INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Cell culture
Generation of retroviral vector
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis
Cell proliferation and cell cycle assay
Apoptosis assay
Flow cytometry analysis
Data analysis
RESULTS
HoxB4 overexpression inhibits the expansion of cell size and granularity in Ba/F3 cells
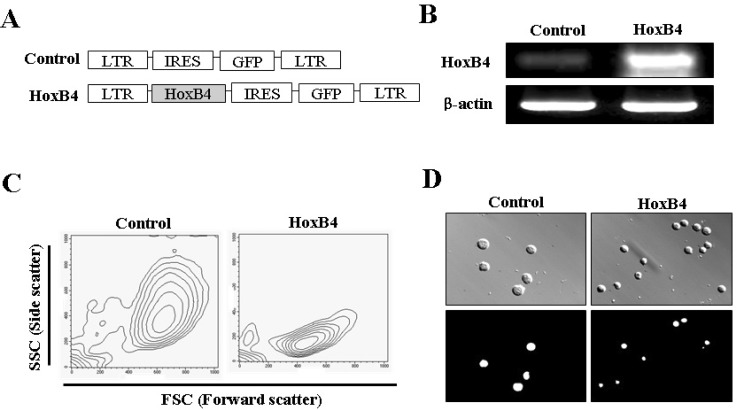 | Fig. 1Retroviral vectors and phenotype induced by HoxB4 in Ba/F3 cells. (A) Constructs of MSCV-GFP and MSCV-HoxB4 retroviral vectors. Schematic representation of the MSCV-HoxB4-IRES-GFP construct and the MSCV-IRES-GFP control vector are shown. (B) Confirmation of HoxB4 expression in Ba/F3 cells. Using cDNA from both infected cells, we examined the effect of HoxB4-expressing Ba/F3 cells using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). (C) Phenotype of Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells. The morphology of the HoxB4-infected cells was demonstrated via FSC (forward scatter) and SSC (side scatter) in fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. (D) Photomicrograph of Ba/F3 cells with HOXB4 overexpression. Upper panels, cell images observed under condition of phase contrast illumination; Lower panel, GFP fluorescence images in cells corresponding to phase contrast images. Representative pictures are shown from at least three independent experiments. Magnification ×400. |
HoxB4 promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in the absence of survival signals
 | Fig. 2Biological activities of HoxB4 in Ba/F3 cells. (A) Proliferation rate of Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells. 2×103 Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were cultured with 5 ng/ml IL-3 (survival cytokine) in 96-well plates for 3 days and cell proliferation activity was assessed via MTT assay. Data are expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD). *p<0.05 in comparison with control cells. (B) Alteration of the cell cycle by HoxB4. Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HOXB4 cells were stained with PI and detected by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) after incubation in normal culture conditions. Data are expressed as mean±SD. (C) Inhibitory effect of apoptotic cell death by HoxB4. Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were incubated without IL-3 (-) for 24 h, and then the apoptotic cell death of Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells was measured using the Annexin V and PI assay with FACS. The data express the rate of double-negative (live), single-positive (early apoptosis and necrosis), and double-positive (late apoptosis) cells. |
HoxB4 prevents apoptotic cell death under conditions of cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase
 | Fig. 3Biological effects of HoxB4 in cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. (A) HoxB4 in the cell cycle. Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were incubated with 100 nM DOX for 24 h, and then the DNA content was determined by PI staining with flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry data and the percentage of cells at each stage of the cell cycle are shown. These data represent the mean±standard deviation (SD) from 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05 in comparison with control cells. (B) Apoptosis assay of Ba/F3 cells infected with HoxB4. Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were incubated with media containing 100 nM DOX. After staining with Annexin V-PE and PI, we performed flow cytometry. The data represent the proportions of double-negative (live), single-positive (early apoptosis and necrosis), and double-positive (late apoptosis) cells. |
HoxB4 prohibits apoptotic cell death by Fas stimulation
 | Fig. 4Biological activities of HoxB4 in conditions that stimulate the Fas (CD95) apoptotic signaling pathway. (A) Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were cultured with 100 nM DOX for 24 h, recovered, and stained with anti-Fas (CD95) antibody, and immune fluorescence was quantified by flow cytometric analysis. Numbers in the upper parts of histogram curves indicate the positive intensity values of Fas expression in cells. The graph was obtained from left two panels and represents fold changes between results from Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells in the presence of DOX. *p<0.05 in comparison with control cells. (B) Stimulation of the Fas apoptotic signal pathway. Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were treated with 1 µg/ml agonistic antibody (clone Jo2) for 24 h and analyzed by flow cytometry after staining with Annexin V-PE and PI. The data represent the proportions of double-negative (live), single-positive (early apoptosis and necrosis), and double-positive (late apoptosis) cells. (C) Stimulation of Fas induced by DOX. Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were treated with 1 µg/ml agonistic antibody (clone Jo2) and 100 nM DOX for 24 h and analyzed by flow cytometry after staining with Annexin V-PE and PI. The data express the proportions of double-negative (live), single-positive (early apoptosis and necrosis), and double-positive (late apoptosis) cells. (D) Photomicrograph of cells incubated with DOX and Jo2 antibody. Ba/F3-GFP and Ba/F3-HoxB4 cells were seeded in 24-well plates (5×105 cells in each well) and incubated with complete media, 100 nM DOX or 1 µg/ml Jo2 antibody and after 24 h, the morphology change of cells were observed in each well. Magnification ×40. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download