Abstract
To elucidate the mechanism of cyclic nucleotides, such as adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) and guanosine 3,5-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP), in the regulation of human gastric motility, we examined the effects of forskolin (FSK), isoproterenol (ISO) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on the spontaneous, high K+ and acetylcholine (ACh)-induced contractions of corporal circular smooth muscle in human stomach. Gastric circular smooth muscle showed regular spontaneous contraction, and FSK, ISO and SNP inhibited its phasic contraction and basal tone in a concentration-dependent manner. High K+ (50 mM) produced sustained tonic contraction, and ACh (10 μM) produced initial transient contraction followed by later sustained tonic contraction with superimposed phasic contractions. FSK, ISO and SNP inhibited high K+-induced tonic contraction and also ACh-induced phasic and tonic contraction in a reversible manner. Nifedipine (1 μM), inhibitor of voltage-dependent L-type calcium current (VDCCL), almost abolished ACh-induced phasic contractions. These findings suggest that FSK, ISO and SNP, which are known cyclic nucleotide stimulators, inhibit smooth muscle contraction in human stomach partly via inhibition of VDCCL.
References
Andersson R., Nilsson K. Cyclic AMP and calcium in relaxation in intestinal smooth muscle. Nature New Biol. 238:119–120. 1972.

Bulbring E., Tomita T. The action of isoprenaline on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 304:277–296. 1980.
Casteels R., Raeymakers L. The action of acethylcholine and catecholamines on an intracellular calcium store in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 194:511–569. 1979.
Farrelly AM., Ro S., Callaghan BP., Khoyi MA., Fleming N., Horowitz B., Sanders KM., Keef KD. Expression and function of KCNH2 (HERG) in the human jejunum. Am J Physiol. 284:G883–G895. 2003.

Geeson J., Larsson K., Hourani SMO., Toms NJ. Sodium nitroprusside-induced rat fundus relaxation is ryanodine-sensitive and involves L-type Ca2+ channel and small conductance Ca2+-sensitive K+ channel components. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 22:297–301. 2002.
Hocke M., Schöne U., Richert H., Görnert P., Keller J., Layer P., Stallmach A. Every slow-wave impulse is associated with motor activity of the human stomach. Am J Physiol. 296:G709–716. 2009.

Huizinga JD., Farraway L., Den Hertog A. Effect of voltage and cyclic AMP on frequency of slow-wave-type action potentials in canine colon smooth muscle. J Physiol. 442:31–45. 1991.

Huizinga JD., Thuneberg L., Kluppel M., Malysz J., Mikkelsen HB., Bernstein A. W/Kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature. 373:347–349. 1995.

Ishikawa T., Hume JR., Keef KD. Regulation of Ca2+ channels by cAMP and cGMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 73:1128–1137. 1993.
Jin JG., Murthy KS., Grider JR., Makhlouf GM. Activation of distict cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways by relaxant agents in isolated gastric muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 264:G470–G477. 1993.
Katsuki S., Arnold C., Murad F. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerine and nitric oxide in various tissue preparations and comparison to the effects of sodium azide and hydroxylamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 3:23–35. 1997.
Katzka DA., Morad M. Properties of calcium channels in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. J Physiol. 413:175–197. 1989.

Kim CH., Rhee PL., Rhee JC., Kim YI., So I., Kim KW., Park MK., Uhm DY., Kang TM. Hypotonic swelling increases L-type calcium current in smooth muscle cells of the human stomach. Exp Physiol. 85:497–504. 2000.

Kim MK., Han IS., Koh SD., Perrino BA. Role of CaM kimase II and phospholamban in SNP-induced relaxation of murine gastric fundus smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 291:C337–C347. 2006.
Kim MK., Perrino BA. CaM kimase II activation and phospholamban phosphorylation by SNP in murine gastric antrum smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 292:G1045–G1054. 2007.
Kim SJ., Ahn SC., Kim JK., Kim YC., So I., Kim KW. Changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration induced by L-type Ca2+ channel current in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. Am J Physiol. 8273:C1947–C1956. 1997.
Koh SD., Sanders KM. Modulation of Ca2+ current in canine colonic myocytes by cyclic nucleotide-dependent mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 271:C794–C803. 1996.
Matsumoto Y., Ito M., Tsuge M., Matsuo T., Tanaka S., Haruma K., Chayama K. Ecabet sodium induces neuronal nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide synthesis and gastric adaptative relaxation in the human stomach. J Gastroenterol. 44:1118–1124. 2009.
Meisheri KD., van Breemen C. Effects of b-adrenergic stimulation on calcium movements in rabbit aortic smooth muscle: relationship with cyclic AMP. J Physiol. 331:429–441. 1982.
Muraki K., Bolton TB., Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. Effect of isoprenaline on Ca2+ channel current in single smooth muscles isolated from taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. J Physiol. 471:563–582. 1993.
Nishimura J., van Breemen C. Direct regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements by second messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 163:929–935. 1989.

Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Modulation of ionic currents in smooth muscle balls of the rabbit intestine by intracellularly perfused ATP and cyclic AMP. Pflügers Arch. 408:465–473. 1987.

Ozaki H., Blondfield DP., Hori M., Sanders KM., Publicover NG. Cyclic AMP-mediated regulation of excitation-contraction coupling in canine gatric smooth muscle. J Physiol. 447:351–372. 1992.
Quignard JF., Frapier JM., Harricane MC., Albat B., Nargeot J., Richard S. Voltage-gated calcium channel current in human coronary myocytes. Regulation by cyclic GMP and nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 99:185–193. 1997.
Ruiz-Velasco V., Zhong J., Hume JR., Keef KD. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by cyclic nucleotide cross activation of opposing protein kinases in rabbit portal vein. Circ Res. 82:557–565. 1998.
Sanders KM. A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 111:492–515. 1996.

Sato K., Sanders KM., Gerthoffer WT., Publicover NG. Sources of calcium utilized in cholinergic responses in canine colonic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 267:C1666–C1673. 1994.

Schultz KD., Schultz K., Schultz G. Sodium nitroprusside and other smooth muscle relaxants increase cyclic GMP levels in rat ductus deferens. Nature. 265:750–751. 1977.
Severi C., Tattoli I., Corleto VD., Maselli MA., Trisolini P., Delle Fave G. Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor subtypes and signaling pathways involved in relaxation of human stomach. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 18:1009–1018. 2006.
Smith TK., Ward SM., Zhang L., Buxton ILO., Gerthoffer WT., Sanders KM., Keef KD. β-Adrenergic inhibition of electrical and mechanical activity in canine colon: role of cAMP. Am J Physiol. 264:G708–G717. 1993.
Taguchi K., Ueda M., Kubo T. Effects of cAMP and cGMP on L-type calcium channl currents in rat mesenteric artery cells. Jpn J Pharmacol. 74:179–186. 1997.
Tonini M., Giorgio RDc., Ponti EDc., Sternini C., Spelta V., P Dionigi., Barbara G., Stanghellini V., Corinaldesi R. Role of nitric oxide-and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing neurons in human gastric fundus strip relaxations. Br J Pharmacol. 129:12–20. 2000.
Wang XY., Zarate N., Soderholm JD., Bourgeois JM., Liu LW., Huizinga JD. Ultrastructural injury to interstitial cells of Cajal and communication with mast cells in Crohn's disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 19:349–364. 2007.

Yu YC., Guo HS., Li Y., Piao L., Li L., Li ZL., Xu WX. Role of calcium mobilization in sodium nitroprusside-induced increase of calcium-activated potassium currents in gastric circular myocytes of guinea-pig. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 24:819–825. 2003.
Zhu HL., Hirst GDS., Ito Y., Teramoto N. Modulation of voltage-dependent Ba2+ currents in the guinea-pig gastric antrum by cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 146:129–138. 2005.
Fig. 1.
Characterization of gastric corporal circular muscle motility in human. (A) Human gastric smooth muscle shows regular contraction with 0.3 g and 4.2 cycles/min (n=13). (B, C) High K+ and ACh produce tonic and phasic contraction in human stomach (n=7∼11).
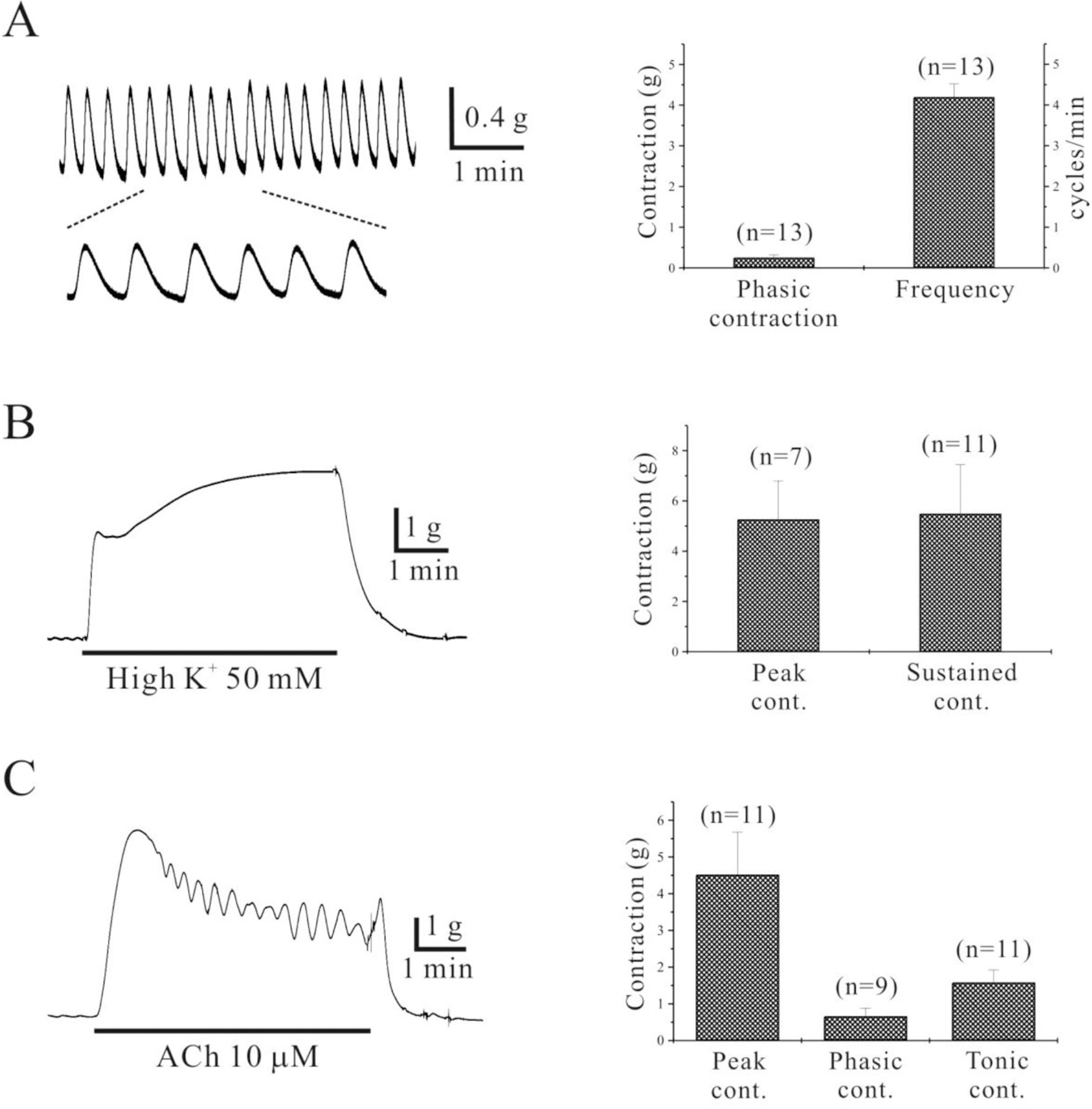
Fig. 2.
Inhibitory effect of forskolin (FSK), isoproterenol (ISO) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on spontaneous contraction of human stomach. (A) SNP (3 and 5 μM) inhibited spontaneous contraction and decreased basal tone of human stomach. FSK also inhibited spontaneous contraction and the inhibitory effects of FSK and SNP are summarized in (B). Inhibitory effect of ISO on spontaneous contraction of human stomach is also summarized in (C). Asterisks show a statistical significance (p<0.05).
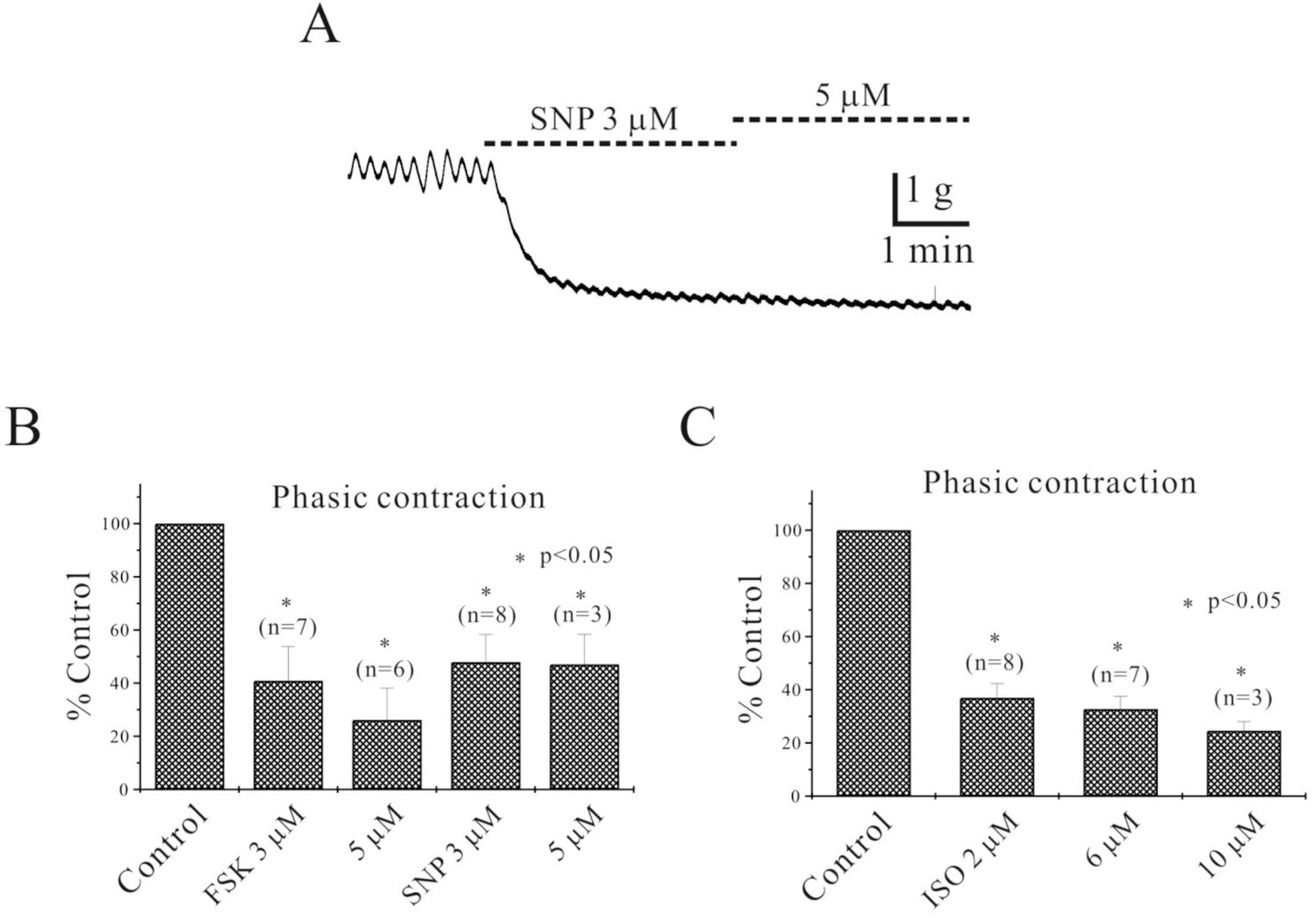
Fig. 3.
Effect of FSK, ISO and SNP on high K+-induced contraction in human stomach. (A) High K+ (50 mM) produced tonic contraction in human stomach, and it was inhibited by 3, 5 and 10 μM FSK to 53%, 51% and 23% of the control, respectively (n=3∼4). (B) 3, 5 and 10 μM SNP inhibited high K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction to 65%, 54% and 46% of the control, respectively (n=4∼5). Inhibitory effects of FSK, SNP and ISO on high K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction of human stomach are summarized in (C∼E). Asterisks show a statistical significance (p<0.05).
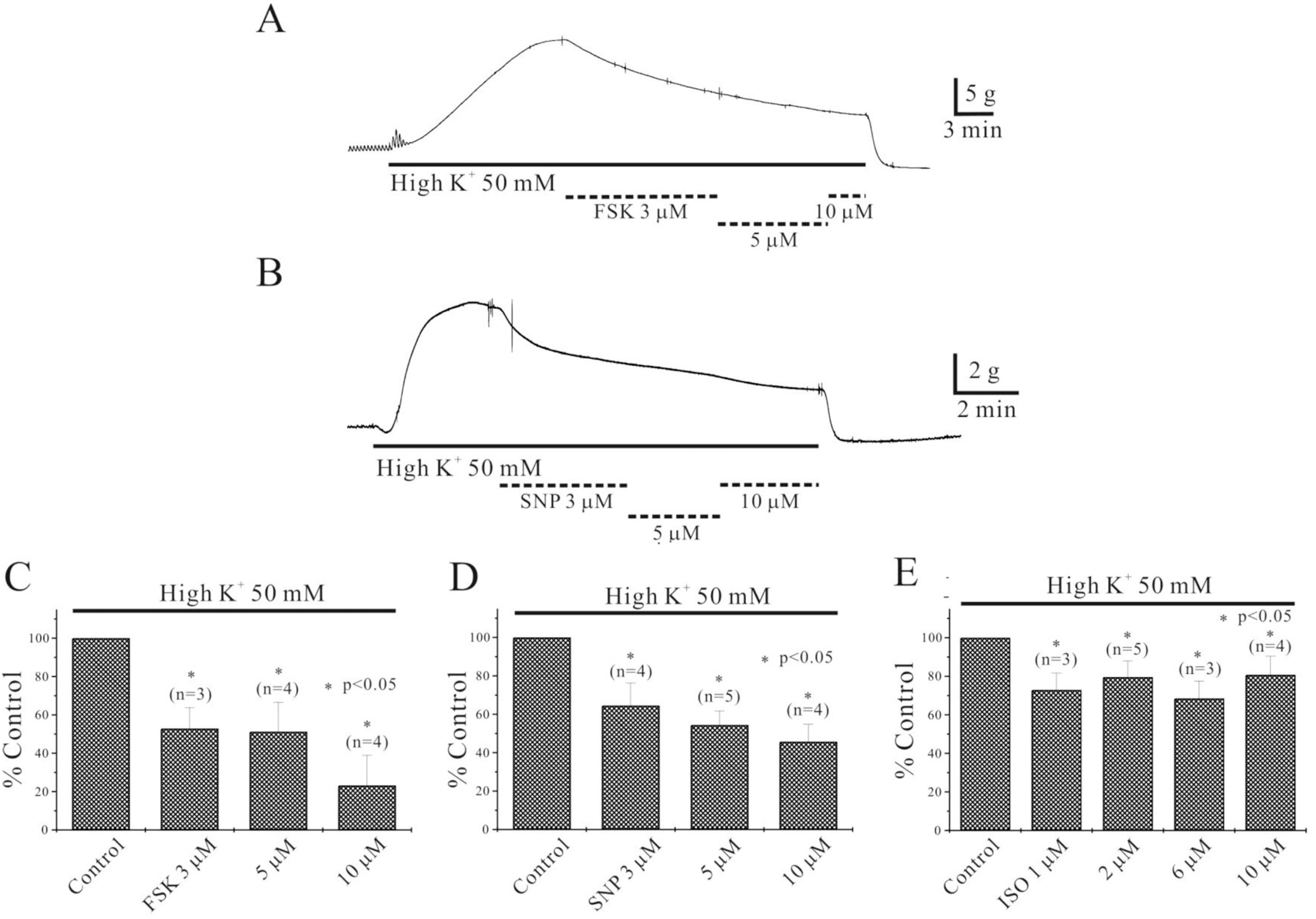
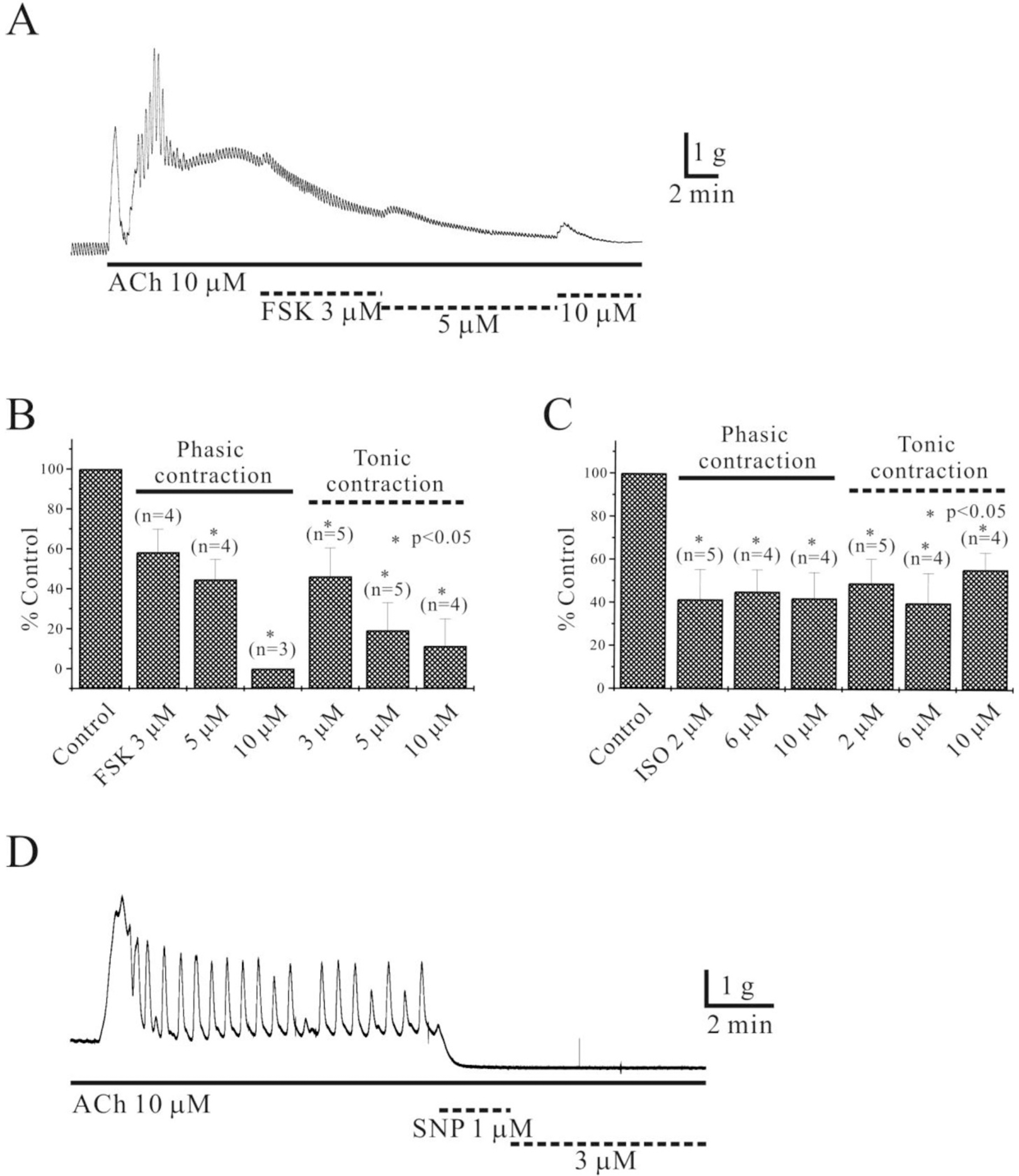
Fig. 4.
Effects of FSK, ISO and SNP on acetylcholine (ACh)-induced contraction in human stomach. FSK, ISO and SNP inhibited ACh-induced contraction in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) FSK (3, 5 and 10 μM) inhibited ACh-induced phasic and tonic contraction (n=3∼5). Inhibitory effect of FSK on ACh-induced contraction is summarized in (B). Similar inhibitory effect on ACh-induced contraction by both SNP and ISO was observed, as shown in (C) and (D). Asterisks show a statistical significance (p<0.05).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download