Abstract
Our previous study demonstrated that flavone inhibits vascular contractions by decreasing the phosphorylation levelof the myosin phosphatase target subunit (MYPT1). In the present study, we hypothesized that flavone attenuates vascular contractions through the inhibition of the RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Rat aortic rings were denuded of endothelium, mounted in organ baths, and contracted with either 30 nM U46619 (a thromboxane A2 analogue) or 8.0 mM NaF 30 min after pretreatment with either flavone (100 or 300 μM) or vehicle. We determined the phosphorylation level of the myosin light chain (MLC20), the myosin phophatase targeting subunit 1 (MYPT1) and the protein kinase C-potentiated inhibitory protein for heterotrimeric myosin light chain phophatase of 17-kDa (CPI17) by means of Western blot analysis. Flavone inhibited, not only vascular contractions induced by these contractors, but also the levels of MLC20 phosphorylation. Furthermore, flavone inhibited the activation of RhoA which had been induced by either U46619 or NaF. Incubation with flavone attenuated U46619-or NaF-induced phosphorylation of MYPT1Thr855 and CPI17Thr38, the downstream effectors of Rho-kinase. In regards to the Ca2+-free solution, flavone inhibited the phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr855 and CPI17Thr38, as well as vascular contractions induced by U46619. These results indicate that flavone attenuates vascular contractions, at least in part, through the inhibition of the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
Ajay M., Achike FI., Mustafa MR. Modulation of vascular reactivity in normal, hypertensive and diabetic rat aortae by a non-antioxidant flavonoid. Pharmacol Res. 55:385–391. 2007.

Ajay M., Gilani AU., Mustafa MR. Effects of flavonoids on vascular smooth muscle of the isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 74:603–612. 2003.

Azam MA., Yoshioka K., Ohkura S., Takuwa N., Sugimoto N., Sato K., Takuwa Y. Ca2+-independent, inhibitory effects of cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate on Ca2+ regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2alpha, Rho, and myosin phosphatase in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320:907–916. 2007.
Cassidy A., Hanley B., Lamuela-Raventos RM. Isoflavones, lignans and stilbenes – origins, metabolism and potential importance to human health. J Sci Food Agricult. 80:1044–1062. 2000.

Chan EC., Pannangpetch P., Woodman OL. Relaxation to flavones and flavonols in rat isolated thoracic aorta: mechanism of action and structure-activity relationships. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 35:326–333. 2000.

Duarte J., Perez Vizcaino F., Utrilla P., Jiménez J., Tamargo J., Zarzuelo A. Vasodilatory effects of flavonoids in rat aortic smooth muscle. Structure-activity relationships. Gen Pharmacol. 24:857–862. 1993.

Duffy C., Perez K., Partridge A. Implications of phytoestrogen intake for breast cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:260–277. 2007.

Eto M., Ohmori T., Suzuki M., Furuya K., Morita F. A novel protein phosphatase-1 inhibitory protein potentiated by protein kinase C. Isolation from porcine aorta media and characterization. J Biochem (Tokyo). 118:1104–1107. 1995.
Fitzpatrick DF., Hirschfield SL., Coffey RG. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxing activity of wine and other grape products. Am J Physiol. 265:H774–778. 2000.

Fukata Y., Amano M., Kaibuchi K. Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 22:32–39. 2001.

Ghisdal P., Vandenberg G., Morel N. Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries. J Physiol. 551:855–867. 2003.

Gohla A., Schultz G., Offermanns S. Role for G(12)/G(13) in agonist-induced vascular smooth muscle cell contraction. Circ Res. 87:221–227. 2000.
Hart MJ., Jiang X., Kozasa T., Roscoe W., Singer WD., Gilman AG., Sternweis PC., Bollag G. Direct stimulation of the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of p115 RhoGEF by Galpha13. Science. 280:2112–2114. 1998.
Herrera MD., Zarzuelo A., Jimenez J., Marhuenda E., Duarte J. Effects of flavonoids on rat aortic smooth muscle contractility: Structure-activity relationships. Gen Pharmacol. 27:273–277. 1996.

Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 267:8719–8722. 1992.

Jeon SB., Jin F., Kim JI., Kim SH., Suk K., Chae SC., Jun JE., Park WH., Kim IK. A role for Rho kinase in vascular contraction evoked by sodium fluoride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 343:27–33. 2006.

Jeon SB., Kim G., Kim JI., Seok YM., Kim SH., Suk K., Shin HM., Lee YH., Kim IK. Flavone inhibits vascular contraction by decreasing phosphorylation of the myosin phosphatase target subunit. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 34:1116–1120. 2007.

Johns DG., Dorrance AM., Leite R., Weber DS., Webb RC. Novel signaling pathways contributing to vascular changes in hypertension. J Biomed Sci. 7:431–443. 2000.

Kim IK., Park TG., Kim YH., Cho JW., Kang BS., Kim CY. Heat-shock response is associated with enhanced contractility of vascular smooth muscle in isolated rat aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 369:402–407. 2004.

Kim JI., Jeon SB., Baek I., Seok YM., Shin HM., Kim IK. Heat shock augments myosin phosphatase target-subunit phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 356:718–722. 2007.

Kimura K., Ito M., Amano M., Chihara K., Fukata Y., Nakafuku M., Yamamori B., Feng J., Nakano T., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A., Kaibuchi K. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Science. 273:245–248. 1996.

Ko F., Huang T., Teng C. Vasodilatory action mechanisms of apigenin isolated from Apium graveolens in rat thoracic aorta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1115:69–74. 1991.
Koyama M., Ito M., Feng J., Seko T., Shiraki K., Takase K., Hartshorne DJ., Nakano T. Phosphorylation of CPI-17, an inhibitory phosphoprotein of smooth muscle myosin phosphatase, by Rhokinase. FEBS Lett. 475:197–200. 2000.

Kureishi Y., Kobayashi S., Amano M., Kimura K., Kanaide H., Nakano T., Kaibuchi K., Ito M. Rho-associated kinase directly induces smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 272:12257–12260. 1997.

Lee HA., Seong Y., Lee WJ., Kim I. 17β-Estradiol inhibits calcium-dependent, but not calcium-independent, contraction in isolated rat aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 371:152–157. 2005.

Machha A., Mustafa MR. Chronic treatment with flavonoids prevents endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rat aorta. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 46:36–40. 2005.

Most MM. Estimated phytochemical content of the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet is higher than in the Control Study Diet. J Am Diet Assoc. 104:1725–1727. 2004.

National Institutes of Health. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. NIH publication No. 85-23, revised edn. NIH, Bethesda, MD. 1996.
Pang H., Guo Z., Su W., Xie Z., Eto M., Gong MC. RhoA-Rho kinase pathway mediates thrombin- and U-46619-induced phosphorylation of a myosin phosphatase inhibitor, CPI-17, in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 289:352–360. 2005.

Ricketts ML., Moore DD., Banz WJ., Mezei O., Shay NF. Molecular mechanisms of action of the soy isoflavones includes activation of promiscuous nuclear receptors. A review J Nutr Biochem. 16:321–330. 2005.
Sakurada S., Takuwa N., Sugimoto N., Takuwa Y. Rho activation in excitatory agonist-stimulated vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 281:C571–578. 2001.

Somyo AP., Somyo AV. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev. 83:1325–1358. 2003.
Tsai MH., Jiang MJ. Rho-kinase-mediated regulation of receptor-agonist-stimulated smooth muscle contraction. Pflugers Arch. 435:223–232. 2006.

Wang Y., Yoshioka K., Azam MA., Takuwa N., Sakurada S., Kayaba Y., Sugimoto N., Inoki I., Kimura T., Kuwaki T., Takuwa Y. Class II phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha-isoform regulates Rho, myosin phosphatase and contraction in vascular smooth muscle. Biochem J. 394:581–592. 2006.
Wilson DP., Susnjar M., Kiss E., Sutherland C., Walsh MP. Thromboxane A2-induced contraction of rat caudal arterial smooth muscle involves activation of Ca2+ entry and Ca2+ sensitization: Rho-associated kinase-mediated phosphorylation of MYPT1 at Thr-855, but not Thr-697. Biochem J. 389:763–774. 2005.
Wirth A., Benyó Z., Lukasova M., Leutgeb B., Wettschureck N., Gorbey S., Orsy P., Horváth B., Maser-Gluth C., Greiner E., Lemmer B., Schütz G., Gutkind JS., Offermanns S. G12-G13-LARG-mediated signaling in vascular smooth muscle is required for salt-induced hypertension. Nat Med. 14:64–68. 2008.

Zenebe W., Pechanova O., Bernatova I. Protective effects of red wine polyphenolic compounds on the cardiovascular system. Exp Clin Cardiol. 6:153–158. 2001.
Go to : 
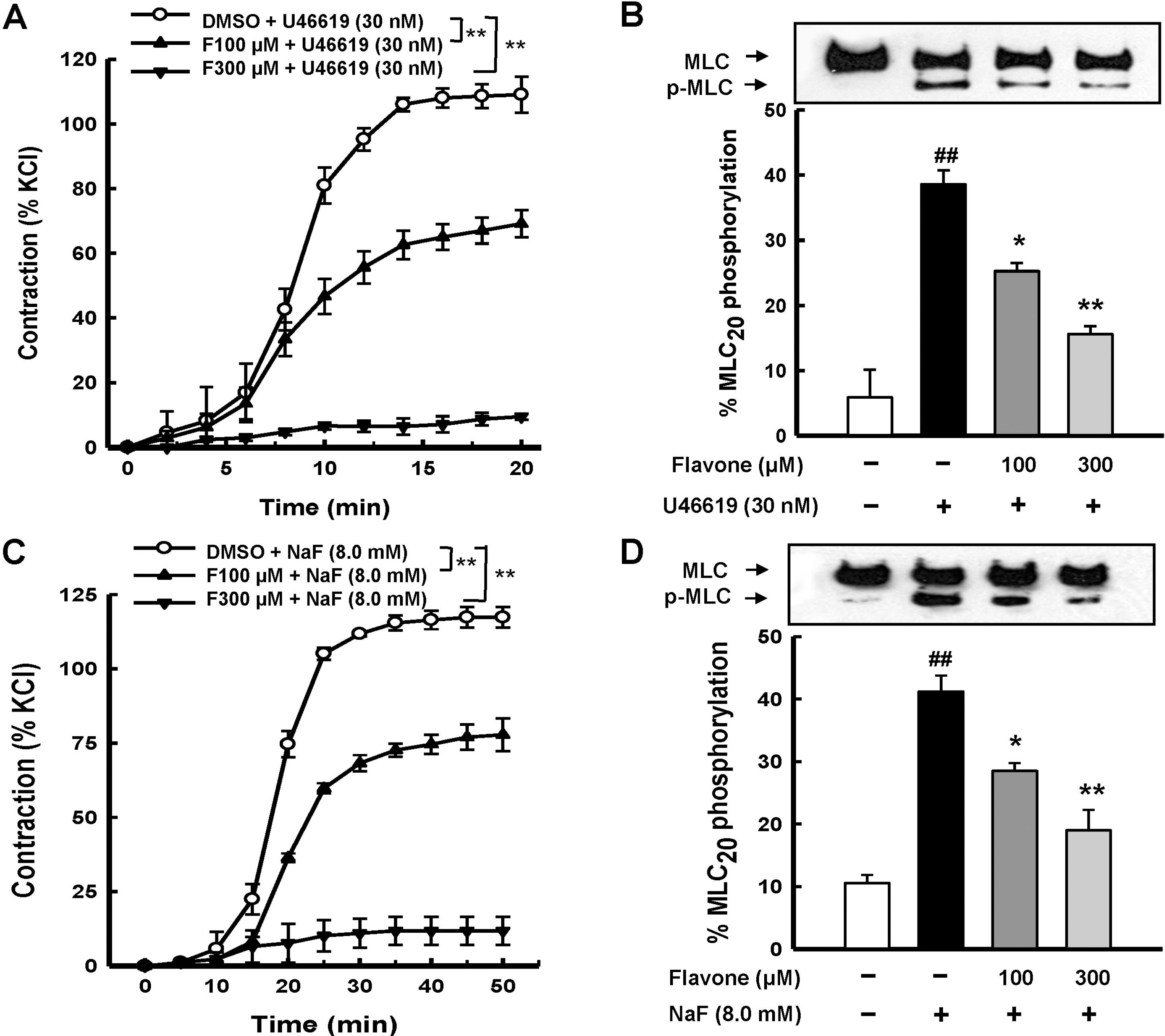 | Fig. 1.Inhibitory effect of flavone on contractions and the phosphorylation level of MLC20 induced by U46619 or NaF in rat aorta. U46619 (30 nM) (A) or NaF (8.0 mM) (C) was each added to elicit tension 30 min after pretreatment with flavone (100 or 300 μM) or vehicle to denuded aortic rings. Developed tension is expressed as a percentage of the maximum contractions to 50 mM KCl (4 aortic rings). When the tension reached plateaus, the phosphorylation levelof MLC20 in response to U46619 (B) or NaF (D) was measured and was expressed as a percentage of the total MLC20 (4 aortic rings). Data are expressed as means with vertical bars showing S.E.M. ##p<0.01 vs. basal. ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01 vs. U46619 or NaF alone. (A) and (C) were analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA whereas (B) and (D) by one-way ANOVA followed by the post-hoc Tukey's test. |
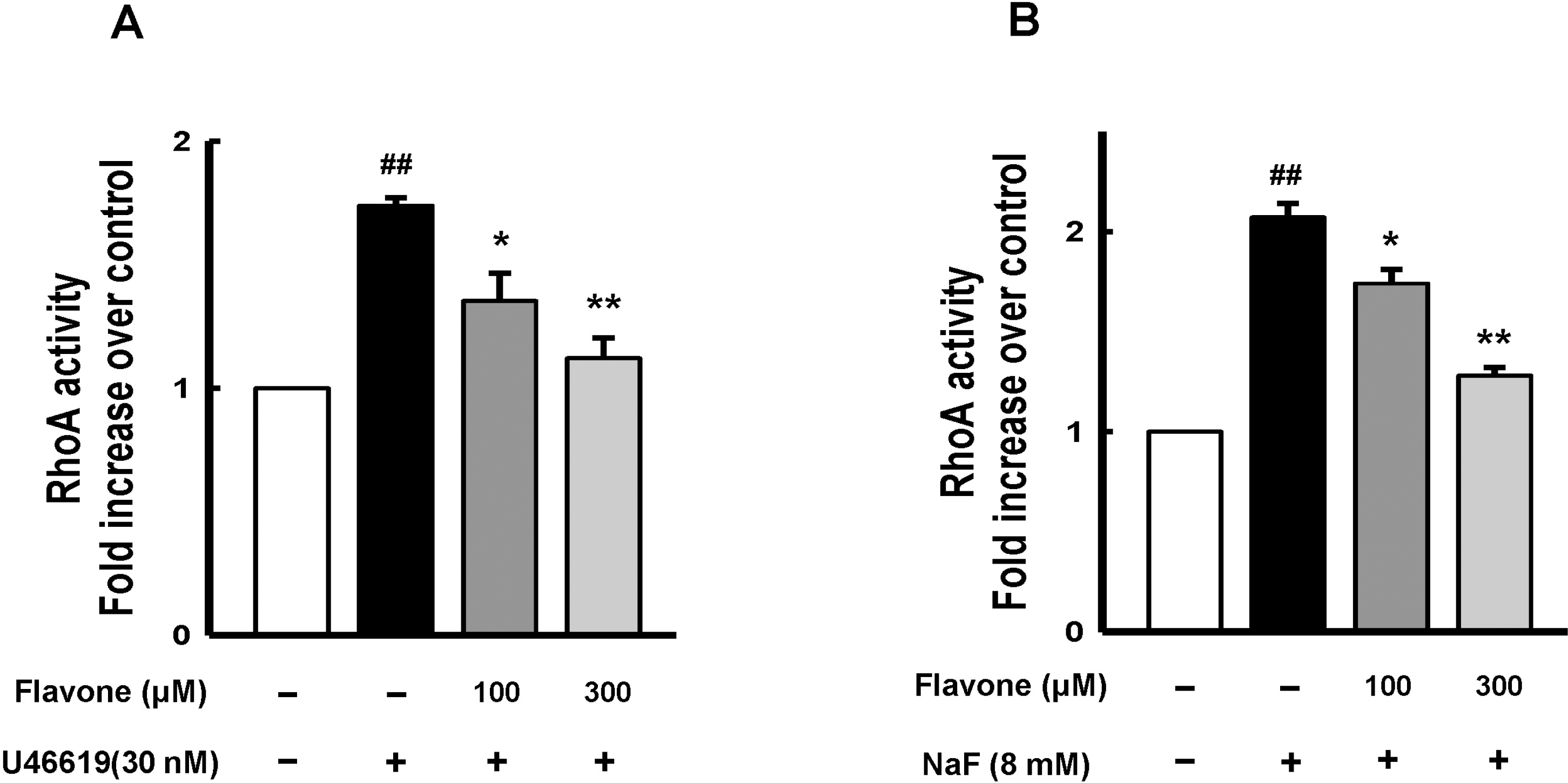 | Fig. 2.Inhibitory effect of flavone on RhoA activation induced by U46619 or NaF in rat aorta. RhoA activation was assessed by G-LISA™ Activation Assay (4 aortic rings). Thirty nM U46619 (A) or 8 mM NaF (B) was each added to elicit tension 30 min after pretreatment with flavone (100 or 300 μM) or vehicle to denuded aortic rings. Absorbance at the control (OD of about 0.4) was expressed as 1 arbitrary unit. Data were expressed as means with vertical bars showing S.E.M. ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01 vs. U46619 or NaF alone. ##p<0.01 vs. basal (one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey's test). |
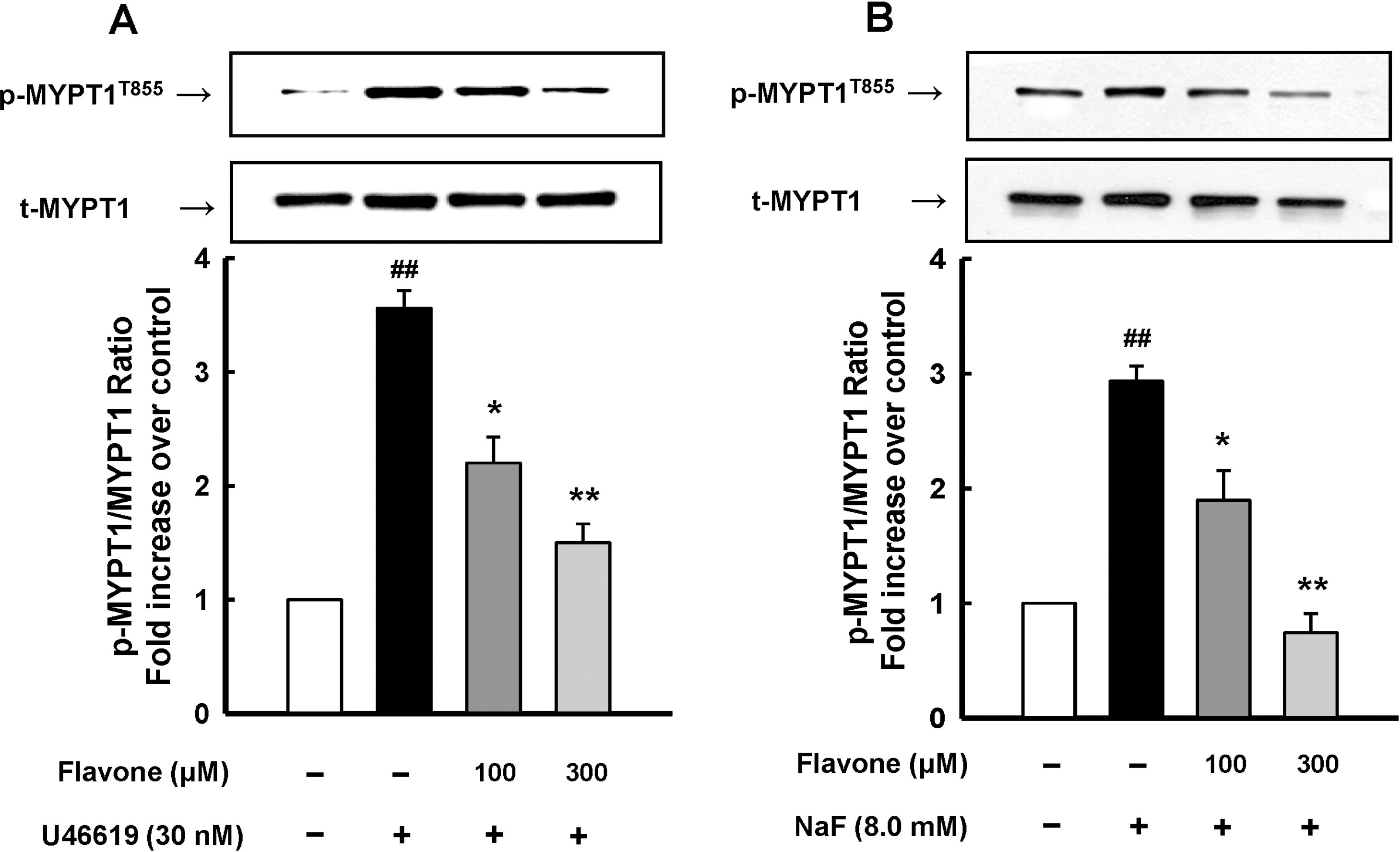 | Fig. 3.Inhibitory effect of flavone on the phosphorylation of MYPT1 induced by U46619 or NaF in rat aorta. U46619 (A) or NaF (B) was added to elicit tension 30 min after pretreatment with flavone (100 or 300 μM) or vehicle to denuded aortic rings. MYPT1 phosphorylation at Thr855 was assessed by Western blot analysis after treatment with 30 nM U46619 or 8 mM NaF. Upper and lower bands in representative Western blots were probed with anti-pMYPT1 and anti-MYPT1 antibodies, respectively. Densitometry shows that the ratio of density of phosphorylated MYPT1 (upper) to that of total MYPT1 (lower) for the control was expressed as 1 arbitrary unit (5 aortic rings). Data are expressed as means with vertical bars showing S.E.M. ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01 vs. U46619 or NaF alone. ##p<0.01 vs. basal (one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey's test). |
 | Fig. 4.Inhibitory effect of flavone on the phosphorylation of CPI17 induced by U46619 or NaF in rat aorta. U46619 (A) or NaF (B) was added to elicit tension 30 min after pretreatment with flavone (100 or 300 μM) or vehicle to denuded aortic rings. The phosphorylation of CPI17 at Thr38 was assessed by Western blots after treatment with 30 nM U46619 or 8 mM NaF. Upper and lower bands in representative Western blots were probed with anti-pCPI17 and anti-CPI17 antibodies, respectively. Densitometry shows that the ratio of density of phosphorylated CPI17 (upper) to that of total CPI17 (lower) for the control was expressed as 1 arbitrary unit (5 aortic rings). Data are expressed as means with vertical bars showing S.E.M. ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01 vs. U46619 or NaF alone. ##p<0.01 vs. basal (one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey's test). |
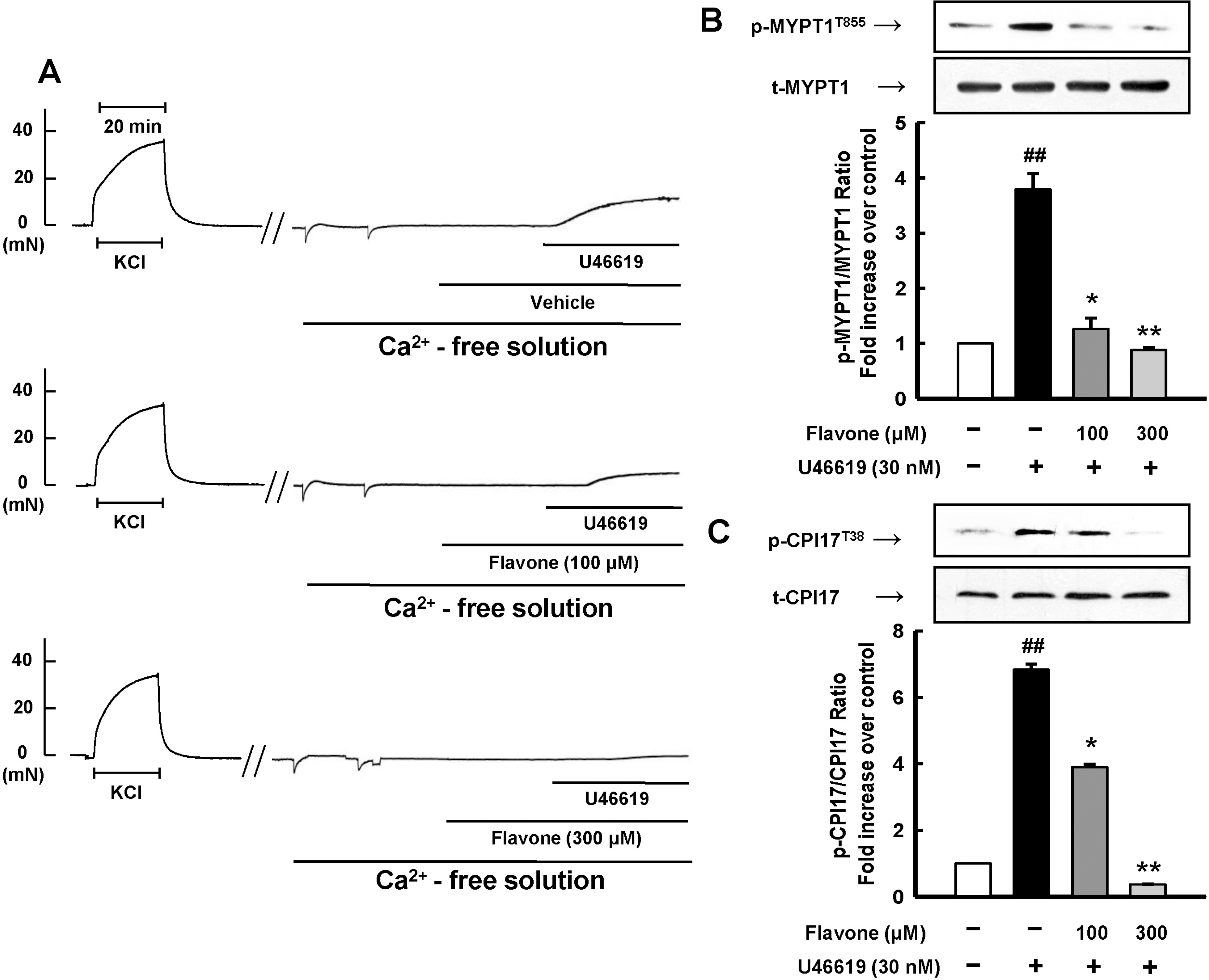 | Fig. 5.Inhibitory effect of flavone on contractions and phosphorylation of MYPT1Thr855 and CPI17Thr38 induced by U46619 in a Ca2+-free solution. (A) Representative tracings of the development of isometric tension showed that, after initial reference contractions to KCl (50 mM) were obtained, the aortic rings were incubated in a Ca2+-free solution for 40 min, pretreated with either 100 or 300 μM flavone or vehicle for 30 min and then challenged with the addition of U46619 in a Ca2+-free solution (3 aortic rings). Phosphorylation of MYPT1 at Thr855 (B) and CPI17 at Thr38 (C) was assessed by western blots 15 min after treatment with U46619 (30 nM) or vehicle. Data are expressed as means with vertical bars showing S.E.M. ∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01 vs. U46619 or NaF alone. ##p<0.01 vs. basal (one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey's test). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download