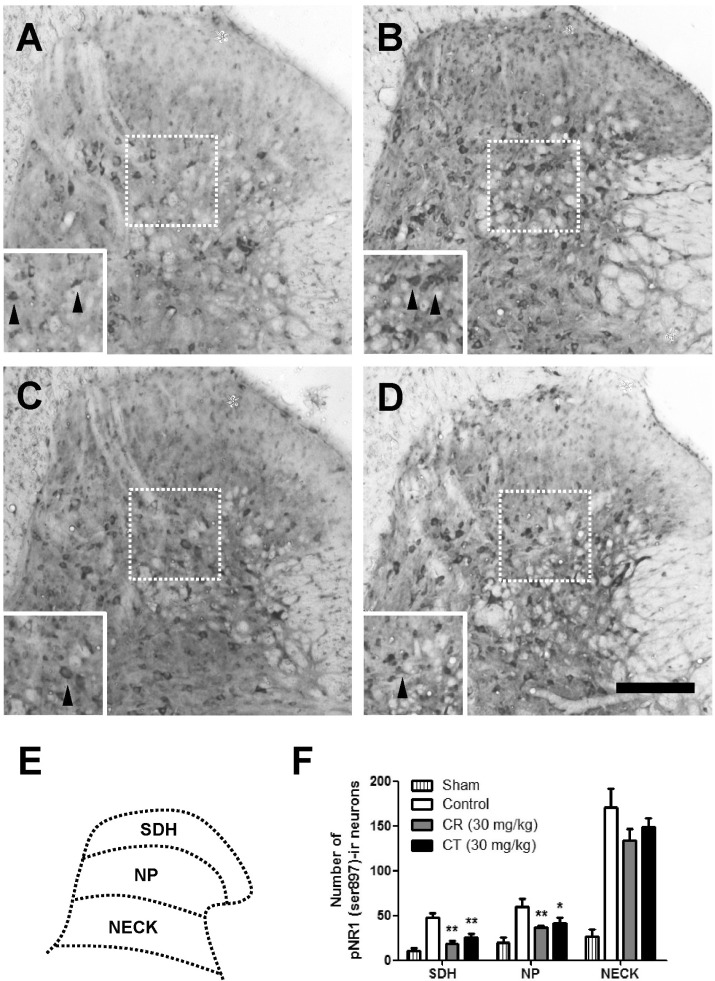 | Fig. 3Effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) and Corydalis tuber (CT) on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit (pNR1) in induction phase. The number of pNR-1 positive neurons was significantly increased by CCI surgery (B) as compared with Sham group (A). Treatment of CR or CT (30 mg/kg) in the induction phase significantly reduced the number of pNR1-immunoreactive neurons both in superficial dorsal horn (SDH) and nucleus proprius (NP) as compared with that of control group (B). However, there is no statistically significant change in neck of dorsal horn (NECK) area. The pNR1 immunoreactivity was observed in Sham (A), control (B), CR (C) and CT (D)-treated groups. Panel (E) shows a diagram depicting the location of the different spinal cord regions analyzed in this study. Results of each group are represented in panel (F). Inserted panels show a magnified image of rectangles in panel A, B, C, and D, respectively. The black arrow heads indicate representative pNR1 neurons. The number of animals is 3 in each group. Scale bar=200 µm. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared to control. |
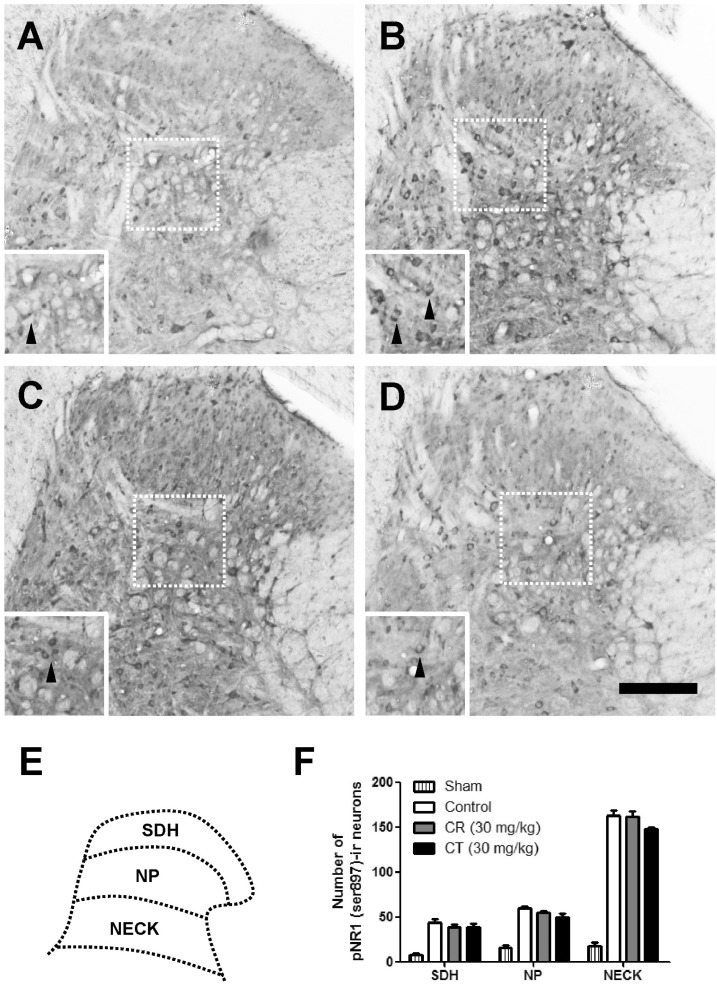 | Fig. 4Effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) and Corydalis tuber (CT) on chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit (pNR1) in maintenance phase. The number of pNR-1 positive neurons was significantly increased by CCI surgery (B) as compared with Sham group (A). Treatment of CR or CT (30 mg/kg) in the maintenance phase did not affect the chronic constriction injury-induced pNR1 in the superficial dorsal horn (SDH), nucleus proprius (NP) and neck of dorsal horn (NECK). The pNR1 immunoreactivity was observed in Sham (A), control (B), CR (C) and CT (D)-treated groups. Panel (E) shows a diagram depicting the location of the different spinal cord regions analyzed in this study. Results of each group are represented in panel (F). Inserted panels show a magnified image of rectangles in panel A, B, C, and D, respectively. The black arrow heads indicate representative pNR1 neurons. The number of animals is 3 in each group. Scale bar=200 µm. |
Rota-rod test
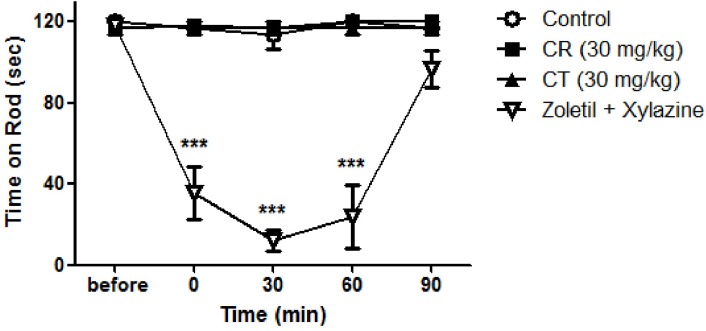 | Fig. 5Effect of Cyperi rhizoma (CR) and Corydalis tuber (CT) on motor function. Rota-rod test revealed that orally treated CR or CT did not affect normal motor function of rats. Positive control drug (Zoletil; 5 mg/kg and xylazine; 0.75 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly suppressed normal motor function. ***p<0.001 compared to control. The number of animals is 3 in each group. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download