Abstract
Defensins, cysteine-rich cationic polypeptides released from neutrophils, are known to have powerful antimicrobial properties. In this study, we sacrificed 30 rats to investigate the effects of α-defensin 1 on detrusor muscle contractions in isolated rat bladder. From the experiments we found relaxing effects of α-defensin 1 on the contractions induced by phenylephrine (PE) but not by bethanechol (BCh) in the detrusor smooth muscles. To determine the mechanisms of the effects of α-defensin 1, the changes of effects on PE-induced contraction by α-defensin 1 pretreatment were observed after pretreatment of Rho kinase inhibitor (Y-27632), protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor (Calphostin C), potent activator of PKC (PDBu; phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate), and NF-κ:B inhibitors (PDTC; pyrrolidinedithio-carbamate and sulfasalazine). The contractile responses of PE (10–9∼10–4 M) were significantly decreased in some concentrations of α-defensin 1 (5×10–9 and 5×10–8 M). When strips were pretreated with NF-κB inhibitors (PDTC and sulfasalazine; 10–7 ∼ 10–6 M), the relaxing responses by α-defensin 1 pretreatment were disappeared. The present study demonstrated that α-defensin 1 has relaxing effects on the contractions of rat detrusor muscles, through NF-κB pathway. Further studies in vivo are required to clarify whether α-defensin 1 might be clinically related with bladder dysfunction by inflammation process.
Go to : 
References
2. Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ. Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:551–557.

3. Nassar T, Akkawi S, Bar-Shavit R, Haj-Yehia A, Bdeir K, Al-Mehdi AB, Tarshis M, Higazi AA. Human alpha-defensin regulates smooth muscle cell contraction: a role for low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. Blood. 2002; 100:4026–4032.
4. Kougias P, Chai H, Lin PH, Yao Q, Lumsden AB, Chen C. Neutrophil antimicrobial peptide alpha-defensin causes endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 43:357–363.
5. Durlu-Kandilci NT, Brading AF. Involvement of Rho kinase and protein kinase C in carbachol-induced calcium sensitization in beta-escin skinned rat and guinea-pig bladders. Br J Pharmacol. 2006; 148:376–384.
6. Meyer-Siegler KL, Iczkowski KA, Vera PL. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is increased in the urine of patients with urinary tract infection: macrophage migration inhibitory factor-protein complexes in human urine. J Urol. 2006; 175:1523–1528.

7. Chang S, Hypolite JA, Mohanan S, Zderic SA, Wein AJ, Chacko S. Alteration of the PKC-mediated signaling pathway for smooth muscle contraction in obstruction-induced hypertrophy of the urinary bladder. Lab Invest. 2009; 89:823–832.

8. Kim JK, Han WH, Lee MY, Myung SC, Kim SC, Kim MK. Testosterone relaxes rabbit seminal vesicle by calcium channel inhibition. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008; 12:73–77.

9. Raj PA, Dentino AR. Current status of defensins and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002; 206:9–18.

10. Selsted ME, Ouellette AJ. Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:551–557.

12. Ganz T. Extracellular release of antimicrobial defensins by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1987; 55:568–571.

13. Harwig SS, Ganz T, Lehrer RI. Neutrophil defensins: purification, characterization, and antimicrobial testing. Methods Enzymol. 1994; 236:160–172.

14. Weichhart T, Haidinger M, Hörl WH, Säemann MD. Current concepts of molecular defence mechanisms operative during urinary tract infection. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008; 38 Suppl. 2:29–38.

15. Kougias P, Chai H, Lin PH, Yao Q, Lumsden AB, Chen C. Neutrophil antimicrobial peptide alpha-defensin causes endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 43:357–363.
16. Moore KH, Simons A, Mukerjee C, Lynch W. The relative incidence of detrusor instability and bacterial cystitis detected on the urodynamic-test day. BJU Int. 2000; 85:786–792.

17. Sibley GN. A comparison of spontaneous and nerve-mediated activity in bladder muscle from man, pig and rabbit. J Physiol. 1984; 354:431–443.

18. Stein PC, Pham H, Ito T, Parsons CL. Bladder injury model induced in rats by exposure to protamine sulfate followed by bacterial endotoxin. J Urol. 1996; 155:1133–1138.

19. Meyer-Siegler KL, Ordorica RC, Vera PL. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is upregulated in an endotoxin-induced model of bladder inflammation in rats. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004; 24:55–63.

20. Taylor JA 3rd, Kuchel GA. Detrusor underactivity: clinical features and pathogenesis of an underdiagnosed geriatric condition. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006; 54:1920–1932.

21. Taylor JA, Zhu Q, Irwin B, Maghaydah Y, Tsimikas J, Pilbeam C, Leng L, Bucala R, Kuchel GA. Null mutation in macrophage migration inhibitory factor prevents muscle cell loss and fibrosis in partial bladder outlet obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 291:F1343–1353.

22. Wang XC, Saban R, Kaysen JH, Saban MR, Allen PL, Benes EN, Hammond TG. Nuclear factor kappa B mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the urinary bladder. J Urol. 2000; 163:993–998.

23. Kinoshita K, Sato K, Hori M, Ozaki H, Karaki H. Decrease in activity of smooth muscle L-type Ca2+ channels and its reversal by NF-kappaB inhibitors in Crohn's colitis model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003; 285:G483–493.
Go to : 
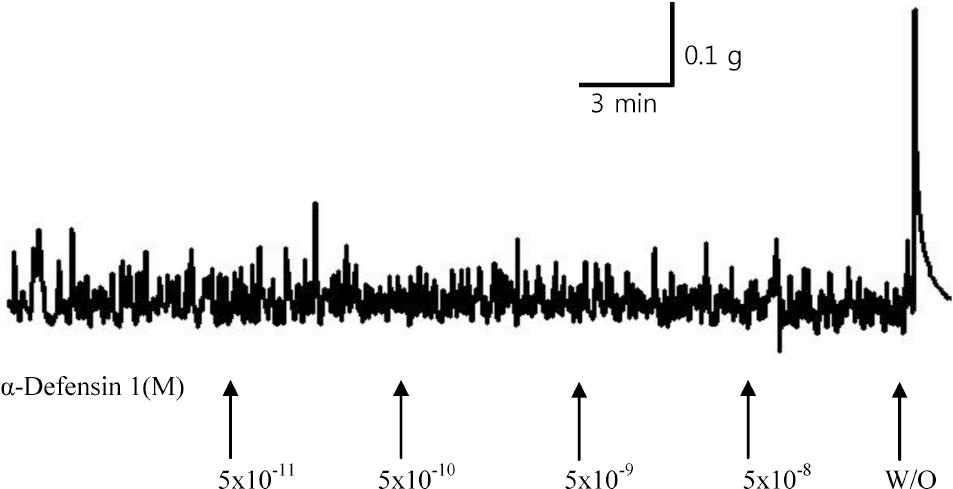 | Fig. 1.Typical representation of α-defensin-induced response of rat urinary bladder strip. No remarkable change was detected (W/O means wash out with PSS). |
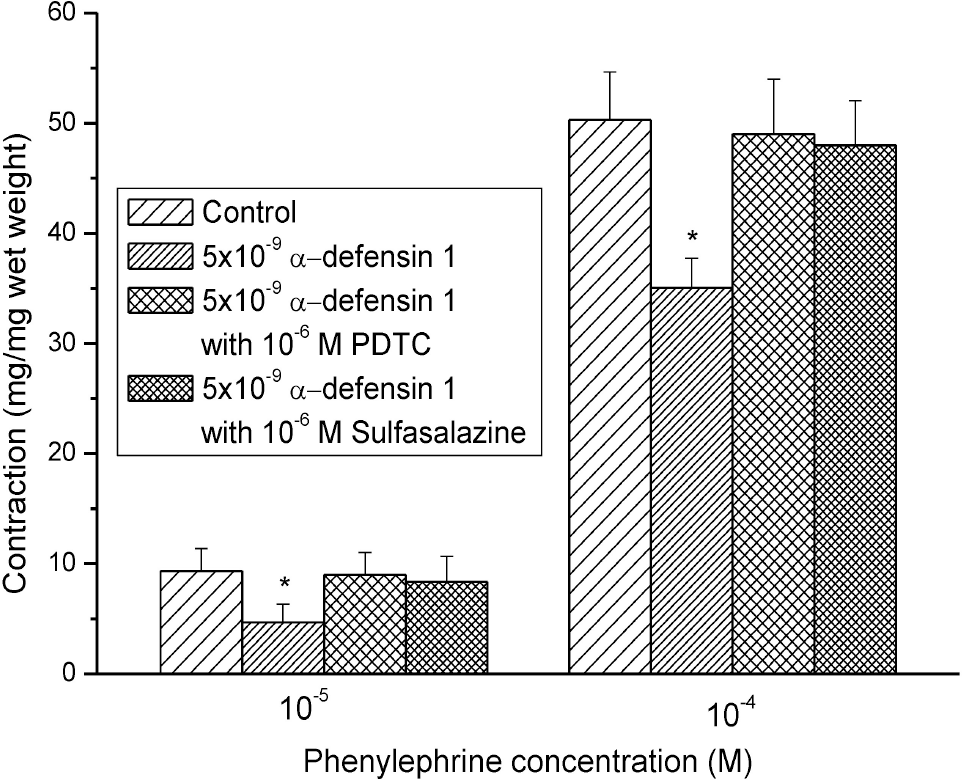
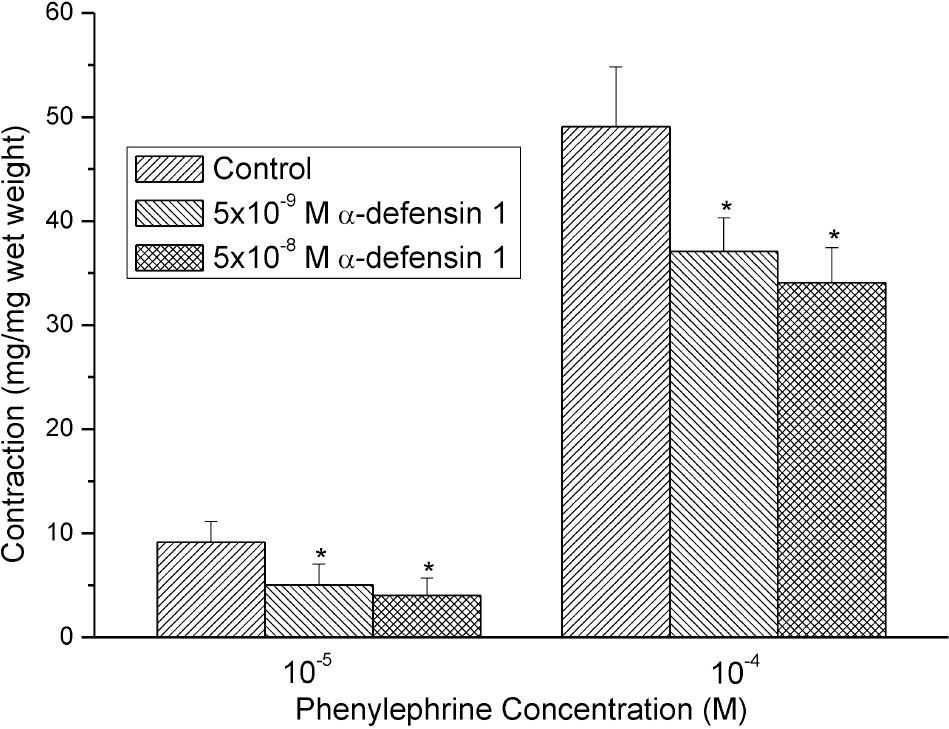 | Fig. 2.Effects of 10–9 M and 10–8 M α-defensin-pretreatment on the PE-induced contractures. The contractile responses were decreased and the effects were statistically significant (n=8, ∗means p<0.05). |
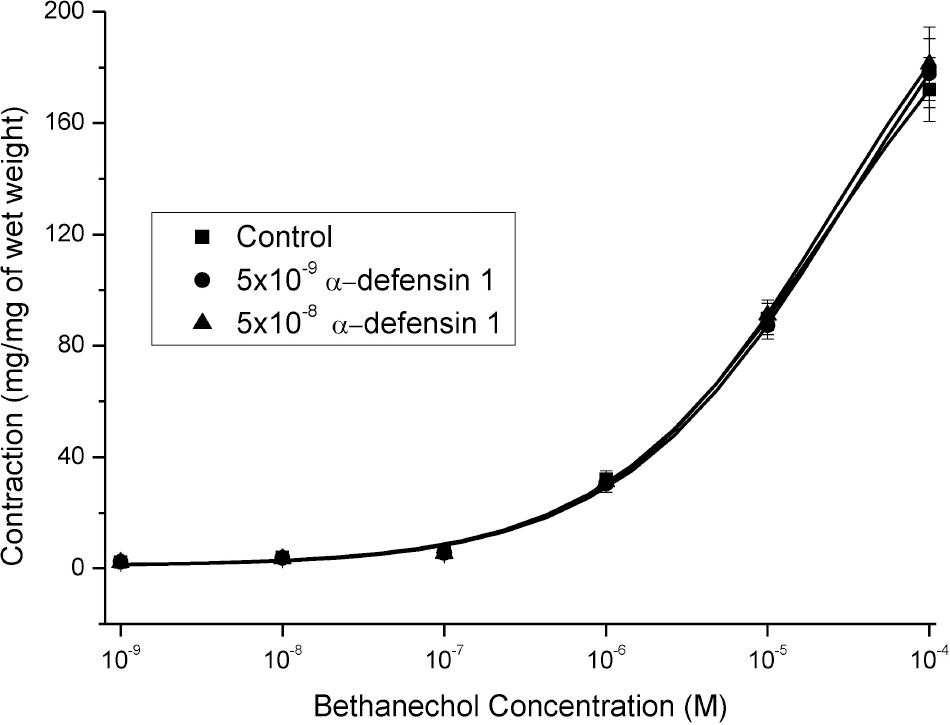 | Fig. 3.Effects of 10–9 M and 10–8 M α-defensin-pretreatment on the BCh-induced contractures. The tensions of contracture were rarely affected by the pretreatments (n=12). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download