Abstract
Recently, Sun et al (2008) reported that the IL6R polymorphism is associated with schizophrenia. Therefore, to detect the association between polymorphisms of interleukin 31 receptor A (IL31RA) and schizophrenia, we genotyped 9 SNPs [rs9292101 (intron 1), rs1009639 (exon 2, Pro43Pro), rs2161582 (intron 2), rs68761890 (intron 5), rs16884629 (intron 6), rs11956465 (intron 12), rs12153724 (intron 12), and rs16884641 (intron 14)] using the Golden Gate assay on Illumina BeadStation 500 GX. Two hundred eighteen patients with schizophrenia and 379 normal subjects were recruited. Patients with schizophrenia were diagnosed according to DSM-IV, and control subjects without history of psychiatric disorders were selected. We used SNPStats, Haploview, HapAnalyzer, SNPAnalyzer, and Helixtree programs for the evaluation of genetic data. Of nine polymorphisms, three SNPs (rs9292101, rs1009639, and rs11956465) were associated with schizophrenia. The rs9292101 and rs11956465 showed significant associations with the risk of schizophrenia in the codominant [rs9292101, odds ratio (OR)=0.74, 95% confidence interval (CI)=0.58~0.95, p=0.017] and recessive (rs11956465, OR=0.64, 95% CI=0.42~0.96, p=0.034) models, respectively. The rs1009639 also was statistically related to schizophrenia in both codominant (OR=0.76, 95% CI=0.60~0.97, p=0.025) and dominant (OR=0.66, 95% CI=0.44~0.98, p=0.035) models. Two linkage disequilibrium (LD) blocks were made. In the analysis of haplotypes, a haplotype (GCT) in block 1 and a haplotype (CCACAG) in block 2 showed significant associations between schizophrenia and control groups (haplotype GCT, frequency=0.509, chi square=4.199, p=0.040; haplotype CCACAG, frequency=0.289, chi square=5.691, p=0.017). The results suggest that IL31RA may be associated with risk of schizophrenia in Korean population.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed.American Psychiatric Press;Washington DC: 1994.
Chen X., Wang X., Hossain S., O'Neill FA., Walsh D., van den Oord E., Fanous A., Kendler KS. Interleukin 3 and schizophrenia: the impact of sex and family history. Mol Psychiatry. 12:273–282. 2007.

Dillon SR., Sprecher C., Hammond A., Bilsborough J., Rosenfeld-Franklin M., Presnell SR., Haugen HS., Maurer M., Harder B., Johnston J., Bort S., Mudri S., Kuijper JL., Bukowski T., Shea P., Dong DL., Dasovich M., Grant FJ., Lockwood L., Levin SD., LeCiel C., Waggie K., Day H., Topouzis S., Kramer J., Kuestner R., Chen Z., Foster D., Parrish-Novak J., Gross JA. Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol. 5:752–760. 2004.

Diveu C., Lelievre E., Perret D., Lak-Hal AH., Froger J., Guillet C., Chevalier S., Rousseau F., Wesa A., Preisser L., Chabbert M., Gauchat JF., Galy A., Gascan H., Morel A. GPL, a novel cytokine receptor related to GP130 and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 278:49850–49859. 2003.

Hanninen K., Katila H., Saarela M., Rontu R., Mattila KM., Fan M., Hurme M., Lehtimaki T. Interleukin-1 beta gene polymorphism and its interactions with neuregulin-1 gene polymorphism are associated with schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 258:10–15. 2008.
Jung KH., Ban JY., Kim HJ., Park HJ., Uhm YK., Kim SK., Kim BS., Kim YJ., Koh IS., Chung J-H. Genetic association study of THRβ polymorphisms with obesity in Korean population. MCT. 4:2008a. in press.
Jung MY., Kim BS., Kim YJ., Koh IS., Chung JH. Assessment between Fyn-related kinase gene polymorphisms and overweight/obesity in Korean population. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 12:83–87. 2008b.
Lang UE., Puls I., Muller DJ., Strutz-Seebohm N., Gallinat J. Molecular mechanisms of schizophrenia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 20:687–702. 2007.

Muller N., Riedel M., Gruber R., Ackenheil M., Schwarz MJ. The immune system and schizophrenia. An integrative view. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 917:456–467. 2000.
Nawa H., Takahashi M., Patterson PH. Cytokine and growth factor involvement in schizophrenia–support for the developmental model. Mol Psychiatry. 5:594–603. 2000.

Papiol S., Molina V., Rosa A., Sanz J., Palomo T., Fananas L. Effect of interleukin-1beta gene functional polymorphism on dorsolateral prefrontal cortex activity in schizophrenic patients. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 144B:1090–1093. 2007.
Schwarz MJ., Kronig H., Riedel M., Dehning S., Douhet A., Spellmann I., Ackenheil M., Moller HJ., Muller N. IL-2 and IL-4 polymorphisms as candidate genes in schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 256:72–76. 2006.

Shirts BH., Wood J., Yolken RH., Nimgaonkar VL. Association study of IL10, IL1beta, and IL1RN and schizophrenia using tag SNPs from a comprehensive database: suggestive association with rs16944 at IL1beta. Schizophr Res. 88:235–244. 2006.
Go to : 
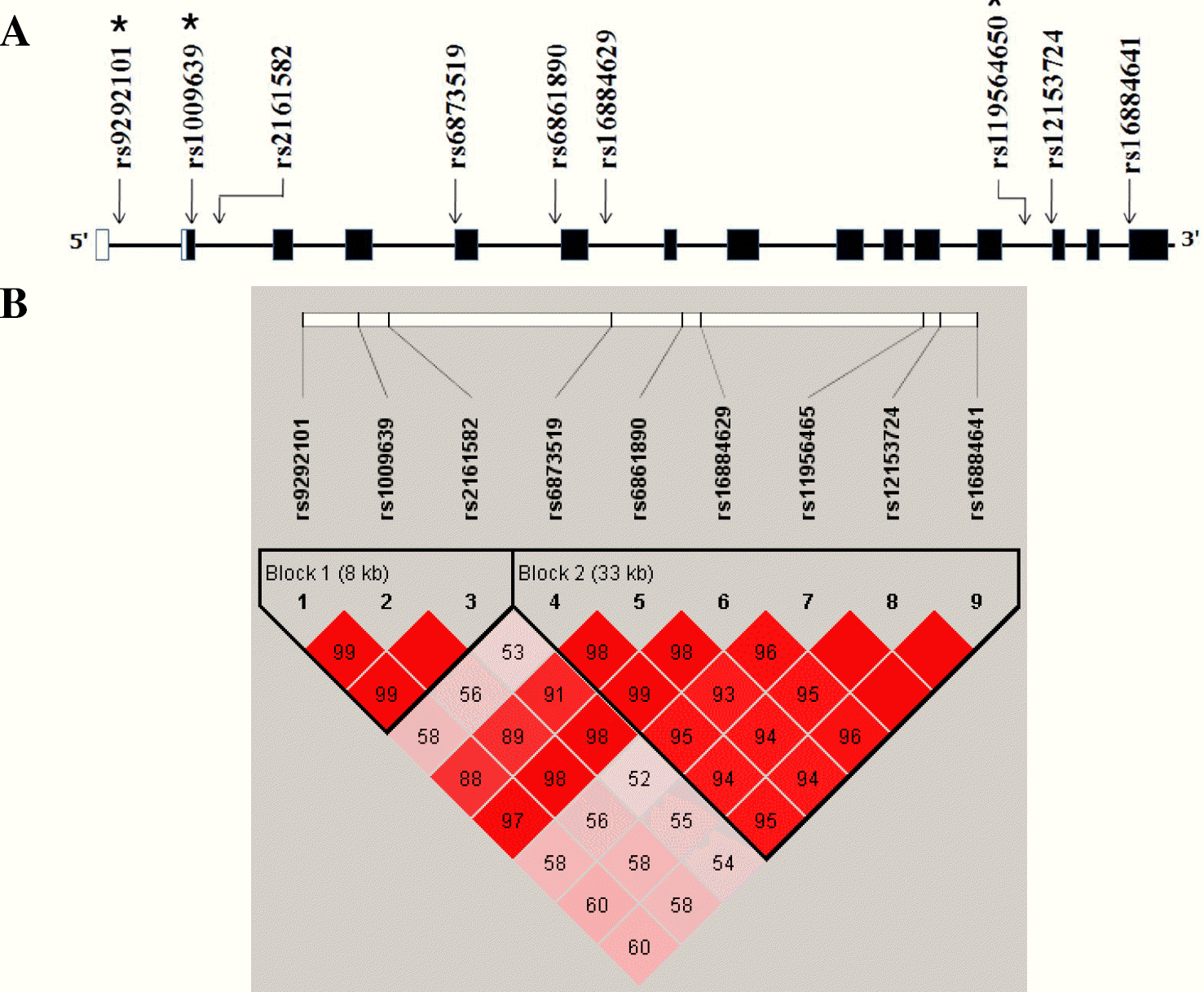 | Fig. 1.Gene map and linkage disequilibrium (LD) in interleukin 31 receptor A (IL31RA) gene. (A) Gene map of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in IL31RA. Exons are marked with box. The coding region is black-boxed and untranslated regions are white- boxed. Asterisk (∗) indicates a significant SNP. Arrow indicates the location of each SNP. (B) LD coefficient (|D'|) and LD blocks among SNPs of IL31RA. Block 1 consists of rs9292101, rs1009639, and rs2161582. Block 2 comprises rs6873519, rs6861890, rs16884629, rs11956465, rs12153724, and rs16884641. |
Table 1.
Logistic regression analysis and genotype frequency of interleukin 31 receptor A (IL31RA) polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia and controls
Genotype distributions are shown as number (%). Odds ratio (OR), 95% confidence interval (CI), and p-values were from logistic regression analysis with codominant, dominant, and recessive models controlling age and gender as covariates. Total number of each SNP is different, because genotypes of some SNPs are unreadable. SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
Table 2.
Haplotype analysis of interleukin 31 receptor A (IL31RA) polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia and controls
Table 3.
Genotype frequencies of interleukin 31 receptor A (IL31RA) polymorphisms in each population
From SNP database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download