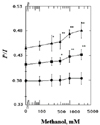
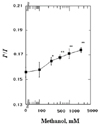
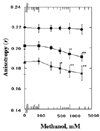
1. Chin JH, Goldstein DB. Effects of low concentrations of ethanol on the fluidity of spin-labeled erythrocyte and brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1977. 13:435–441.
2. Chin JH, Goldstein DB. Drug tolerance in biomembranes: a spin label study of the effects of ethanol. Science. 1977. 196:684–685.
3. Chin JH, Goldstein DB. Membrane-disordering action of ethanol: variation with membrane cholesterol content and depth of the spin label probe. Mol Pharmacol. 1981. 19:425–431.
4. Chin JH, Goldstein DB. Cholesterol blocks the disordering effects of ethanol in biomembranes. Lipids. 1984. 19:929–935.
5. Goldstein DB, Chin JH, Lyon RC. Ethanol disordering of spin-labeled mouse brain membranes: correlation with genetically determined ethanol sensitivity of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982. 79:4231–4233.
6. Avdulov NA, Wood WG, Harris RA. Effects of ethanol on structural parameters of rat brain membranes: relationship to genetic differences in ethanol sensitivity. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1994. 18:53–59.
7. Avdulov NA, Chochina SV, Draski LJ, Deitrich RA, Wood WG. Chronic ethanol consumption alters effects of ethanol in vitro on brain membrane structure of high alcohol sensitivity and low alcohol sensitivity rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1995. 19:886–891.
8. Jang HO, Jeong DK, Ahn SH, Yoon CD, Jeong SC, Jin SD, Yun I. Effects of chlorpromazine HCl on the structural parameters of bovine brain membranes. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. 37:603–611.
9. Jang HO, Shin HG, Yun I. Effects of dimyristoylphosphatidylethanol on the structural parameters of neuronal membrane. Mol Cells. 2004. 17:485–491.
10. Bae MK, Jeong DK, Park NS, Lee CH, Cho BH, Jang HO, Yun I. The effect of ethanol on the physical properties of neuronal membranes. Mol Cells. 2005. 19:356–364.
11. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Molecular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1982. 300:487–493.
12. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Do general anaesthetics act by competitive binding to specific receptors? Nature. 1984. 310:599–601.
13. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Mapping of general anaesthetic target sites provides a molecular basis for cutoff effects. Nature. 1985. 316:349–351.
14. Armbrecht HJ, Wood WG, Wise RW, Walsh JB, Thomas BN, Strong R. Ethanol-induced disordering of membranes from different age groups of C57BL/6NNIA mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983. 226:387–391.
15. Goldstein DB. The effects of drugs on membrane fluidity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984. 24:43–64.
16. Villalaína J, Prietob M. Location and interaction of N-(9-anthroyloxy)-stearicacid probes in corporated in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991. 59:9–16.
17. Mason JT. Properties of phosphatidylcholine bilayers as revealed by mixed-acyl phospholipid fluorescent probes containing n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994. 1194:99–108.
18. Thulborn KR, Sawyer WH. Properties and the locations of a set of fluorescent probes sensitive to the fluidity gradient of the lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978. 511:125–140.
19. Tilley L, Thulborn KR, Sawyer WH. An assessment of the fluidity gradient of the lipid bilayer as determined by a set of n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acids (n=2, 6, 9, 12, 16). J Biol Chem. 1979. 254:2592–2594.
20. Molitoris BA, Hoilien C. Static and dynamic components of renal cortical brush border and basolateral membrane fluidity: role of cholesterol. J Membr Biol. 1987. 99:165–172.
21. Yun I, Cho ES, Jang HO, Kim UK, Choi CH, Chung IK, Kim IS, Wood WG. Amphiphilic effects of local anesthetics on rotational mobility in neuronal and model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. 1564:123–132.
22. Yun I, Kang JS. The general lipid composition and aminophospholipid asymmetry of synaptosomal plasma membrane vesicles isolated from bovine cerebral cortex. Mol Cells. 1990. 1:15–20.
23. Yun I, Kim YS, Yu SH, Chung IK, Kim IS, Baik SW, Cho GJ, Chung YZ, Kim SH, Kang JS. Comparison of several procedures for the preparation of synaptosomal plasma membrane vesicles. Arch Pharm Res. 1990. 13:325–329.
24. Yun I, Yang MS, Kim IS, Kang JS. Bulk vs. transbilayer effects of ethanol on the fluidity of the plasma membrane vesicles of cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Asia Pacific J Pharmacol. 1993. 8:9–16.
25. Yun I, Lee SH, Kang JS. The effect of ethanol on lateral and rotational mobility of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from cultured Mar 18.5 hybridoma cells. J Membr Biol. 1994. 138:221–227.
26. Kang JS, Choi CM, Yun I. Effects of ethanol on lateral and rotational mobility of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from cultured mouse myeloma cell line Sp2/0-Ag14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996. 1281:157–163.
27. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NR, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951. 193:265–275.
28. Dobretsov GE, Spirin MM, Chekrygin OV, Karmansky IM, Dmitriev VM, Vladimirov YuA. A fluorescence study of apolipoprotein localization in relation to lipids in serum low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982. 710:172–180.
29. Sweet WD, Wood WG, Schroeder F. Charged anesthetics selectively alter plasma membrane order. Biochemistry. 1987. 26:2828–2835.
30. Schroeder F, Morrison WJ, Gorka C, Wood WG. Transbilayer effects of ethanol on fluidity of brain membrane leaflets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988. 946:85–94.
31. Wood WG, Gorka C, Schroeder F. Acute and chronic effects of ethanol on transbilayer membrane domains. J Neurochem. 1989. 52:1925–1930.
32. Zachariasse KA, Vaz WL, Sotomayor C, Kühnle W. Investigation of human erythrocyte ghost membranes with intramolecular excimer probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982. 688:323–332.
33. Schachter D. Fluidity and function of hepatocyte plasma membranes. Hepatology. 1984. 4:140–151.
34. Stubbs CD, Williams BW. Fluorescence in membranes: Fluorescence Spectroscopy in Biochemistry. 1992. Vol 3. New York: Plenum Press;231–263.
35. Brasaemle DL, Robertson AD, Attie AD. Transbilayer movement of cholesterol in the human erythrocyte membrane. J Lipid Res. 1988. 29:481–489.
36. Cogan U, Schachter D. Asymmetry of lipid dynamics in human erythrocyte membranes studied with impermeant fluorophores. Biochemistry. 1981. 20:6396–6403.
37. Schachter D, Abbott RE, Cogan U, Flamm M. Lipid fluidity of the individual hemileaflets of human erythrocyte membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983. 414:19–28.
38. Wood WG, Schroeder F, Hogy L, Rao AM, Nemecz G. Asymmetric distribution of a fluorescent sterol in synaptic plasma membranes: effects of chronic ethanol consumption. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990. 1025:243–246.
39. Chabanel A, Abbott RE, Chien S, Schachter D. Effects of benzyl alcohol on erythrocyte shape, membrane hemileaflet fluidity and membrane viscoelasticity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985. 816:142–152.
40. Seigneuret M, Zachowski A, Hermann A, Devaux PF. Asymmetric lipid fluidity in human erythrocyte membrane: new spin-label evidence. Biochemistry. 1984. 23:4271–4275.
41. Curtain CC, Gordon LM, Aloia RC. The role of cholesterol in regulating membrane fluidity: Advances in Membrane Fluidity. 1988. Vol 2. New York: Alan R Liss;1–15.
42. Kier AB, Sweet WD, Cowlen MS, Schroeder F. Regulation of transbilayer distribution of a fluorescent sterol in tumor cell plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986. 861:287–301.
43. Schroeder F, Nemecz G, Wood WG, Joiner C, Morrot G, Ayraut-Jarrier M, Devaux PF. Transmembrane distribution of sterol in the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991. 1066:183–192.
44. Lee YH, Park NS, Kwon JD, Park JS, Shin GB, Lee CS, Jung TS, Choi NJ, Yoon JH, Ok JS, Yoon UC, Bae MK, Jang HO, Yun I. Amphiphilic effects of dibucaine HCl on rotational mobility of n-(9-anthroyloxy)stearic acid in neuronal and model membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 2007. 146:33–42.
45. Janoff AS, Boni LT, Rauch J. Phase-defined domain in biological membranes: Advances in Membrane Fluidity. 1988. Vol 2. New York: Alan R Liss;101–109.
46. Curry S, Lieb WR, Franks NP. Effects of general anesthetics on the bacterial luciferase enzyme from Vibrio harveyi: an anesthetic target site with differential sensitivity. Biochemistry. 1990. 29:4641–4652.
47. Dickinson R, Smith EH, Franks NP, Lieb WR. Synthesis and use of the n-bromododecane-1,12-diols as conformational probes for general anesthetic target sites. J Med Chem. 1993. 36:111–118.
48. Dickinson R, Franks NP, Lieb WR. Thermodynamics of anesthetic/protein interactions. Temperature studies on firefly luciferase. Biophys J. 1993. 64:1264–1271.
49. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Neuron membranes: anaesthetics on the mind. Nature. 1987. 328:113–114.
50. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Do general anaesthetics act by competitive binding to specific receptors? Nature. 1984. 310:599–601.
51. Franks NP, Lieb WR. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1994. 367:607–614.
52. Moss GW, Franks NP, Lieb WR. Modulation of the general anesthetic sensitivity of a protein: a transition between two forms of firefly luciferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991. 88:134–138.
53. Moss GW, Lieb WR, Franks NP. Anesthetic inhibition of firefly luciferase, a protein model for general anesthesia, does not exhibit pressure reversal. Biophys J. 1991. 60:1309–1314.
54. Gonzales RA, Hoffman PL. Receptor-gated ion channels may be selective CNS targets for ethanol. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991. 12:1–3.
55. Sanna E, Concas A, Serra M, Santoro G, Biggio G. Ex vivo binding of t-[35S )butylbicyclophosphorothionate: a biochemical tool to study the pharmacology of ethanol at the gamma-aminobutyric acid-coupled chloride channel. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991. 256:922–928.
56. Manevich EM, Köiv A, Järv J, Molotkovsky JG, Bergelson LD. Binding of specific ligands to muscarinic receptors alters the fluidity of membrane fragments from rat brain. A fluorescence polarization study with lipid-specific probes. FEBS Lett. 1988. 236:43–46.