Abstract
To investigate the intestinal absorption of a fibrinolytic and proteolytic lumbrokinase extracted from Eisenia andrei, we used rat everted gut sacs and an in situ closed-loop recirculation method. We extracted lumbrokinase from Eisenia andrei, and then raised polyclonal antibody against lumbrokinase. Fibrinolytic activity and proteolytic activity in the serosal side of rat everted gut sacs incubated with lumbrokinase showed dose- and time-dependent patterns. Immunological results obtained by western blotting serosal side solution using rat everted gut sacs method showed that lumbrokinase proteins between 33.6 and 54.7 kDa are absorbed mostly by the intestinal epithelium. Furthermore, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometric analysis of plasma fractions obtained by in situ recirculation method confirmed that lumbrokinase F1 is absorbed into blood. These results support the notion that lumbrokinase can be absorbed from mucosal lumen into blood by oral administration.
Go to : 
References
1. Mihara H, Sumi H, Yoneta T, Mizumoto H, Ikeda R, Seiki M, Maruyama M. A novel fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm, lumbricus rubellus. Jpn J Physiol. 1991; 41:461–472.

2. Cho IH, Choi ES, Lim HG, Lee HH. Purification and characterization of six fibrinolytic serine-proteases from earthworm lumbricus rubellus. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004; 37:199–205.

3. Castell JV, Friedrich G, Kuhn CS, Poppe GE. Intestinal absorption of undegraded proteins in men: Presence of bromelain in plasma after oral intake. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273:G139–146.

4. Fan Q, Wu C, Li L, Fan R, Hou Q, He R. Some features of intestinal absorption of intact fibrinolytic enzyme iii-1 from lumbricus rubellus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001; 1526:286–292.

5. Fujita M, Hong K, Ito Y, Misawa S, Takeuchi N, Kariya K, Nishimuro S. Transport of nattokinase across the rat intestinal tract. Biol Pharm Bull. 1995; 18:1194–1196.

6. Vilhardt H, Lundin S. In vitro intestinal transport of vasopressin and its analogues. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986; 126:601–607.
7. Lee CK, Shin JS, Kim BS, Cho IH, Kim YS, Lee EB. Antithrombotic effects by oral administration of novel proteinase fraction from earthworm eisenia andrei on venous thrombosis model in rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2007; 30:475–480.

8. Choi NS, Kim BY, Lee JY, Yoon KS, Han KY, Kim SH. Relationship between acrylamide concentration and enzymatic activity in an improve single fibrin zymogram gel system. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002; 35:236–238.
9. Zhou J, Fan R. Wu C, He RQ. Assay of lumbrokinase with a chromophoric substrate. Protein Pept Lett. 1997; 4:409–414.
10. Kim SH, Choi NS, Lee WY. Fibrin zymography: a direct analysis of fibrinolytic enzymes on gels. Anal Biochem. 1998; 263:115–116.

11. Schanker LS, Tocco DJ, Brodie BB, Hogben CA. Absorption of drugs from the rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958; 123:81–88.
12. Mortz E, Krogh TN, Vorum H, Gorg A. Improved silver staining protocols for high sensitivity protein identification using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight analysis. Proteomics. 2001; 1:1359–1363.

13. Landry F, Lombardo CR, Smith JW. A method for application of samples to matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight targets that enhances peptide detection. Anal Biochem. 2000; 279:1–8.

14. Shevchenko A, Jensen ON, Podtelejnikov AV, Sagliocco F, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mortensen P, Boucherie H, Mann M. Linking genome and proteome by mass spectrometry: Large-scale identification of yeast proteins from two dimensional gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996; 93:14440–14445.

Go to : 
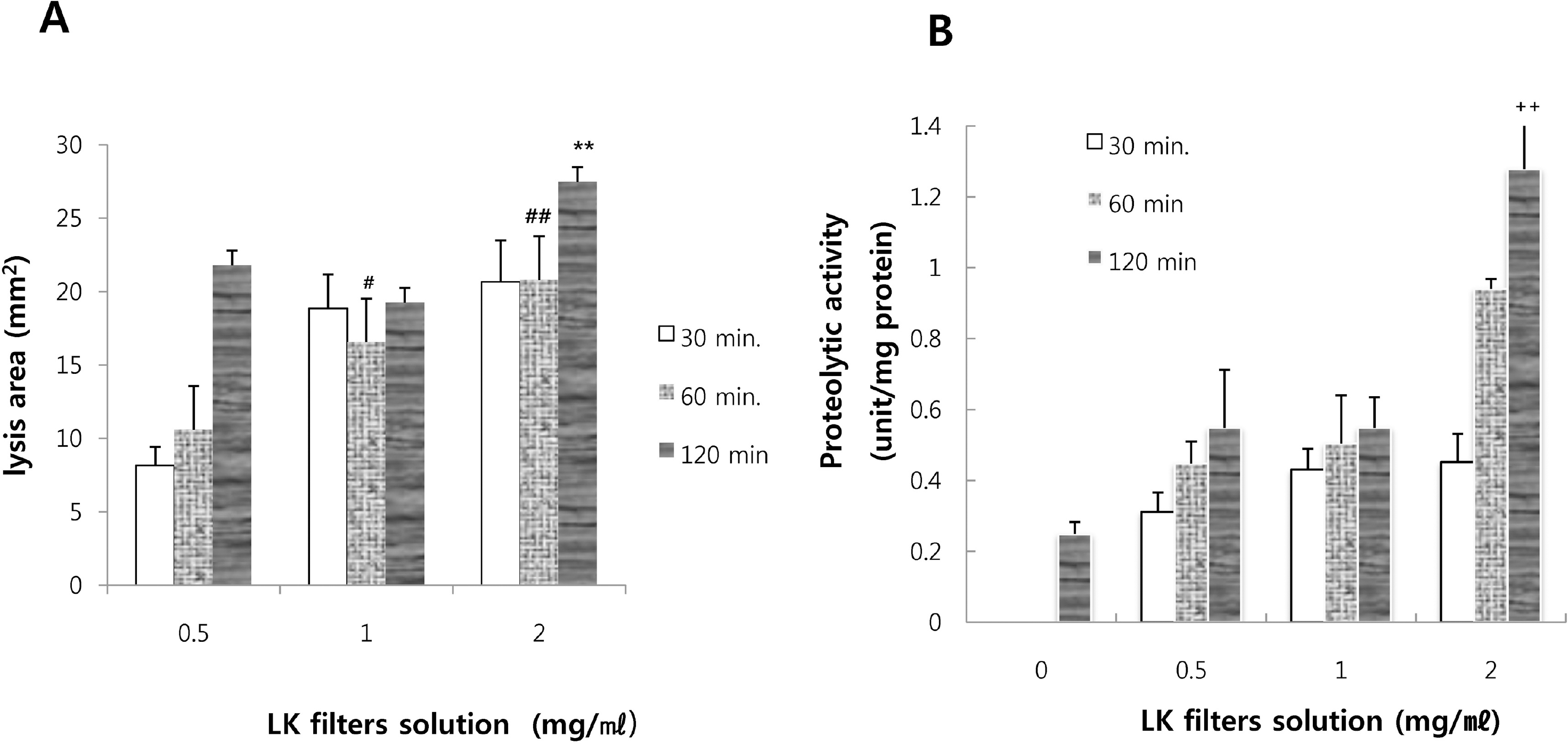 | Fig. 1.Measurement of fibrinolytic (A) and proteolytic activities (B). The lumbrokinase solutions (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg/ml) were added to Krebs solution on the mucosal sides of small intestine segments. To detect mucosal-to-serosal lumbrokinase transport, aliquots of serosal medium were taken at different times (30, 60, and 120 min, respectively) during incubation, and their fibrinolytic and proteolytic activities were measured. Data are means±SEs from 5 rats. #p<0.01, ##p<0.001 vs. the value obtained with lumbrokinase solution (0.5 mg/ml) at 60 min, ∗∗p<0.001 vs. the value obtained with lumbrokinase solution (0.5 mg/ml) at 120 min, ++p<0.001 vs. control. |
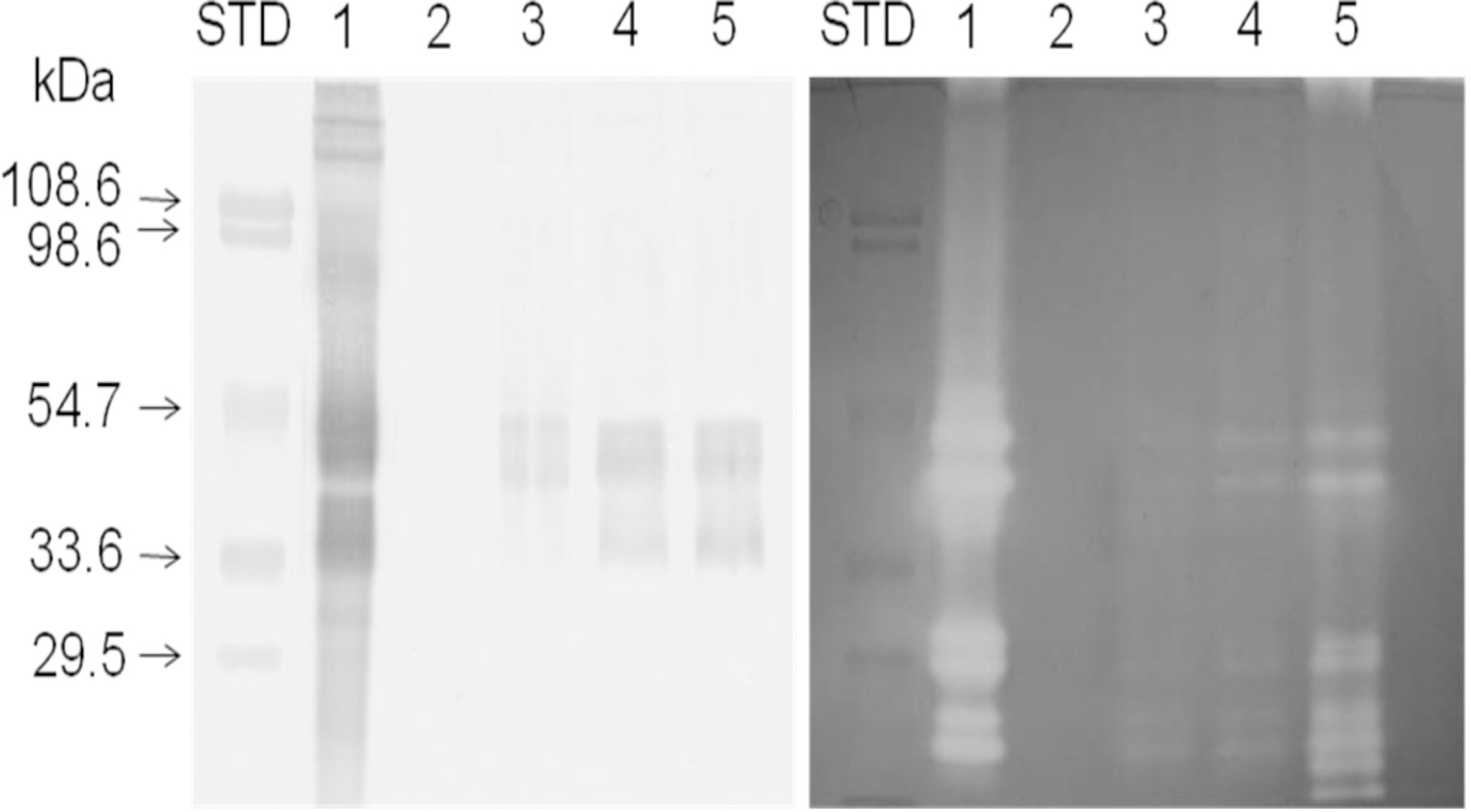 | Fig. 2.Immunoblot and zymogram analyses. Western blotting (left panel) using lumbrokinase polyclonal antibody and fibrin zymography (right panel) using fibrin incorporated in gel were carried out (lane 1: 20 μg of lumbrokinase, lane 2: serosal medium incubated without lumbrokinase for 120 min, lanes 3∼5: serosal media incubated with 2 mg/ml lumbrokinase for 30, 60, and 120 min, respectively). Molecular weight standard markers were applied to the left of lane1 in each panel. The blots shown are representative of experiments performed in triplicate. |
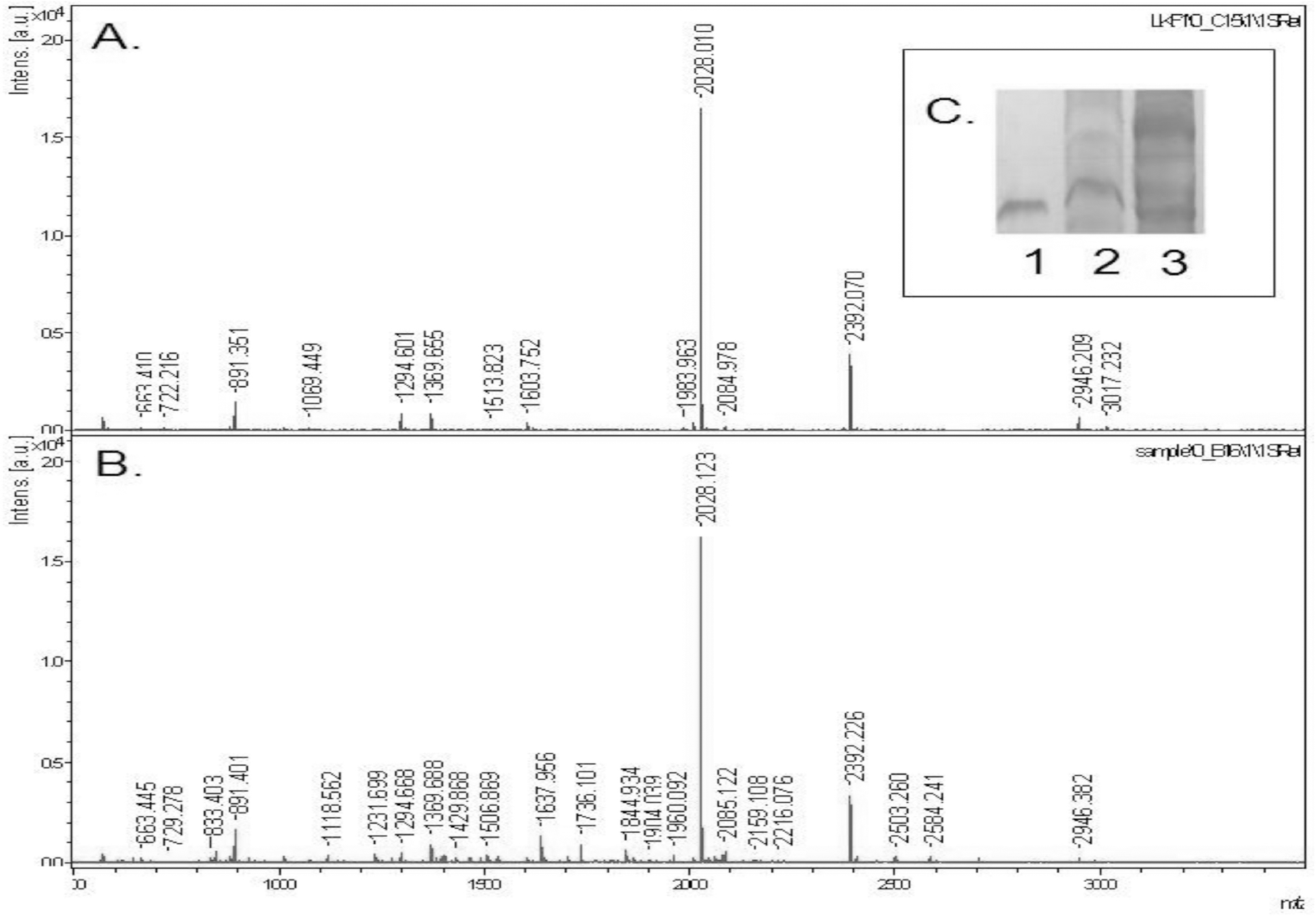 | Fig. 3.MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Lumbrokinase F1 was separated from plasma obtained by in situ recirculation method, and subjected to 15% SDS-PAGE (Fig. 3C, lane 1- lumbrokinase F1 standard, lane 2: blank plasma without lumbrokinase F1, lane 3: plasma with lumbrokinase F1 for 1 h). The band corresponding to the molecular weight of lumbrokinase F1 was excised and eluted, and the concentrated protein was treated with trypsin. Tryptic digests were analyzed by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (Fig. 3A: the spectrum of lumbrokinase F1 (lane 1 of Fig. 3C); Fig. 3B: the spectrum of the plasma obtained from rats with lumbrokinase F1 (lane 3 of Fig. 3C). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download