Abstract
In our previous study, we found that spermine and putrescine inhibited spontaneous and acetylcholine (ACh)-induced contractions of guinea-pig stomach via inhibition of L-type voltage- dependent calcium current (VDCCL). In this study, we also studied the effect of spermidine on mechanical contractions and calcium channel current (IBa), and then compared its effects to those by spermine and putrescine. Spermidine inhibited spontaneous contraction of the gastric smooth muscle in a concentration-dependent manner (IC50=1.1±0.11 mM). Relationship between inhibition of contraction and calcium current by spermidine was studied using 50 mM high K+-induced contraction: Spermidine (5 mM) significantly reduced high K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction to 37±4.7% of the control (p<0.05), and inhibitory effect of spermidine on IBa was also observed at a wide range of test potential in current/voltage (I/V) relationship. Pre- and post-application of spermidine (5 mM) also significantly inhibited carbachol (CCh) and ACh-induced initial and phasic contractions. Finally, caffeine (10 mM)-induced contraction which is activated by Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR), was also inhibited by pretreatment of spermidine (5 mM). These findings suggest that spermidine inhibits spontaneous and CCh-induced contraction via inhibition of VDCCL and Ca2+ releasing mechanism in guinea-pig stomach.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
Aihara H., Otomo S., Isobe Y., Ohzeki M., Igarashi K., Hirose S. Polyamine inhibition of gastric ulceration and seretion in rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 32:1733–1736. 1983.
Chideckel EW., Fedan JS., Mike P. Polyamines and putrescine relax respiratory tract smooth muscle in the guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 116:187–190. 1985.
De Meis L. Relaxing effect of of spermine and spermidine on intact and glycerol-treated muscle. Am J Physiol. 212:92–96. 1967.
Drouin H., Hermann A. Intracellular action of spermine on neuronal Ca2+ and K+ currents. Eur J Neurosci. 6:412–419. 1994.
Fernandez AI., Cantabrana B., Sanchez M., Hidalgo A. Extracellular and intracellular effects of polyamines on smooth muscle contractions. Life Sci. 57:855–861. 1995.
Gomez M., Hellstrand P. Effects of polyamines on voltage-activated calcium channels in guinea-pig intestinal smooth muscle. Pflügers Arch. 430:501–507. 1995.

Gomez M., Hellstrand P. Endogenous polyamines modulate Ca2+ channel activity in guinea-pig intestinal smooth muscle. Pflügers Arch. 438:445–451. 1999.
Hamill OP., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth FJ. Improved pathch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch. 391:85–100. 1981.
Hashimoto H., Unemoto T., Hayashi M. Inhibitory action of spermine on the contractions of rat uterus. Am J Physiol. 225:743–746. 1973.

Hougaard DM., Fujiwara K., Larsson LI. Immunocytochemical localization of polyamines in normal and neoplastic cells. Comparisons to the formaldehyde-fluorescamine and o-phthalal-dehyde methods. Histochem J. 19:643–650. 1987.
Igarashi K., Kashiwagi K. Polyamines: mysterious modulators of cellular functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 271:559–564. 2000.

Isenberg G., Klöckner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by pre-incubation in a “K-B-medium”. Pflügers Arch. 424:431–438. 1982.
Katzka DA., Morad M. Properties of calcium channels in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. J Physiol. 413:175–197. 1989.

Kim SJ., Ahn SC., Kim JK., Kim YC., So I., Kim KW. Changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration induced by L-type Ca2+ channel current in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. Am J Physiol. 8273:C1947–1956. 1997.
Kim SJ., Min KY., Kim YC., Lee SJ., So I., Kim KW. Inhibitory effect of caffeine on carbachol-induced nnonselective cationic current in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. Kor J Physiol Pharmacol. 2:353–359. 1998.
Kim YC., Sim JH., Kim YH., Kwon SC., Lee SJ., Kim SR., Kim DW., Park SM., Youn SJ., Lee SJ., Xing de-Gang., Xu WX., Kim KW. Effect of polyamines on contractility of guinea-pig gastric smooth muscle. J Kor Med Sci. 22:48–56. 2007.
Lopatin AN., Markhina EN., Nichols CG. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism for intrinsic rectification. Nature. 372:366–369. 1994.
Martin JS., Tansy MF. Comparison of the inhibitory effects of spermine, papaverine and adrenaline upon isolated segments of the rat small intestine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1986. 13:87–90. 1986.

Maruta K., Mizoguchi Y., Osa T. Effects of polyamines on the mechanical and electrical activities of the isolated circular muscle of rat uterus. Jpn J Physiol. 36:903–915. 1985.

Nagasaki K., Kasai M. Channel selectivity and gating specificity of calcium-induced calcium release channel in isolated sarco-plasmic reticulum. J Biochem. 96:1769–1775. 1984.
Nilsson BO., Hellstrand P. Effects of polyamines on intracellular calcium and mechanical activity in smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. Acta Physiol Scand. 148:37–43. 1993.

Nishimura K., Shiina R., Kashiwagi K., Igarashi K. Decrease in polyamines with aging and their ingestion from food and drink. J Biochem. 139:81–90. 2006.

Palade P. Drug induced calcium release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. III. Block of calcium-induced calcium release by organic polyamines. J Biol Chem. 262:6149–6154. 1987.
Peulen O., Deloyer P., Dandrifosse G. Short-term effects of spermine ingestion on the small intestine: a comparison of suckling and weaned rats. Reprod Nutr Dev. 44:353–364. 2004.

Sato K., Sanders KM., Gerthoffer WT., Publicover NG. Sources of calcium utilized in cholinergic responses in canine colonic smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 267:C1666–C1673. 1994.

Schoemaker H. Polyamines allosterically modulate [3H] nitrendipine binding to the voltage-sensitive calcium in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 225:167–169. 1992.
Swärd K., Nillsson B-O., Hellstrand P. Polyamines increase Ca2+ sensitivity in permeabilized smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum. Am J Physiol. 266:C1754–C1763. 1994.
Tansy MF., Martin JS., Landin WF., Kendall FM., Melamed S. Spermine and spermidine as inhibitors of gastrointestinal motor activity. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 154:74–80. 1982.
Go to : 
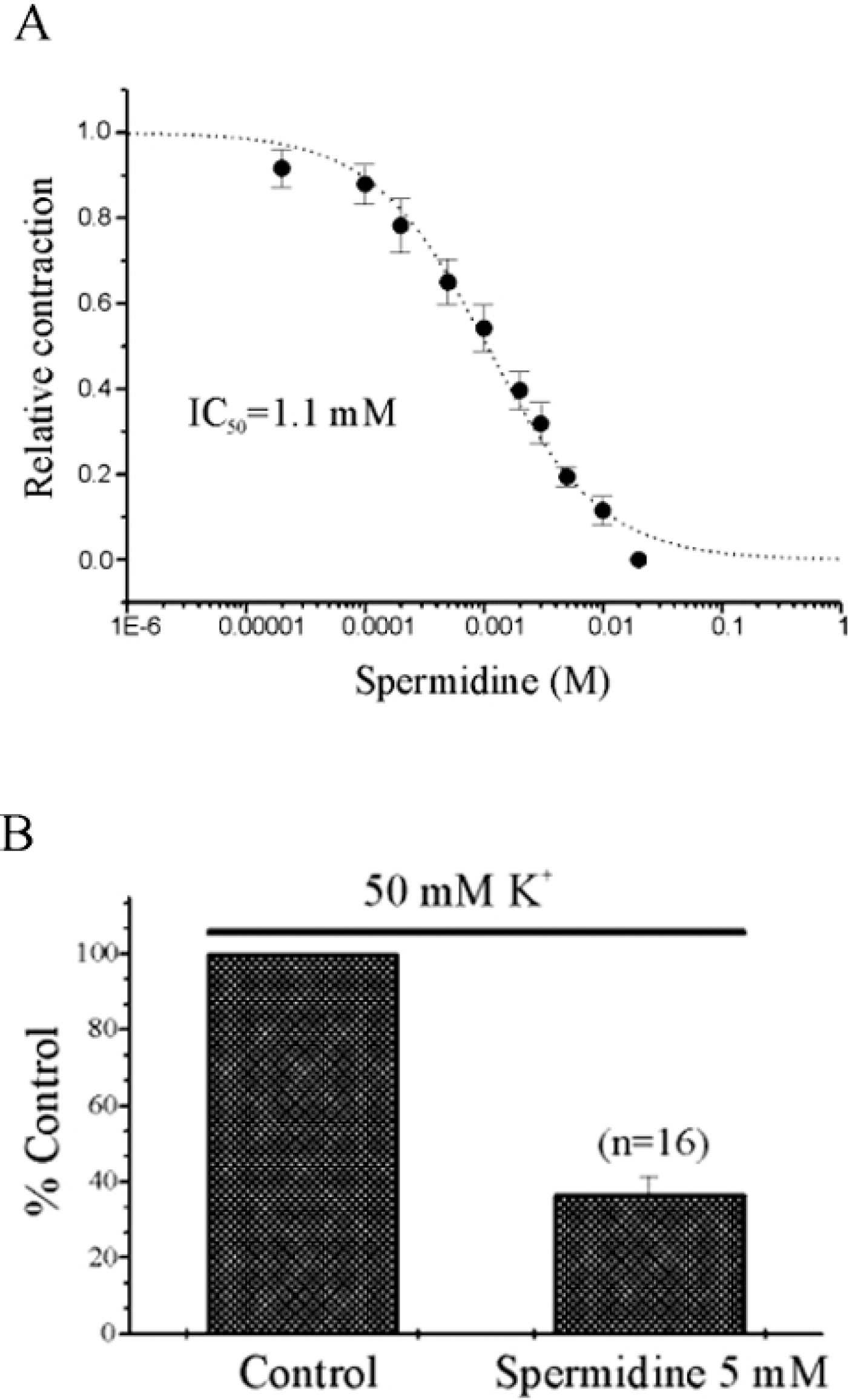 | Fig. 1.Effect of spermidine on isometric and high K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction in guinea-pig gastric smooth muscle. Effects of spermidine on isometric contraction were studied by using vertical chamber system. (A) Spermidine causes relaxation in a concentration-dependent manner. Relative contractions at various concentrations of spermine were plotted and fitted by the non-linear regression equation (IC50=1.1 mM). (B) High K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction was compared by pretreatment of spermidine (5 mM) before re-application of High K+ solution. Such a high K+ (50 mM)-induced contraction was significantly inhibited by the pretreatment with 5 mM spermidine (p<0.05). |
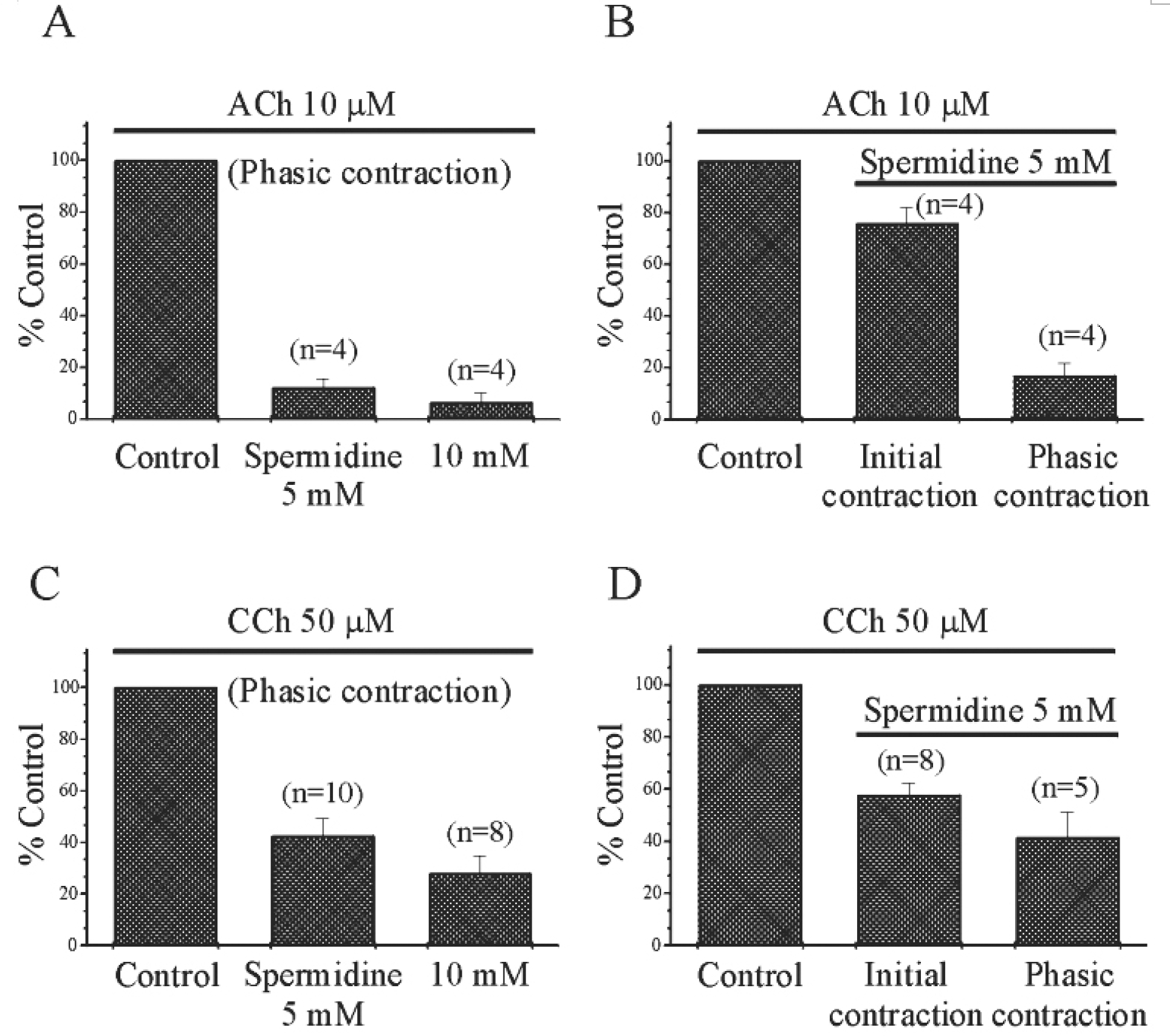 | Fig. 2.Inhibitory effect of spermidine on muscaranic receptor agonist-stimulated contraction via regulation of VDCCL. Acethylcholine (ACh, 10 μM) and carbachol (CCh, 50 μM) were applied to guinea-pig gastric smooth muscle. ACh- and CCh-induced transient initial and sustained phasic contractions were studied in the presence or absence of spermidine. (A and C) When 5 mM spermidine was applied to ACh- and CCh-induced sustained contractions, those contractions were inhibited to 12% and 43% of the control, respectively. (B) When 5 mM spermidine was pre-treated before the second application of ACh, ACh-induced transient initial and sustained phasic contractions were inhibited to 76% and 17% of the control, respectively. (D) When 5 mM spermidine was applied before the second application of CCh, CCh-induced transient initial and sustained phasic contractions were also inhibited to 58% and 42% of the control, respectively. |
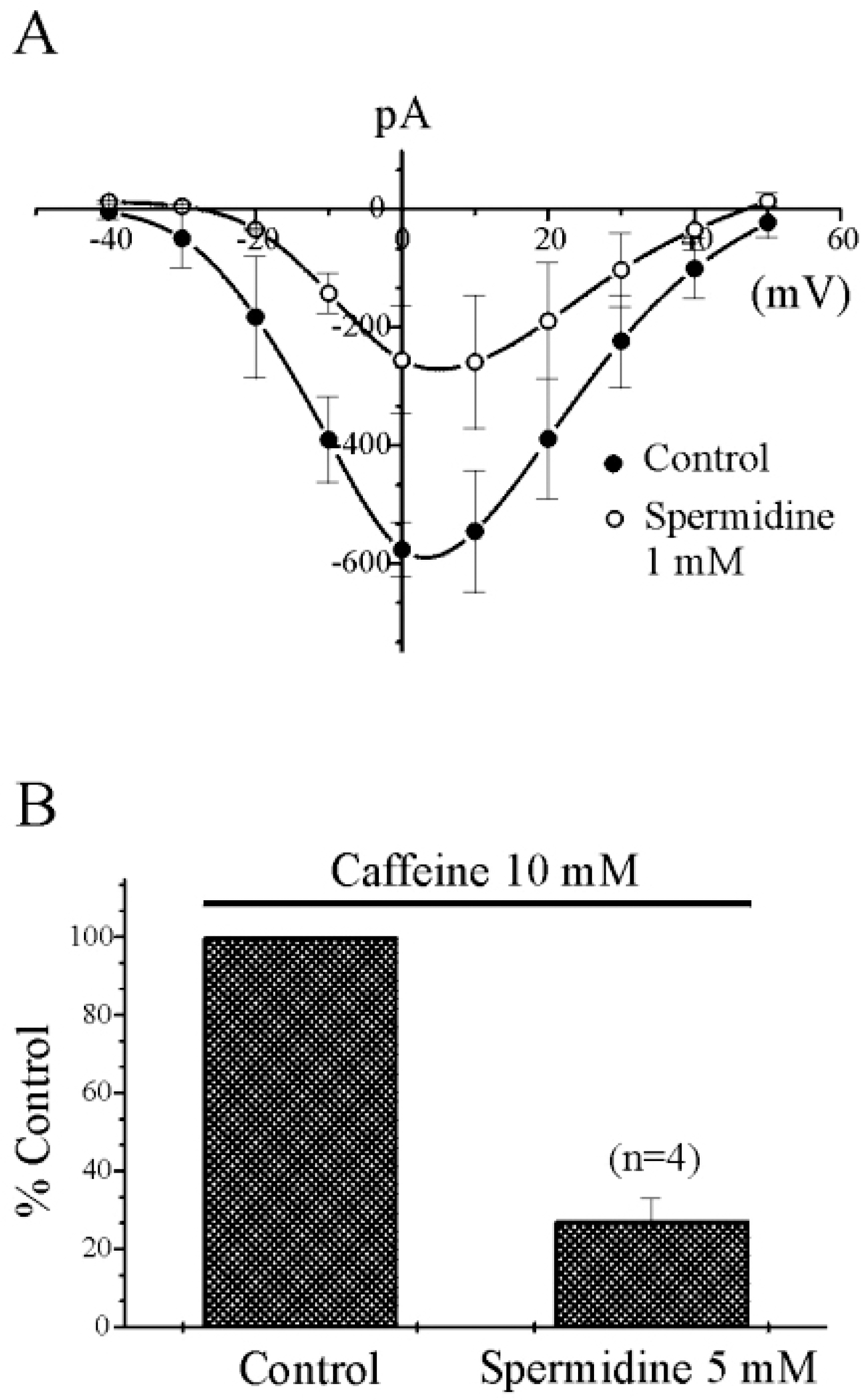 | Fig. 3.Effect of spermidine on IBa and caffeine-induced contraction in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. (A) IBa was recorded under the condition in which extracellular Ca2+ was replaced by 10 mM Ba2+. I/V relationship of IBa by spermidine is shown by averaged responses in the presence and absence of spermidine (closed circle, Control; open circle, 1 mM spermidine). Inhibition of IBa was observed at whole potential ranges tested. (B) Caffeine (10 mM)-induced contraction was compared with pretreatment of spermidine (5 mM) before re-application of caffeine. Caffeine-induced contraction was significantly inhibited by pretreatment with 5 mM spermidine (p<0.05). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download