Abstract
Epidermal keratinocytes overgrow in response to ultraviolet-B (UVB), which may be associated with skin photoaging and cancer development. Recently, we found that HIF-1α controls the keratinocyte cell cycle and thereby contributes to epidermal homeostasis. A further study demonstrated that HIF-1α is down-regulated by UVB and that this process is involved in UVB-induced skin hyperplasia. Therefore, we hypothesized that the forced expression of HIF-1α in keratinocytes would prevent UVB-induced keratinocyte overgrowth. Among several agents known to induce HIF-1α, pyrithione-zinc (Py-Zn) overcame the UVB suppression of HIF-1α in cultured keratinocytes. Mechanistically, Py-Zn blocked the degradation of HIF-1α protein in keratinocytes, while it did not affect the synthesis of HIF-1α. Moreover, the p21 cell cycle inhibitor was down-regulated after UVB exposure, but was robustly induced by Py-Zn. In mice repeatedly irradiated with UVB, the epidermis became hyperplastic and HIF-1α disappeared from nuclei of epidermal keratinocytes. However, a cream containing Py-Zn effectively prevented the skin thickening and up-regulated HIF-1α to the normal level. These results suggest that Py-Zn is a potential agent to prevent UVB-induced photoaging and skin cancer development. This work also provides insight into a molecular target for treatment of UVB-induced skin diseases.
Go to : 
References
1. Melnikova VO, Ananthaswamy HN. Cellular and molecular events leading to the development of skin cancer. Mutat Res. 2005; 571:91–106.

2. Marrot L, Meunier JR. Skin DNA photodamage and its biological consequences. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58:S139–S148.

3. Ouhtit A, Muller HK, Davis DW, Ullrich SE, McConkey D, Ananthaswamy HN. Temporal events in skin injury and the early adaptive responses in ultraviolet-irradiated mouse skin. Am J Pathol. 2000; 156:201–207.

4. Lee JK, Kim JH, Nam KT, Lee SH. Molecular events associated with apoptosis and proliferation induced by ultraviolet-B radiation in the skin of hairless mice. J Dermatol Sci. 2003; 32:171–179.

5. El-Abaseri TB, Putta S, Hansen LA. Ultraviolet irradiation induces keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia through the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Carcinogenesis. 2006; 27:225–231.

6. Wang GL, Semenza GL. Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:1230–1237.

7. Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY, Semenza GL. Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Genes Dev. 1998; 12:149–162.
8. Koshiji M, Kageyama Y, Pete EA, Horikawa I, Barrett JC, Huang LE. HIF-1α induces cell cycle arrest by functionally counteracting Myc. EMBO J. 2004; 23:1949–1956.
9. Cho YS, Bae JM, Chun YS, Chung JH, Jeon YK, Kim IS, Kim MS, Park JW. HIF-1α controls keratinocyte proliferation by up-regulating p 21(WAF1/Cip1). Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008; 1783:323–333.
10. Cho YS, Kim CH, Park JW. Involvement of HIF-1α in UVB-induced epidermal hyperplasia. Mol Cells. 2009; 28:537–543.
11. Chun YS, Choi E, Kim GT, Lee MJ, Lee MJ, Lee SE, Kim MS, Park JW. Zinc induces the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, but inhibits the nuclear translocation of HIF-1β, causing HIF-1 inactivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 268:652–656.
12. Lim JH, Park JW, Kim MS, Park SK, Johnson RS, Chun YS. Bafilomycin induces the p21-mediated growth inhibition of cancer cells under hypoxic conditions by expressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Mol Pharmacol. 2006; 70:1856–1865.
13. Cho H, Lee HY, Ahn DR, Kim SY, Kim S, Lee KB, Lee YM, Park H, Yang EG. Baicalein induces functional hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and angiogenesis. Mol Pharmacol. 2008; 74:70–81.
14. Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB. A novel approach of proteomics and transcriptomics to study the mechanism of action of the antioxidant-iron chelator green tea polyphenol (–)-epigallo-catechin-3-gallate. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007; 43:546–556.

15. Park SE, Park JW, Cho YS, Ryu JH, Paick JS, Chun YS. HIF-1α promotes survival of prostate cells at a high zinc environment. Prostate. 2007; 67:1514–1523.
16. Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF. Regulation of hypoxiainducible factor 1α is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:7987–7992.
17. Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004; 5:343–354.

18. Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, Otterness DM, Loomis DC, Kaper F, Giaccia AJ, Abraham RT. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 22:7004–7014.
19. Lang KJ, Kappel A, Goodall GJ. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α mRNA contains an internal ribosome entry site that allows efficient translation during normoxia and hypoxia. Mol Biol Cell. 2002; 13:1792–1801.
20. Arsham AM, Plas DR, Thompson CB, Simon MC. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling is neither required for hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1α nor sufficient for HIF-1-dependent target gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:15162–15170.
21. Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mimnaugh EG, Martinez A, Cuttitta F, Neckers LM. Hsp90 regulates a von Hippel Lindau-independent hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-degradative pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:29936–29944.
22. Luo W, Zhong J, Chang R, Hu H, Pandey A, Semenza GL. Hsp70 and CHIP selectively mediate ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α but Not HIF-2α. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:3651–3663.
23. Pierard-Franchimont C, Goffin V, Decroix J, Pierard GE. A multicenter randomized trial of ketoconazole 2% and zinc pyrithione 1% shampoos in severe dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2002; 15:434–441.
24. Bailey P, Arrowsmith C, Darling K, Dexter J, Eklund J, Lane A, Little C, Murray B, Scott A, Williams A, Wilson D. A doubleblind randomized vehicle-controlled clinical trial investigating the effect of ZnPTO dose on the scalp vs. antidandruff efficacy and antimycotic activity. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2003; 25:183–188.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.Chemical structures of the test compounds. (A) Bafilomycin A1, (B) baicalein, (C) epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), (D) pyrithione-zinc (Py-Zn). |
 | Fig. 2.HIF-1α levels in keratinocytes. (A) Effects of test compounds on HIF-1α expression. After HaCaT cells had been cultured to a cell density of 80 ∼ 100%, the cells were treated with various compounds for 4 hours. The cells were harvested and subjected to immunoblotting for HIF-1α and β-tubulin. Concentration: bafilomycin A1, 5 nM; baicalein, 200 μM; EGCG, 500 μM; pyrithione-zinc (Py-Zn), 2 μM. (B) HIF-1α levels after UVB irradiation. HaCaT cells were pretreated with bafilomycin A1 or Py-Zn at the concentrations indicated 2 hours before UVB irradiation, and transiently irradiated with 15 mJ/cm2 of UVB. Two hours later, HaCaT cells were harvested for immunoblotting. (C) Time course of Py-Zn-induced HIF-1α expression. HaCaT cells were treated with 2 μM Py-Zn, harvested at the indicated time, and then subjected to immunoblotting. |
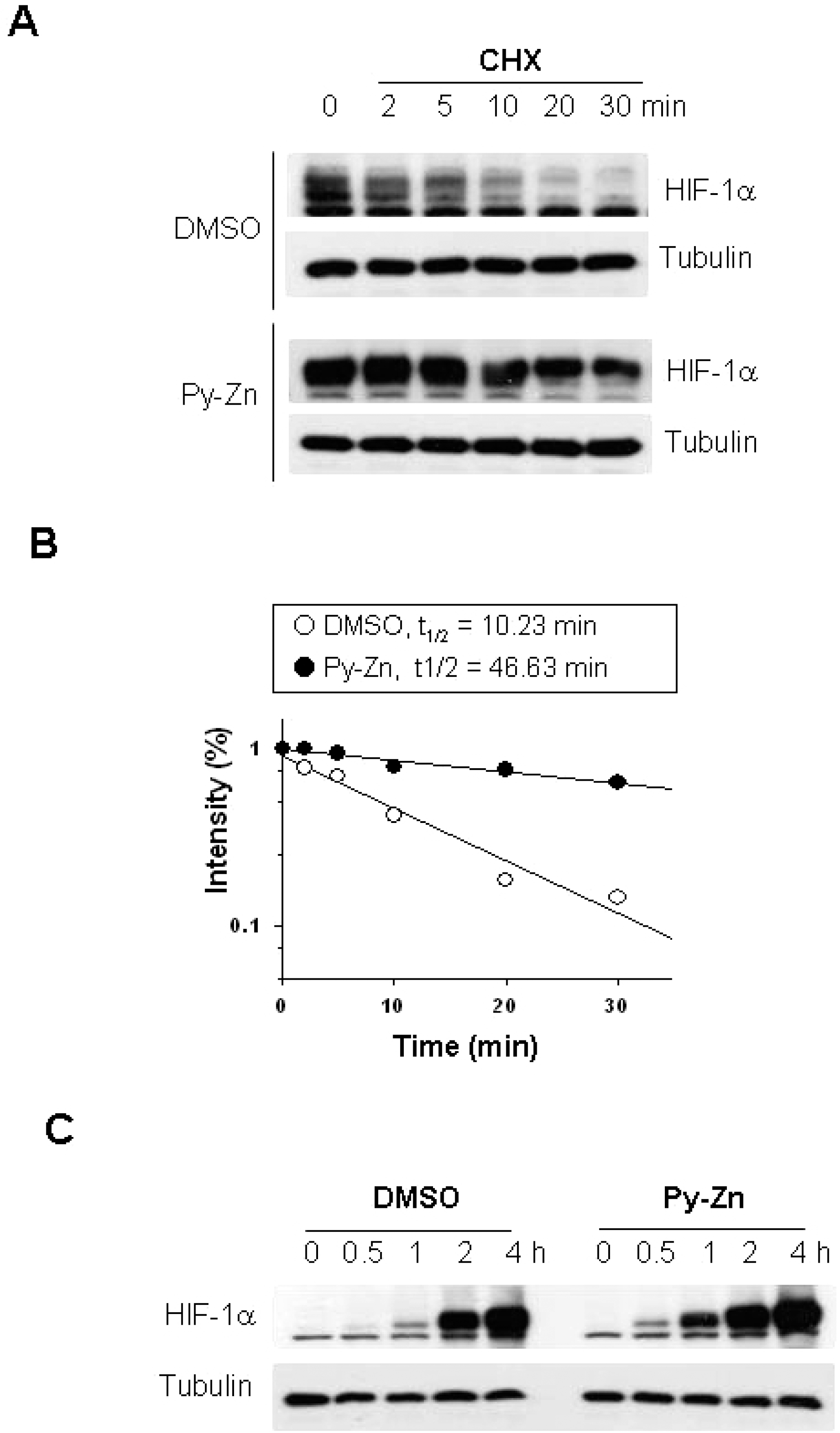 | Fig. 3.Py-Zn stabilizes HIF-1α in keratinocytes. (A) HIF-1α protein stability. HaCaT cells were pretreated with DMSO vehicle or 2 μM Py-Zn for 1 hour, and then further treated with 60 μg/ml of cycloheximide (CHX). Cells were harvested at the indicated time, and HIF-1α levels were analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) Half-lives of HIF-1α proteins. The protein band densities were quantified using ImageJ and plotted as a function of time (first-order kinetics). (C) HIF-1α protein synthesis. HaCaT cells were treated with 60 μg/ml of cycloheximide for 30 min to remove remaining HIF-1α. To initiate HIF-1α synthesis, cells were washed with PBS and incubated in fresh media containing 10 μM MG132, and HIF-1α levels were determined at the indicated time by immunoblotting. |
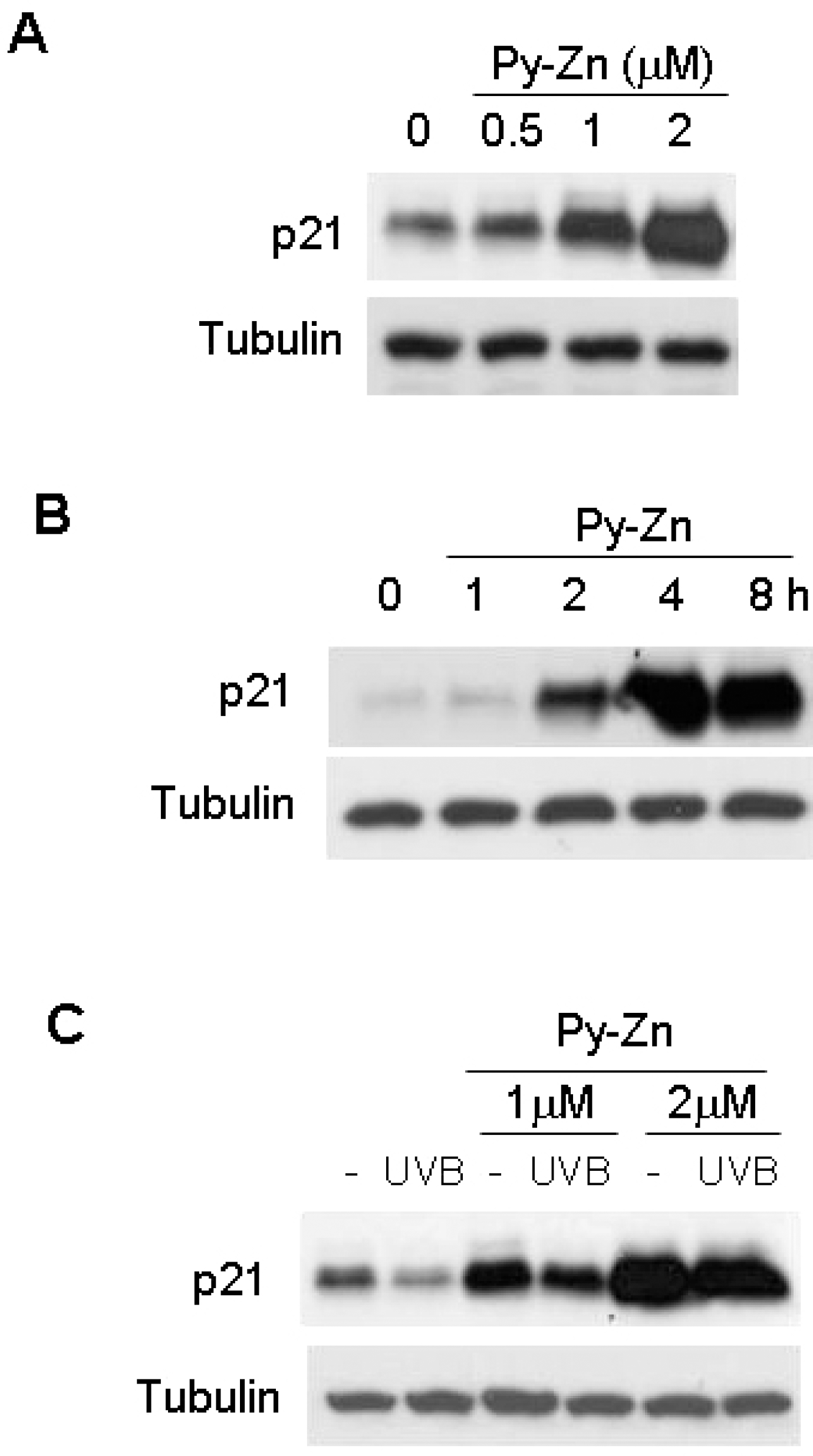 | Fig. 4.p21 levels in keratinocytes. (A) Effect of Py-Zn on p21 expression in keratinocytes. HaCaT cells were treated with Py-Zn at the concentrations indicated for 4 hours and then harvested for immunoblotting. (B) Time course of Py-Zn-induced p21 expression. HaCaT cells were treated with 2 μM Py-Zn, harvested at the indicated time, and then subjected to immunoblotting with anti-p21 antiserum. (C) p21 levels after UVB irradiation. HaCaT cells were pretreated with Py-Zn at the indicated concentrations 2 hours before UVB irradiation, and irradiated with 15 mJ/cm2 of UVB. Two hours later, HaCaT cells were harvested for immunoblotting. |
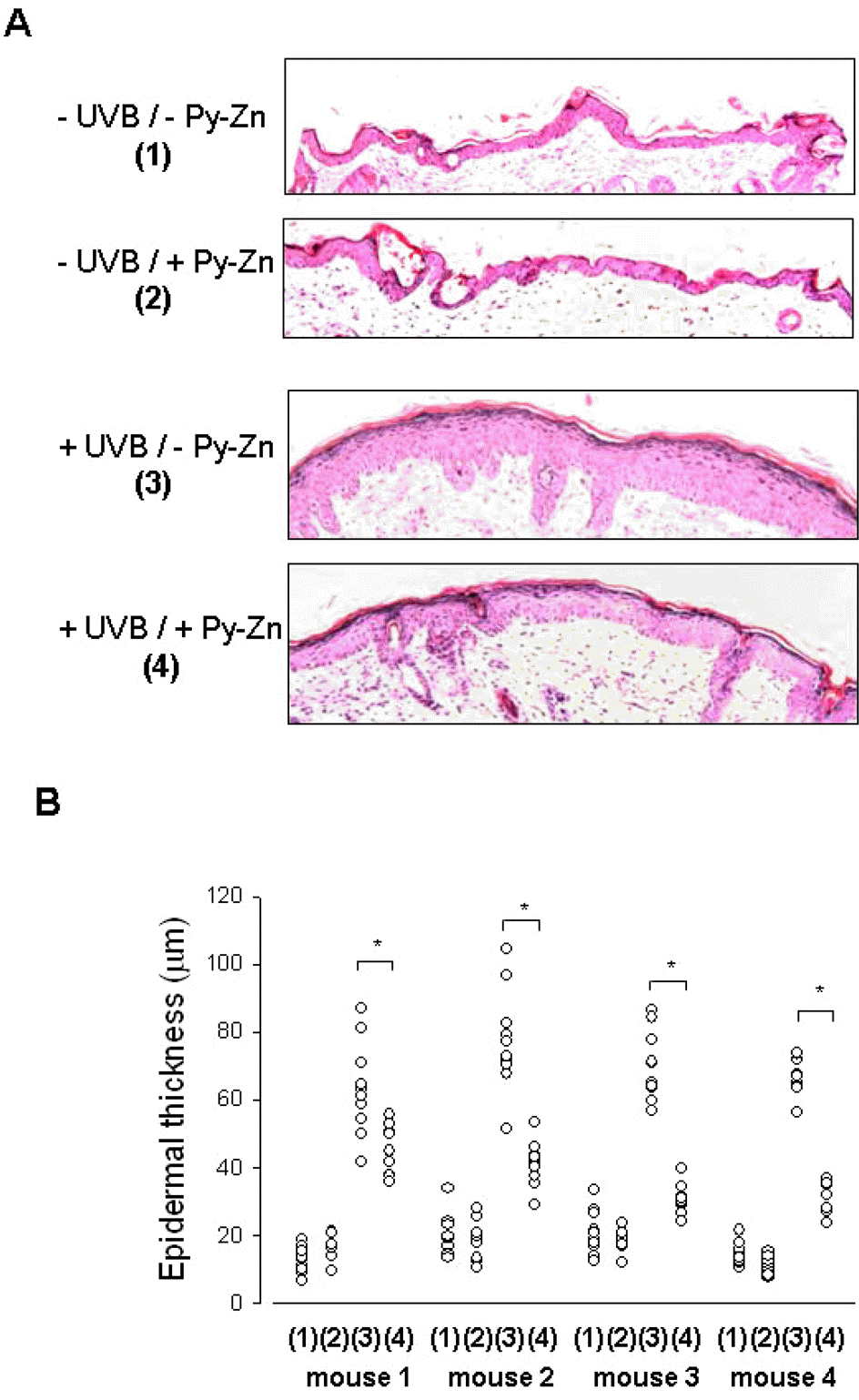 | Fig. 5.
In vivo effect of Py-Zn on UVB-induced skin hyperplasia. The back skin of each mouse was divided into four parts: the right lower quadrant for – UVB/ – Py-Zn (1), the right upper quadrant for –UVB/ + Py-Zn (2), the left lower quadrant for +UVB/–Py-Zn (3), the left upper quadrant for +UVB/+Py-Zn (4). Four mice were pretreated with PEG or 1% Py-Zn PEG cream 4 hours before UVB irradiation and then exposed to 460 mJ/cm2 of UVB once a day for four days. Back skins were excised, fixed, and embedded into paraffin blocks. (A) H&E staining of mouse skin. Skin specimens were obtained from 10 different sites per quadrant of each mouse and stained with H&E. (B) The thickness of the epidermis was analyzed at a magnification of 100×. The results were obtained from four mice (mouse 1∼4). ∗Denotes p<0.05 between two groups. |
 | Fig. 6.
In vivo effect of Py-Zn on UVB-induced HIF-1α suppression. (A) HIF-1α staining. The skin specimens were obtained as described in Fig. 5 and stained with anti-HIF-1α antibody. Nuclear HIF-1α was identified at a magnification of 100×. (B) Numbers of HIF-1α-positive keratinocytes. Three different slides per quadrant were stained and counted, and the data were collected from tissues of four mice (12 slides per group). ∗Denotes p<0.05 between two groups. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download