Abstract
Exercise-mediated physical treatment has attracted much recent interest. In particular, swimming is a representative exercise treatment method recommended for patients experiencing muscular and cardiovascular diseases. The present study sought to design a swimming-based exercise treatment management system. A survey questionnaire was completed by participants to assess the prevalence of muscular and cardiovascular diseases among adult males and females participating in swimming programs at sport centers in metropolitan regions of country. Using the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) technique, weighted values of indices were determined, to maximize participant clarity. A patient management system model was devised using information technology. The favorable results are evidence of the validity of this approach. Additionally, the swimming-based exercise management system can be supplemented together with analyses of weighted values considering connectivity between established indices.
Go to : 
References
Basmajian JV. Therapeutic exercise in the management of rheumatic disease. J Theumatol. 14:22–25. 1987.
Beaufrere B., Morio B. Fat and protein redistribution with aging: metabolic considerations. Eur J Nutr. 54(Suppl 3):S48–S53. 2000.
Buskirk ER. Introduction on to the symposium, Exercise in the treatment of obesity. Med Sci Sports Exer. 18:10–18. 1985.
Chang D. Application of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur J Oper Res. 53:649–655. 1996.
Derogatis LR., Lipman RS., Covi L. SCL-90: An outpatient psychiatric rating scale-preliminary report. Psychopharmacol Bulletin. 9:13–27. 1973.
Elkarmi F., Mustafa I. Increasing the utilization of solar energy technologies (SET) in Fordan. Energy Police. 21:978–984. 1993.
Kang S., Kang M., Lee H., Lee H., Jin Y. Development of water exercise program for improving cardiopulmonary capability and physical strength for patients of coronary artery diseases. Korean Sport Med J. 21:151–160. 2003.
Kim K., Won H. Simplified Mental Diagnosis Inspection (SCL-90) Korean edition standardization research II. Hanyang University Theses Collection No. 12:24–30. 1984.
Kim M. Unpublished theses of master degree at Ehwa Women's University, Research on motivation and level of satisfaction of participants according to types of living sports. 21–23. 1997.
Kim S. Impacts of swimming exercises on physical building and serum lipid of female seniors. Korean Sport Res. 19:131–140. 2008.
Lee S. Unpublished dissertation of doctor degree of Seoul University, a study on relationship between social sport activities of seniors and satisfaction of life. 80–85. 1992.
Long KA., Lee EJ., Swank SA. Effects of deep water exercise on aerobic capacity in older women. Med Sci Sports Exer. 28:S210. 1996.
Ministry of Health & Welfare. Introduction to projects of senior welfare. 1–12. 2007.
Ruoti R., Troup J., Berger R. The effects of non-swimming water exercise on older adult”. J Sports Phys Ther. 19:140–144. 1994.
Saaty TL. The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw-Hill, New York, 429–443. 1980.
Stamford BA. Endurance and strength training outcomes on cognitively impaired and cognitively intact older adults: A meta-analysis”. J Nutr Health Aging. 12:401–409. 1998.

Yang S., Park B. Actual status survey of muscular diseases and analyses research. J Korean Inst Plant Eng. 7:41–52. 2002.
Zadeh LA. Fuzzy Set, Inform Cont No. Information and Contrl. 8:338. 1965.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Subject characteristics based on questionnaire responses
| People with experiences of muscular diseases | People with experiences of cardiovascular diseases | Other∗ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C sport center located in Seoul city | 19 | 7 | 11 | 37 |
| T sport center located in Suwon city | 16 | 6 | 8 | 30 |
| J sport center located in Incheon city | 17 | 8 | 4 | 29 |
| Total | 52 | 21 | 23 | 96 |
Table 2.
Age characteristics of study participants
| Age (years) | People with experiences of muscular diseases | People with experiences of cardiovascular diseases | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 + | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 31∼39 | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| 40∼49 | 19 | 6 | 25 |
| 50∼59 | 23 | 11 | 34 |
| 60 + | 4 | 2 | 6 |
| Total | 52 | 21 | 73 |
Table 3.
Indices for treatment management of swimming exercises
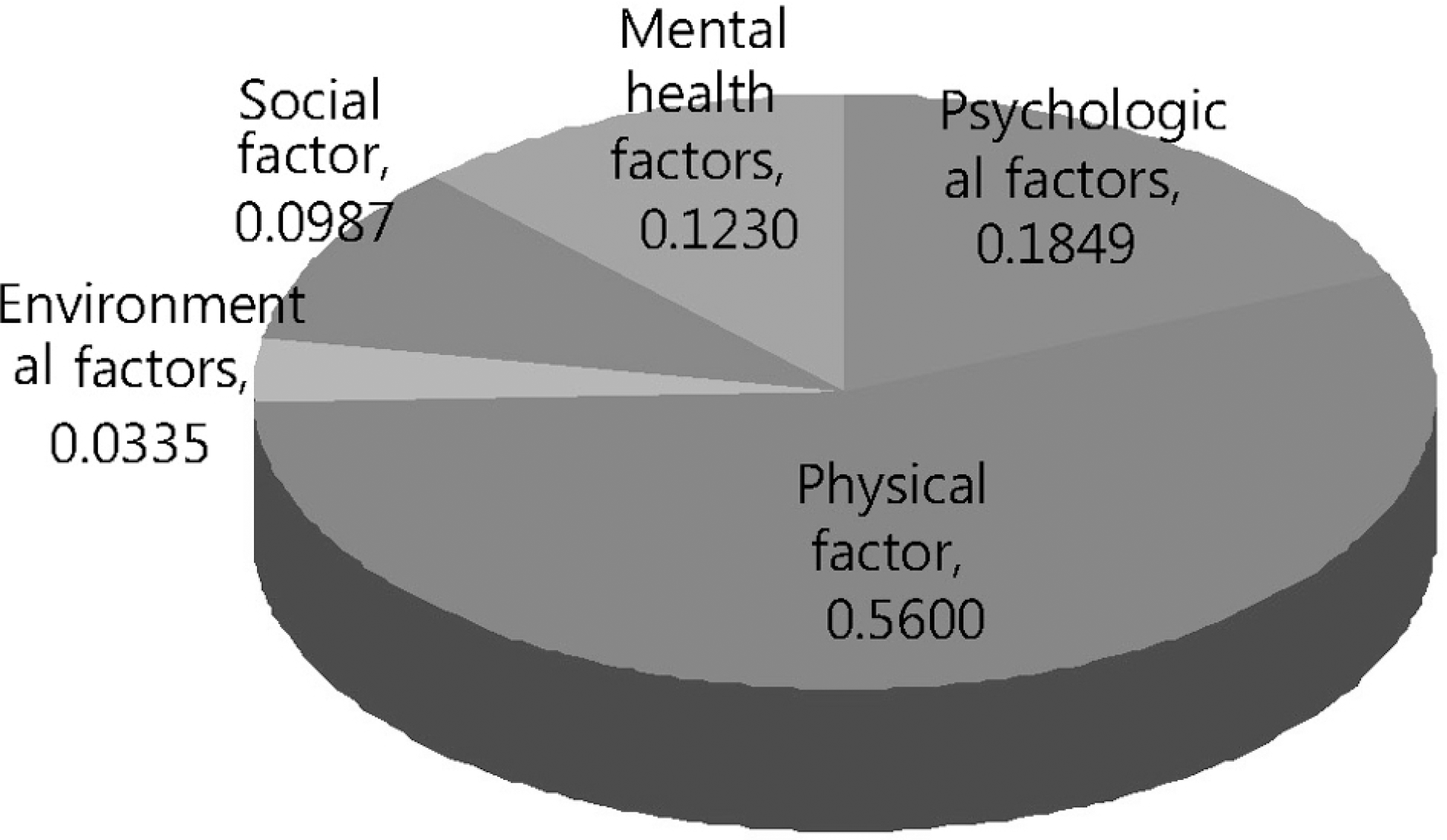
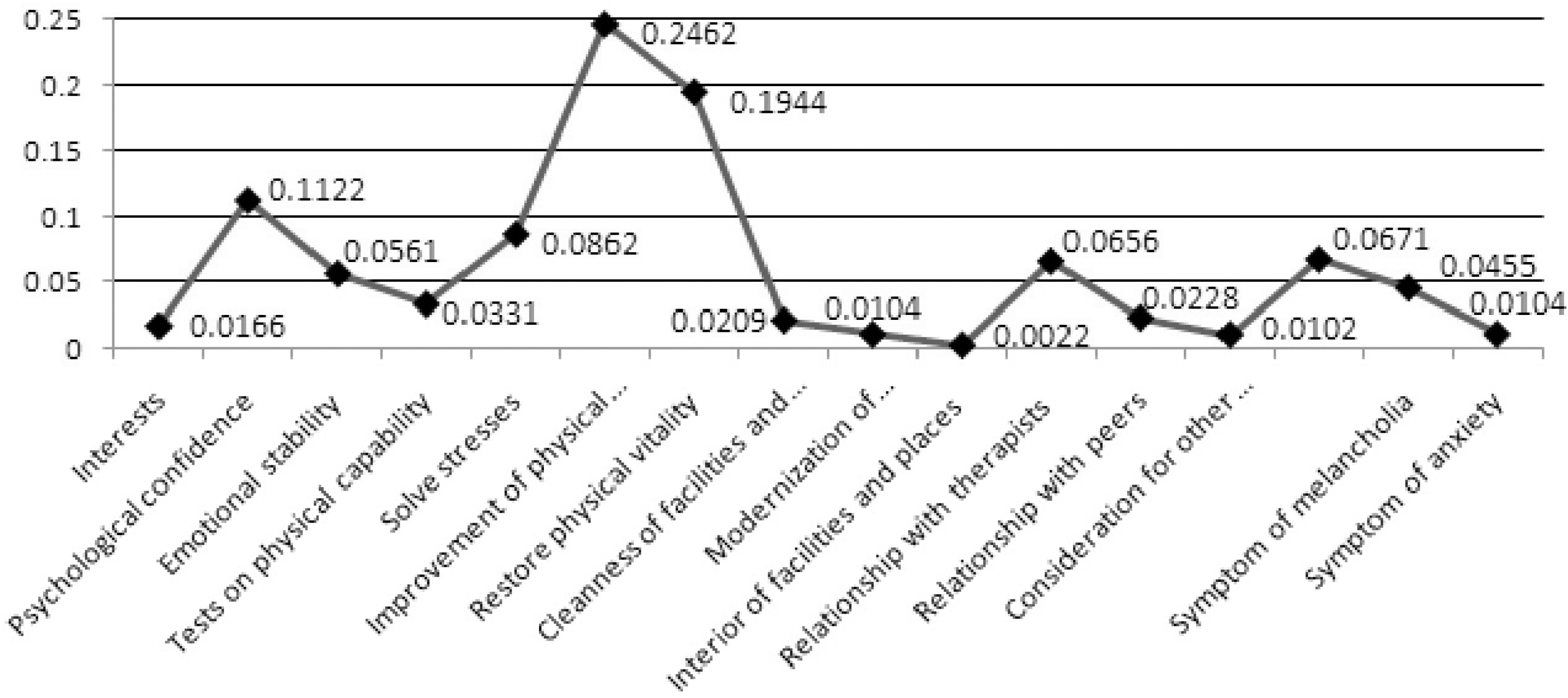
Table 4.
Weighted value between factors influencing exercise treatment and priority rankings




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download