ABBREVIATIONS
TEA
APA
Glib
L-NNA
ODQ
sGC
4-AP
KV channel
NO
NANC
GI tract
KBC
NBC
TTX
ATR
ACh
SNP
[Ca2+]i
VDCCL
ICC
INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Tissue preparation for isometric contraction
Solution and drugs
Statistics
RESULTS
Isometric contraction of circular smooth muscle in corpus greater curvature (GC) of human stomach
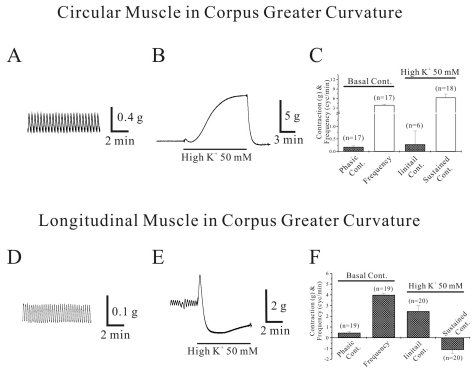 | Fig. 1Isometric contraction of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle of corpus greater curvature (GC). Circular muscle of human gastric corpus GC showed spontaneous contraction (A). In panel (B), high-K+ produced initial and tonic contraction. Data was summarized in (C). Longitudinal muscles of corpus GC also showed spontaneous contraction (D). However, high K+ produced sustained relaxation (E). Each data from circular and longitudinal muscle were summarized in (C, F). |
Isometric contraction of longitudinal smooth muscle in corpus GC of human stomach
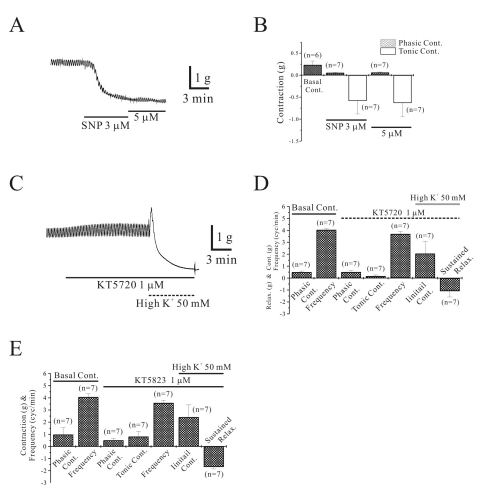 | Fig. 2Effect of protein kinase inhibitors on high K+-induced relaxation of longitudinal smooth muscle of corpus GC. Sodium nitroprusside (SNP)-induced relaxation of longitudinal muscle was studied. SNP (3~5 µM) produced relaxation (A) and data was summarized in (B). High K+-induced relaxation was also studied in the presence of KT 5720, which is known to inhibit PKA. As shown in (C) and (D), high K+-induced sustained relaxation was not affected by pretreatment of KT 5720. High K+-induced relaxation was also studied by pretreatment of KT 5823, inhibitor of PKG. In the presence of KT 5823 (1 µM), high K+ produced sustained relaxation too (E). |
Effect of L-NNA on high K+-induced relaxation in longitudinal smooth muscle of corpus GC of human stomach
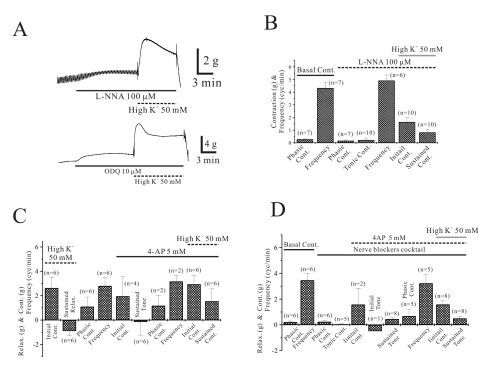 | Fig. 3Effect of L-NNA, ODQ and 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) on high K+-induced relaxation of longitudinal smooth muscle of corpus GC. High K+-induced relaxation was also studied in the presence of L-NNA. As shown in (A) and (B), high K+-induced relaxation was blocked relaxation and transited it to contraction by pretreatment of L-NNA and ODQ. Data was summarized in (B). Effect of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), KV channel blocker, on high K+-induced relaxation. In the presence or absence of NBC, pretreatment of 4-AP blocked relaxation and transited it to contraction (C, D). |
Effects of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) on high K+-induced relaxation of longitudinal smooth muscle in human gastric corpus GC
Isometric contraction of circular smooth muscle of corpus lesser curvature (LC) of human stomach
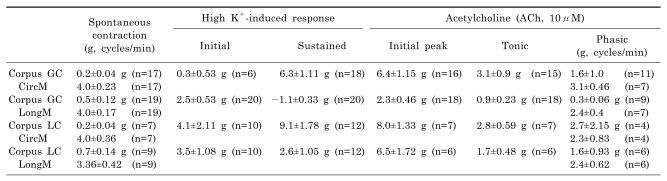
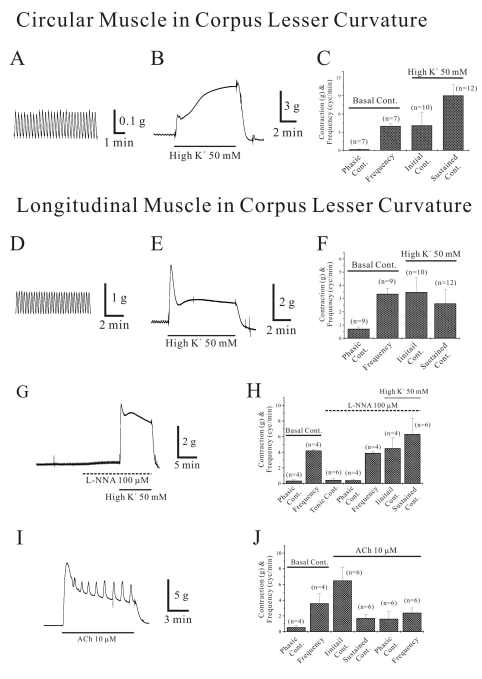 | Fig. 4Isometric contraction of circular smooth muscle of corpus lesser curvature (LC) of human stomach. Contractile properties of circular and longitudinal smooth muscles of corpus LC was studied. Circular muscle of human gastric corpus LC showed spontaneous contraction (A). In panel (B), high-K+ produced initial and tonic contraction. Data was summarized in (C). Meanwhile, longitudinal muscles of corpus LC also showed spontaneous contraction (D). However, high K+ produced initial contraction followed by weak contraction in longitudinal muscle of corpus LC (E). Data was summarized in (F). We also studied effect of L-NNA on high K+-induced contraction in longitudinal muscle of corpus LC (G). L-NNA (100 µM) produced tonic (0.5 g) and phasic contractions (0.4 g) and high K+ in the presence of L-NNA produced initial (4.5 g) and sustained contraction (6.3 g), respectively. Data was summarized in (H). In (I) and (J), ACh-induced contraction is shown. ACh (10 µM) produced initial transient contraction followed by later sustained tonic contraction with superimposed phasic contractions. |
Isometric contraction of longitudinal smooth muscle of corpus LC of human stomach
Isometric contraction of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle in higher portion of corpus GC of human stomach
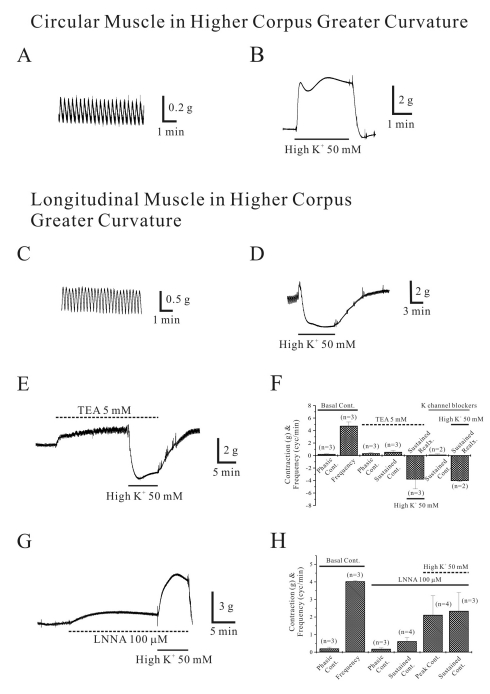 | Fig. 5Isometric contraction of circular and longitudinal muscle of higher portion of corpus GC. Circular muscle of human gastric higher portion of corpus GC showed spontaneous contraction (A). In panel (B), high-K+ produced initial and tonic contraction. Longitudinal muscles also showed spontaneous contraction (C). However, high K+ produced sustained relaxation (D). This relaxation in longitudinal muscle was not affected by pretreatment of TEA 5 mM (E) and K+ channel blockers cocktail (F). However, high K+-induced relaxation was blocked and transited to contraction by pretreatment of L-NNA (G, H). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download