Abstract
Zinc released from excited glutamatergic neurons accelerates amyloid β (Aβ) aggregation, underscoring the therapeutic potential of zinc chelation for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Zinc can also alter Aβ concentration by affecting its degradation. In order to elucidate the possible role of zinc influx in secretase-processed Aβ production, SH-SY5Y cells stably expressing amyloid precursor protein (APP) were treated with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), a zinc ionophore, and the resultant changes in APP processing were examined. PDTC decreased Aβ40 and Aβ42 concentrations in culture media bathing APP-expressing SH-SY5Y cells. Measuring the levels of a series of C-terminal APP fragments generated by enzymatic cutting at different APP-cleavage sites showed that both β- and α-cleavage of APP were inhibited by zinc influx. PDTC also interfered with the maturation of APP. PDTC, however, paradoxically increased the intracellular levels of Aβ40. These results indicate that inhibition of secretase-mediated APP cleavage accounts -at least in part- for zinc inhibition of Aβ secretion.
REFERENCES
Busciglio J., Pelsman A., Wong C., Pigino G., Yuan M., Mori H., Yankner BA. Altered metabolism of the amyloid beta precursor protein is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in Down's syndrome. Neuron. 33:677–688. 2002.
Bush AI., Pettingell WH., Multhaup G., d Paradis M., Vonsattel JP., Gusella JF., Beyreuther K., Masters CL., Tanzi RE. Rapid induction of Alzheimer A beta amyloid formation by zinc. Science. 265:1464–1467. 1994.

Caporaso GL., Gandy SE., Buxbaum JD., Greengard P. Chloroquine inhibits intracellular degradation but not secretion of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 89:2252–2256. 1992.

Caragounis A., Du T., Filiz G., Laughton KM., Volitakis I., Sharples RA., Cherny RA., Masters CL., Drew SC., Hill AF., Li QX., Crouch PJ., Barnham KJ., White AR. Differential modulation of Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta-peptide accumulation by diverse classes of metal ligands. Biochem J. 407:435–450. 2007.
Cherny RA., Atwood CS., Xilinas ME., Gray DN., Jones WD., McLean CA., Barnham KJ., Volitakis I., Fraser FW., Kim Y., Huang X., Goldstein LE., Moir RD., Lim JT., Beyreuther K., Zheng H., Tanzi RE., Masters CL., Bush AI. Treatment with a copper-zinc chelator markedly and rapidly inhibits beta-amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. Neuron. 30:665–676. 2001.
Chinery R., Brockman JA., Peeler MO., Shyr Y., Beauchamp RD., Coffey RJ. Antioxidants enhance the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents in colorectal cancer: a p53-independent induction of p21WAF1/CIP1 via C/EBPbeta. Nat Med. 3:1233–1241. 1997.
Corrigan FM., Reynolds GP., Ward NI. Hippocampal tin, aluminum and zinc in Alzheimer's disease. Biometals. 6:149–154. 1993.

Dineley KE., Votyakova TV., Reynolds IJ. Zinc inhibition of cellular energy production: implications for mitochondria and neurodegeneration. J Neurochem. 85:563–570. 2003.

Frederickson CJ. Neurobiology of zinc and zinc-containing neurons. Int Rev Neurobiol. 31:145–238. 1989.

Furukawa K., Sopher BL., Rydel RE., Begley JG., Pham DG., Martin GM., Fox M., Mattson MP. Increased activity-regulating and neuroprotective efficacy of alpha-secretase-derived secreted amyloid precursor protein conferred by a C-terminal heparinbinding domain. J Neurochem. 67:1882–1896. 1996.
Glenner GG., Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 120:885–890. 1984.

Iseki A., Kambe F., Okumura K., Niwata S., Yamamoto R., Hayakawa T., Seo H. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits TNF-alpha-dependent activation of NF-kappaB by increasing intracellular copper level in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 276:88–92. 2000.
Kim CH., Kim JH., Hsu CY., Ahn YS. Zinc is required in pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett. 449:28–32. 1999a.
Kim CH., Kim JH., Xu J., Hsu CY., Ahn YS. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate induces bovine cerebral endothelial cell death by increasing the intracellular zinc level. J Neurochem. 72:1586–1592. 1999b.

Kosik KS., Joachim CL., Selkoe DJ. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 83:4044–4048. 1986.

Lambert MP., Barlow AK., Chromy BA., Edwards C., Freed R., Liosatos M., Morgan TE., Rozovsky I., Trommer B., Viola KL., Wals P., Zhang C., Finch CE., Krafft GA., Klein WL. Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95:6448–6453. 1998.
Lee JY., Cole TB., Palmiter RD., Suh SW., Koh JY. Contribution by synaptic zinc to the gender-disparate plaque formation in human Swedish mutant APP transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99:7705–7710. 2002.

Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle PA. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 12:2005–2015. 1993.

Meziane H., Dodart JC., Mathis C., Little S., Clemens J., Paul SM., Ungerer A. Memory-enhancing effects of secreted forms of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in normal and amnestic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95:12683–12688. 1998.
Pahlsson P., Spitalnik SL. The role of glycosylation in synthesis and secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 331:177–186. 1996.
Pahlsson P., Shakin-Eshleman SH., Spitalnik SL. N-linked glycosylation of beta-amyloid precursor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 189:1667–1673. 1992.
Selkoe DJ. Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 399:A23–31. 1999.

Su Y., Ryder J., Ni B. Inhibition of Abeta production and APP maturation by a specific PKA inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 546:407–410. 2003.
Tomita S., Kirino Y., Suzuki T. Cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein (APP) by secretases occurs after O-glycosylation of APP in the protein secretory pathway. Identification of intracellular compartments in which APP cleavage occurs without using toxic agents that interfere with protein metabolism. J Biol Chem. 273:6277–6284. 1998.
Vassar R., Citron M. Abeta-generating enzymes: recent advances in beta- and gamma-secretase research. Neuron. 27:419–422. 2000.
Verhaegh GW., Richard MJ., Hainaut P. Regulation of p53 by metal ions and by antioxidants: dithiocarbamate down-regulates p53 DNA-binding activity by increasing the intracellular level of copper. Mol Cell Biol. 17:5699–5706. 1997.

Walsh DM., Tseng BP., Rydel RE., Podlisny MB., Selkoe DJ. The oligomerization of amyloid beta-protein begins intracellularly in cells derived from human brain. Biochemistry. 39:10831–10839. 2000.
Walsh DM., Klyubin I., Fadeeva JV., Cullen WK., Anwyl R., Wolfe MS., Rowan MJ., Selkoe DJ. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature. 416:535–539. 2002.
Weidemann A., Konig G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum JM., Masters CL., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 57:115–126. 1989.

Wenstrup D., Ehmann WD., Markesbery WR. Trace element imbalances in isolated subcellular fractions of Alzheimer's disease brains. Brain Res. 533:125–131. 1990.

White AR., Du T., Laughton KM., Volitakis I., Sharples RA., Xilinas ME., Hoke DE., Holsinger RM., Evin G., Cherny RA., Hill AF., Barnham KJ., Li QX., Bush AI., Masters CL. Degradation of the Alzheimer disease amyloid beta-peptide by metal-dependent up-regulation of metalloprotease activity. J Biol Chem. 281:17670–17680. 2006.
Fig. 1.
PDTC decreases Aβ levels in the conditioned media. PDTC was added to SH-SY5Y-wt cells at the concentration indicated for 4 h. Aβ40 (A) and Aβ42 (B) in the conditioned media were quantified by sandwich ELISA. Bars represent the means± S.D. of three independent experiments. Control represents no drug treatment. Statistical significance was represented as ∗(p<0.05).
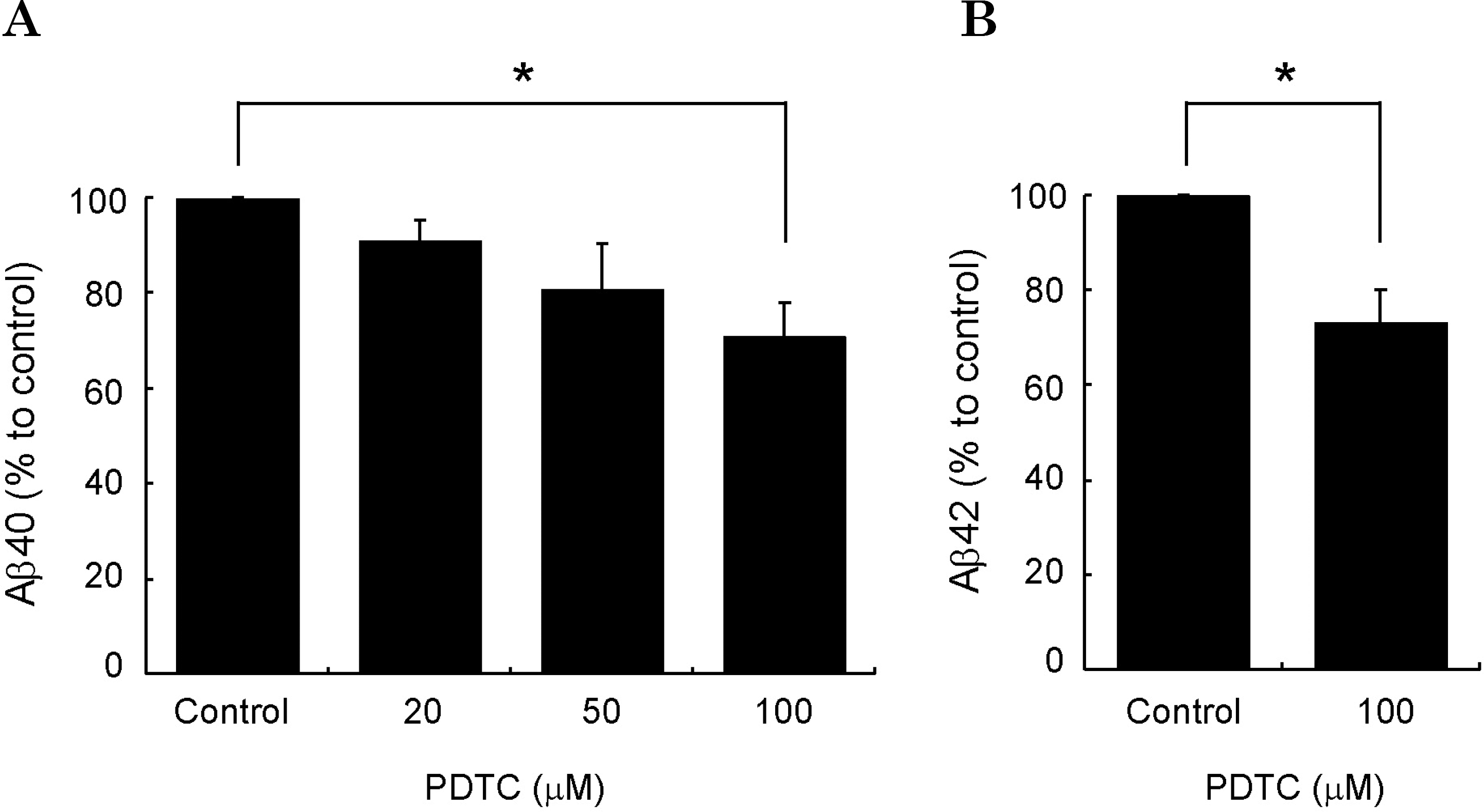
Fig. 2.
Zinc is required for PDTC action. Aβ40 levels in the conditioned media from SH-SY5Y-wt cells were measured by sandwich ELISA (A and B) or by TCA precipitation followed by combined immunoprecipitation and immunoblot assays with Aβ40 antibody (C). (A) SH-SY5Y-wt cells were incubated with or without 100-μM PDTC and/or 10-μM EDTA for 4 h. (B) Serum-deprived SH-SY5Y-wt cells were treated as follows: control, 100-μM PDTC, 100-μM PDTC with 1.5-μM ZnSO4 or 1.5-μM CuSO4, 1.5-μM ZnSO4, and 150-μM ZnSO4 for 4 h. (C) The serum-free conditioned media from SH-SY5Y-wt cells treated with or without PDTC plus 1.5-μM zinc were concentrated by TCA precipitation for Aμ40 assay (see methods). Bars represent the mean±S.D. of three different experiments. Control represents no drug treatment. Statistical significance was represented as ∗(p<0.05).
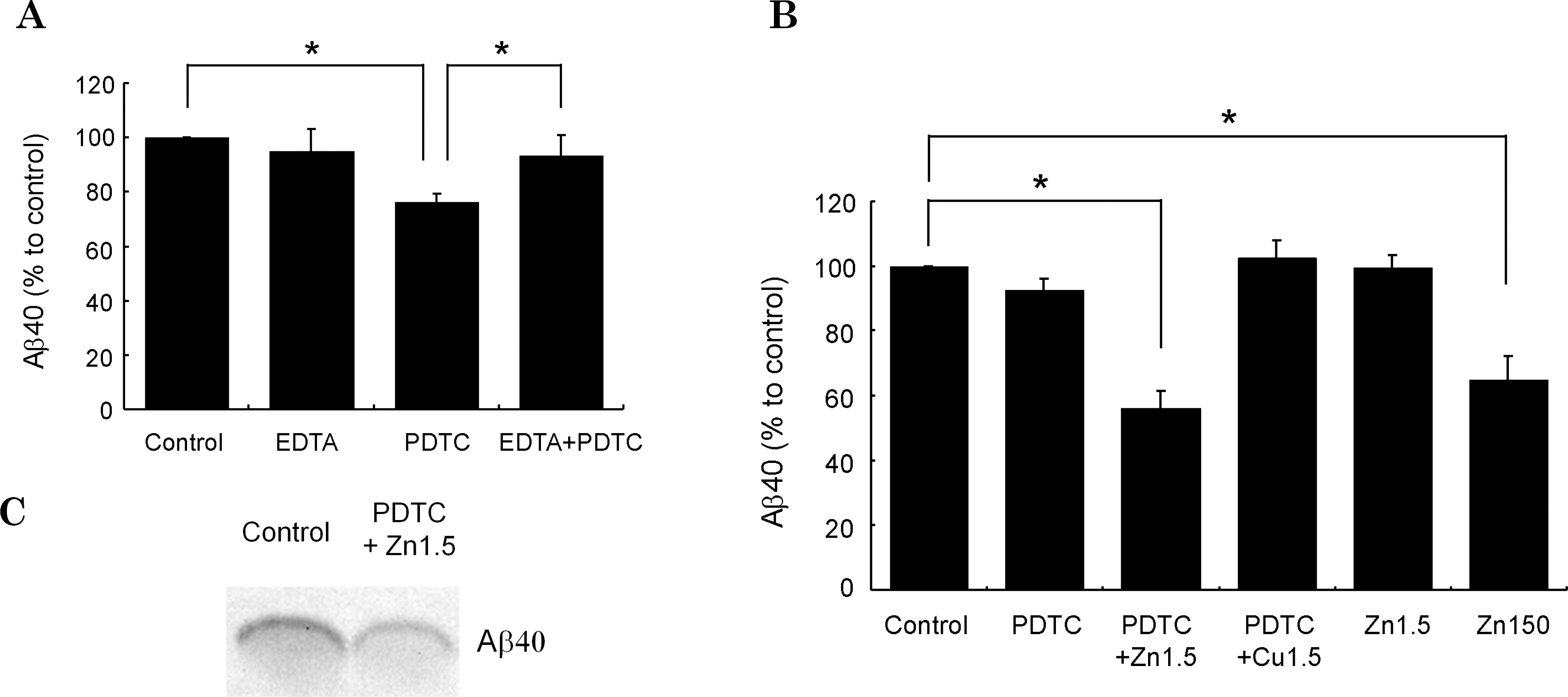
Fig. 3.
APP processing by β- and α-secretase is inhibited by PDTC. The cell lysates (A) or conditioned media (B) of SH-SY5Y-wt cells treated with or without 100-μM PDTC were analyzed by immunoblot assay (B) or combined immunoprecipitation-immunoblot assay (A) (see methods). The amounts of C99 and C83 detected in immunoblot assays with APP C-terminus antibodies were semi-quantified with densitometry. A monoclonal 6E10 antibody (against a.a. 1~17 of human Aβ) was used for the sAPPα assay. Bars represent the means±S.D. of two or three independent experiments. Control represents no drug treatment. Mature APP is represented as mAPP; immature APP, imAPP. Statistical significance was represented as ∗(p<0.05).
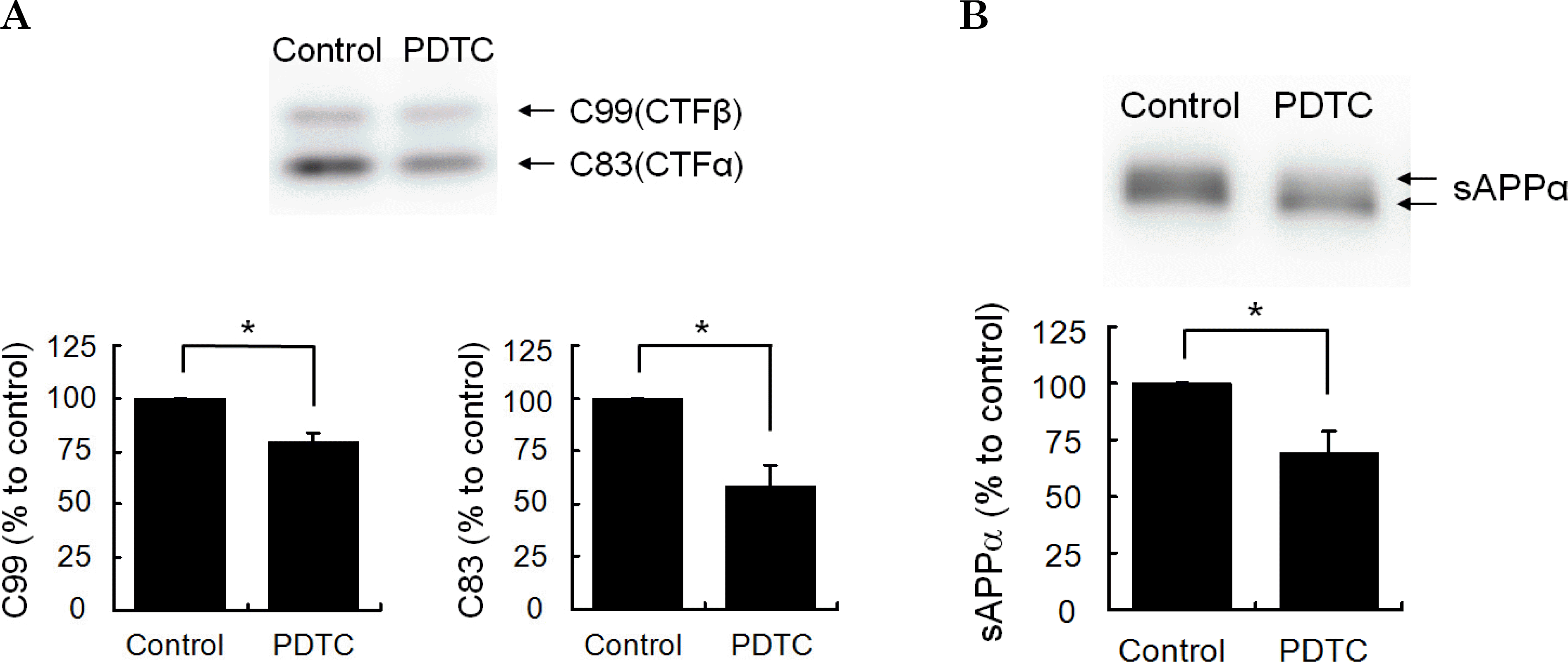
Fig. 4.
PDTC increases intracellular Aβ40. SH-SY5Y-swe cells were incubated with or without 100-μM PDTC for 4 h and then scraped, pelleted and lysed. Aβ40 in the cell lysates was assayed by sandwich ELISA. Bars represent the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. Control represents no drug treatment. Statistical significance was represented as ∗(p<0.05).
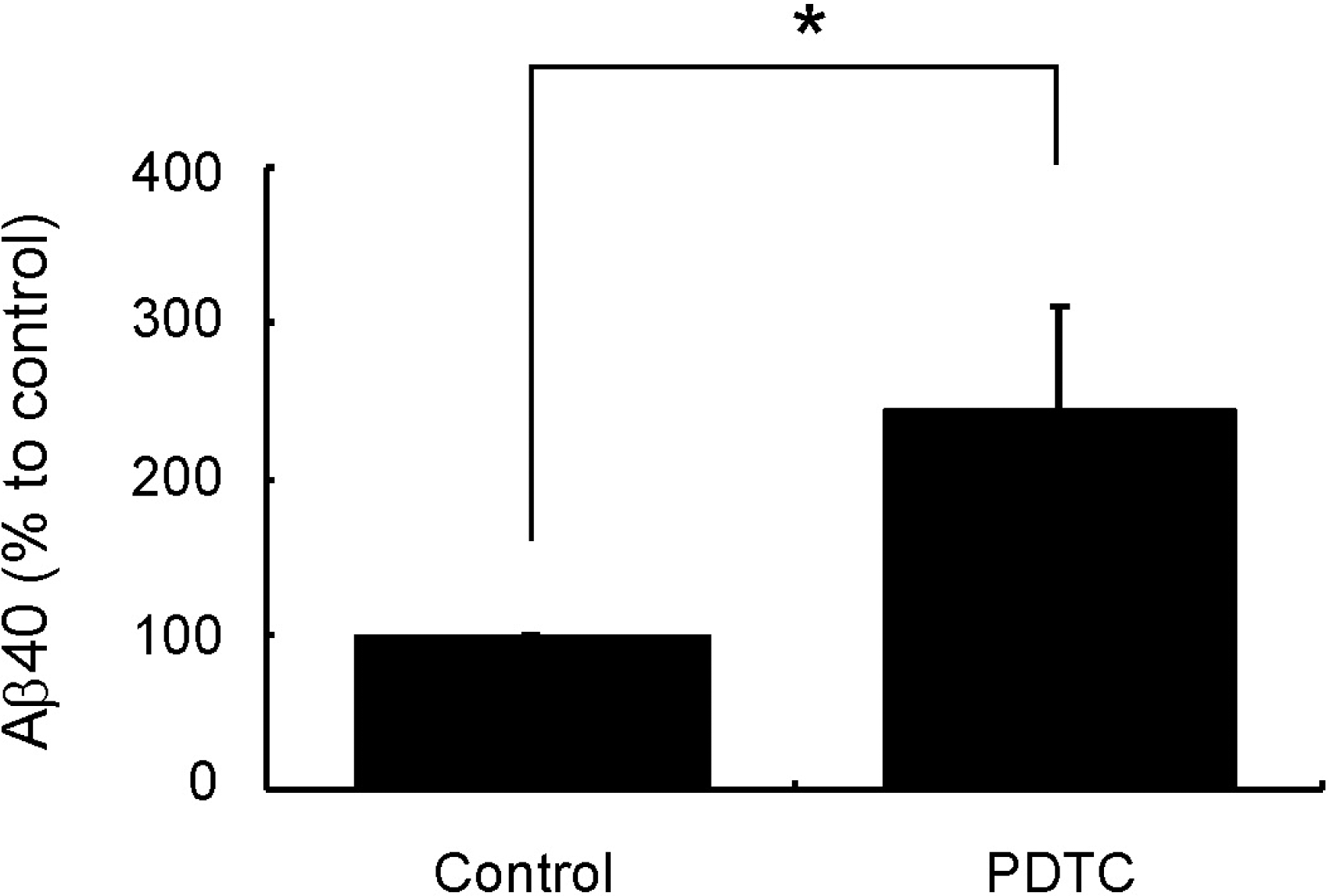
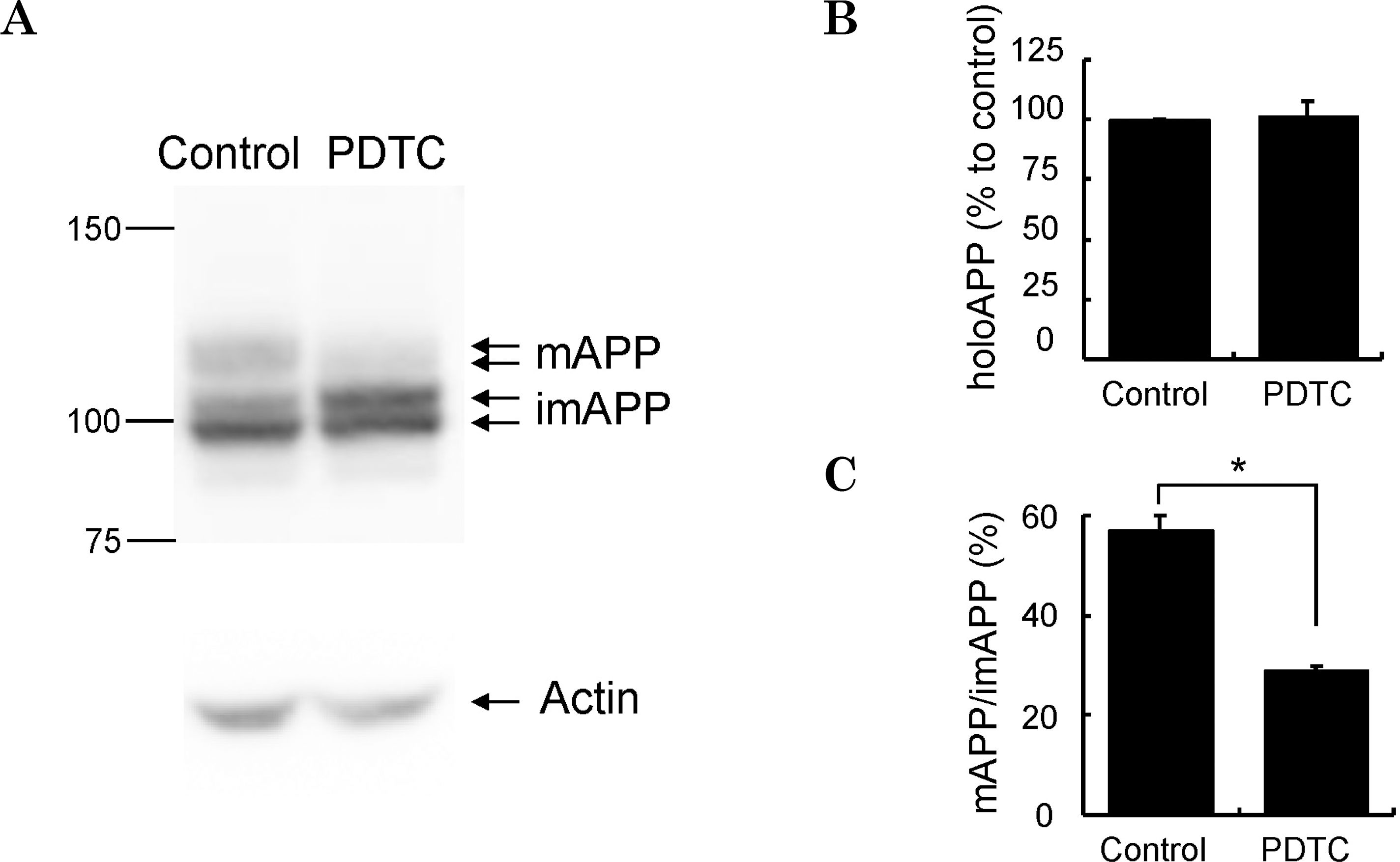
Fig. 5.
Maturation of APP is inhibited by PDTC. Cell lysates of SH-SY5Y-wt cells treated with or without 100-μM PDTC for 4 h were separated in 7% SDS-PAGE. (A) APP was immunoblotted with APP C-terminus antibody. (B) Quantitative analysis of the holoAPP bands (mature form + immature form). Amount of holoAPP was normalized to actin levels. (C) The maturation degree of APP was shown by the percentage of mAPP to imAPP. Bars represent the mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. Control represents no drug treatment. Statistical significance was represented as ∗(p<0.05).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download