Abstract
Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, is an important cellular response that modulates the outcome of the cells which are exposed to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or the genotoxic stress including DNA damaging agents. Although it is known that JNK is activated in response to genotoxic stress, neither the pathways to transduce signals to activate JNK nor the primary sensors of the cells that trigger the stress response have been identified. Here, we report that the receptor interacting protein (RIP), a key adaptor protein of TNF signaling, was required to activate JNK in the cells treated with certain DNA damaging agents such as adriamycin (Adr) and 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C) that cause slow and sustained activation, but it was not required when treated with N-methyl-N-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) and short wavelength UV, which causes quick and transient activation. Our findings revealed that this sustained JNK activation was not mediated by the TNF (tumor necrosis factor) receptor signaling, but it required a functional ATM (ataxia telangiectasia) activity. In addition, JNK inhibitor SP-600125 significantly blocked the Adr-induced cell death, but it did not affect the cell death induced by MNNG. These findings suggest that the sustained activation of JNK mediated by RIP plays an important role in the DNA damage-induced cell death, and that the duration of JNK activation relays a different stress response to determine the cell fate.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1072:129–157. 1991.

Bakkenist CJ., Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 421:499–506. 2003.

Bulavin DV., Saito S., Hollander MC., Sakaguchi K., Anderson CW., Appella E., Fornace AJ Jr. Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation. EMBO J. 18:6845–6854. 1999.

Byun HS., Park KA., Won M., Yang KJ., Shin S., Piao L., Kwak JY., Lee ZW., Park J., Seok JH., Liu ZG., Hur GM. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate protects against tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced necrotic cell death by modulating the recruitment of TNF receptor 1-associated death domain and receptor-interacting protein into the TNF receptor 1 signaling complex: Implication for the regulatory role of protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol. 70:1099–1108. 2006.

Canman CE., Kastan MB. Signal transduction. Three paths to stress relief. Nature. 384:213–214. 1996.
Chen YR., Wang X., Templeton D., Davis RJ., Tan TH. The role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in apoptosis induced by ultraviolet C and gamma radiation. Duration of JNK activation may determine cell death and proliferation. J Biol Chem. 271:31929–31936. 1996.
Coso OA., Chiariello M., Yu JC., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind JS. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 81:1137–1146. 1995.
Derijard B., Hibi M., Wu IH., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis RJ. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 76:1025–1037. 1994.

Devary Y., Rosette C., DiDonato JA., Karin M. NF-kappa B activation by ultraviolet light not dependent on a nuclear signal. Science. 261:1442–1445. 1993.

Fritz G., Kaina B. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 by UV irradiation is inhibited by wortmannin without affecting c-iun expression. Mol Cell Biol. 19:1768–1774. 1999.
Hayakawa J., Depatie C., Ohmichi M., Mercola D. The activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) by DNA-damaging agents serves to promote drug resistance via activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2)-dependent enhanced DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 278:20582–20592. 2003.

Heeres JT., Hergenrother PJ. Poly (ADP-ribose) makes a date with death. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 11:644–653. 2007.
Hur GM., Lewis J., Yang Q., Lin Y., Nakano H., Nedospasov S., Liu ZG. The death domain kinase RIP has an essential role in DNA damage-induced NF-kappa B activation. Genes Dev. 17:873–882. 2003.
Hur GM., Kim YS., Won M., Choksi S., Liu ZG. The death domain kinase RIP has an important role in DNA damage-induced, p53-independent cell death. J Biol Chem. 281:25011–25017. 2006.

Ichijo H., Nishida E., Irie K., ten Dijke P., Saitoh M., Moriguchi T., Takagi M., Matsumoto K., Miyazono K., Gotoh Y. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science. 275:90–94. 1997.

Karin M., Lin A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
Kharbanda S., Ren R., Pandey P., Shafman TD., Feller SM., Weichselbaum RR., Kufe DW. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature. 376:785–788. 1995.
Kyriakis JM., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie EA., Ahmad MF., Avruch J., Woodgett JR. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 369:156–160. 1994.

Lewis C., Low JA. Clinical poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 8:1051–1056. 2007.
Lin Y., Devin A., Cook A., Keane MM., Kelliher M., Lipkowitz S., Liu ZG. The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 20:6638–6645. 2000.
Liu ZG., Baskaran R., Lea-Chou ET., Wood LD., Chen Y., Karin M., Wang JY. Three distinct signalling responses by murine fibroblasts to genotoxic stress. Nature. 384:273–276. 1996.

Osborn MT., Chambers TC. Role of the stress-activated/c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase pathway in the cellular response to adriamycin and other chemotherapeutic drugs. J Biol Chem. 271:30950–30955. 1996.

Pandey P., Raingeaud J., Kaneki M., Weichselbaum R., Davis RJ., Kufe D., Kharbanda S. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by c-Abl-dependent and independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 271:23775–23779. 1996.

Parra M., Lluis F., Miralles F., Caelles C., Munoz-Canoves P. The cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway mediates induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) by the alkylating agent MNNG. Blood. 96:1415–1424. 2000.

Raingeaud J., Whitmarsh AJ., Barrett T., Derijard B., Davis RJ. MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 16:1247–1255. 1996.

Rosette C., Karin M. Ultraviolet light and osmotic stress: activation of the JNK cascade through multiple growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science 274: 1194−1197. 1996.

Sheikh MS., Antinore MJ., Huang Y., Fornace AJ. Ultravioletirradiation-induced apoptosis is mediated via ligand independent activation of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. Oncogene. 17:2555–2563. 1998.
Shu HB., Takeuchi M., Goeddel DV. The tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 signal transducers TRAF2 and c-IAP1 are components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 93:13973–13978. 1996.

Tang F., Tang G., Xiang J., Dai Q., Rosner MR., Lin A. The absence of NF-kappaB-mediated inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation contributes to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 22:8571–8579. 2002.
Tobin D., van Hogerlinden M., Toftgard R. UVB-induced association of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1/TNF receptor-associated factor-2 mediates activation of Rel proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 95:565–569. 1998.

Tournier C., Dong C., Turner TK., Jones SN., Flavell RA., Davis RJ. MKK7 is an essential component of the JNK signal transduction pathway activated by proinflammatory cytokines. Genes Dev. 15:141914–141926. 2001.

Yoshida K., Miki Y., Kufe D. Activation of SAPK/JNK signaling by protein kinase Cdelta in response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 277:48372–48378. 2002.
Zhang Y., Ma WY., Kaji A., Bode AM., Dong Z. Requirement of ATM in UVA-induced signaling and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:3124–3131. 2002.

Zhang S., Lin Y., Kim YS., Hande MP., Liu ZG., Shen HM. c-Jun N-terminal kinase mediates hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death via sustained poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 14:1001–1010. 2007.
Go to : 
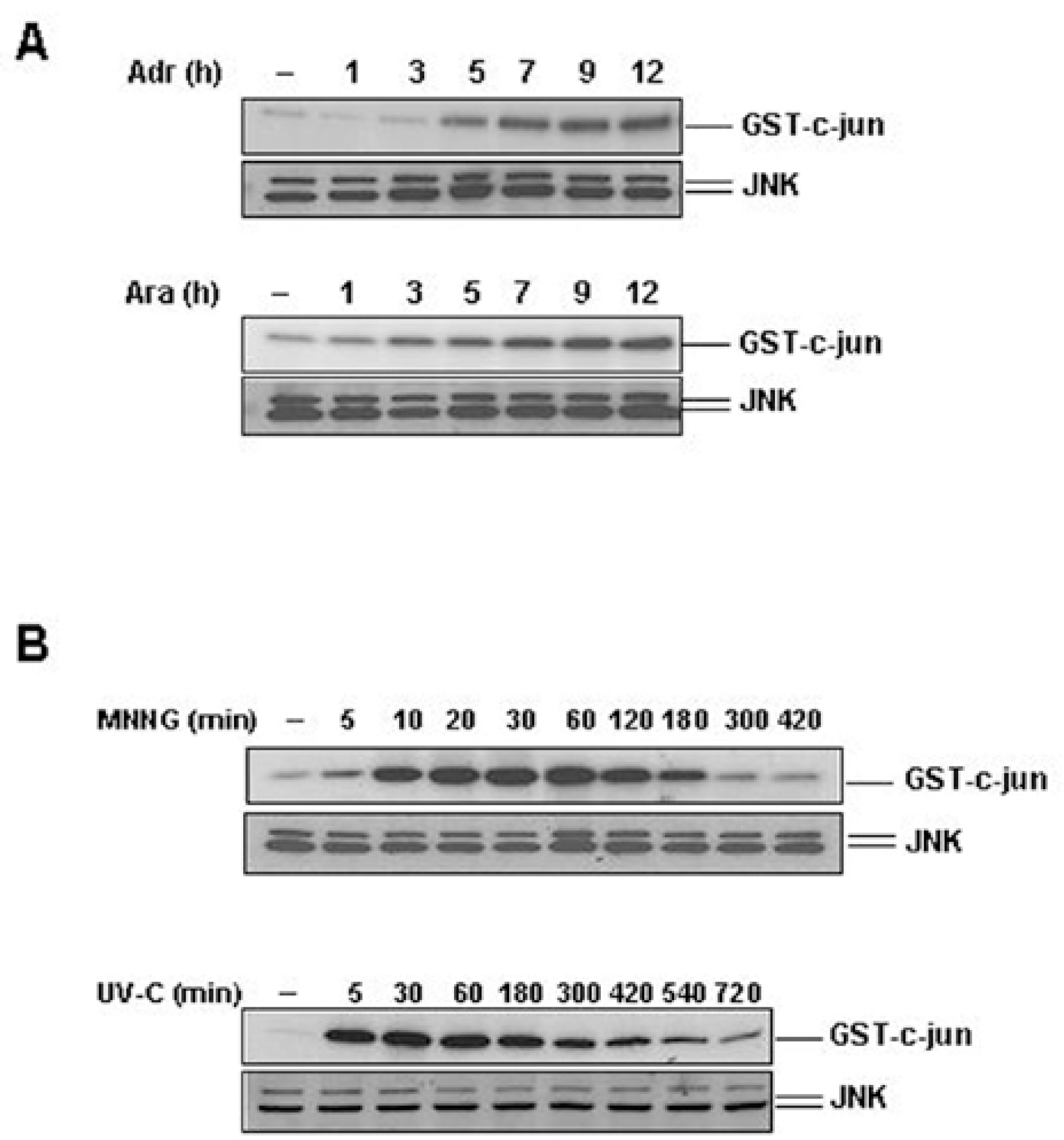 | Fig. 1.Different kinetics of DNA damage-induced JNK activation in response to Adr/Ara-C and MNNG/UV-C treatment. Mouse wild-type (WT) fibroblasts were treated with 10 μg/ml of adriamycin (Adr), 50 μM 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (Ara-C) (A) or 100 μM N-methyl-N(−nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG), or exposed to 20 J/m2 of UV-C (B) for various times as indicated on the figure. Cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti- JNK1 antibody, and its activity was assayed by immune complex kinase assay with [γ-32P]ATP and GST-c-Jun (1~79) as the substrate. GST-c-Jun phosphorylation was assessed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography (upper panel). JNK content was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-JNK antibody (lower panel). |
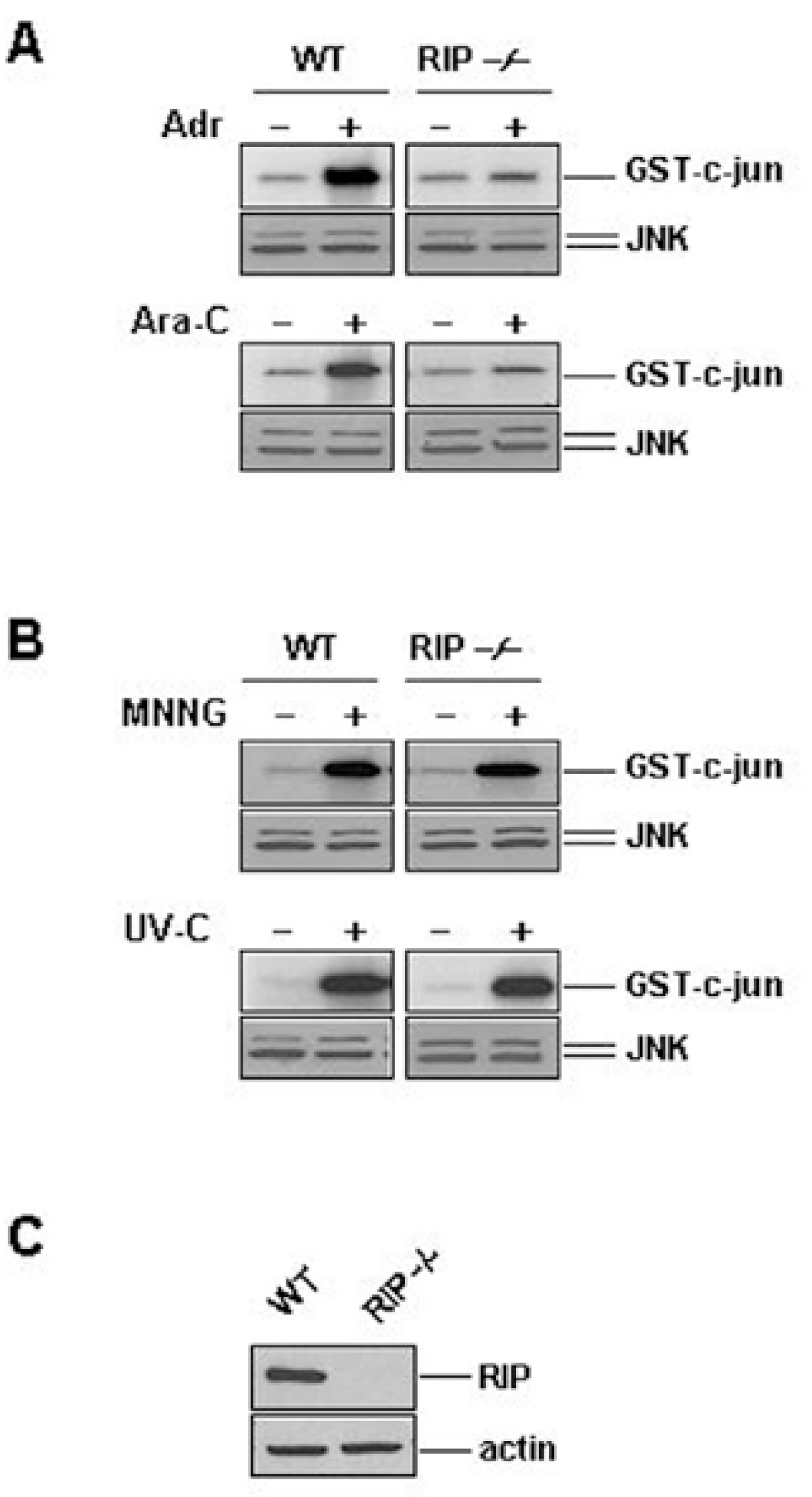 | Fig. 2.RIP plays a role in JNK activation by Adr and Ara-C, but not by MNNG and UV-C. Wild-type (WT) and RIP-/- fibroblasts were left untreated (–) or treated with Adr (10μg/ml) and Ara-C (50μM) for 12 hrs (A), or MNNG (100μM) and exposed to UV (20 J/m2) for 30 min (B). JNK activity and expression were measured as described in the legend of Fig 1. The protein expression levels of RIP and β-actin in WT and RIP-/- fibroblasts. (C) The same amount of cell extracts from each cell line was applied to SDS-PAGE for Western blotting with anti-RIP and anti-β-actin antibodies. |
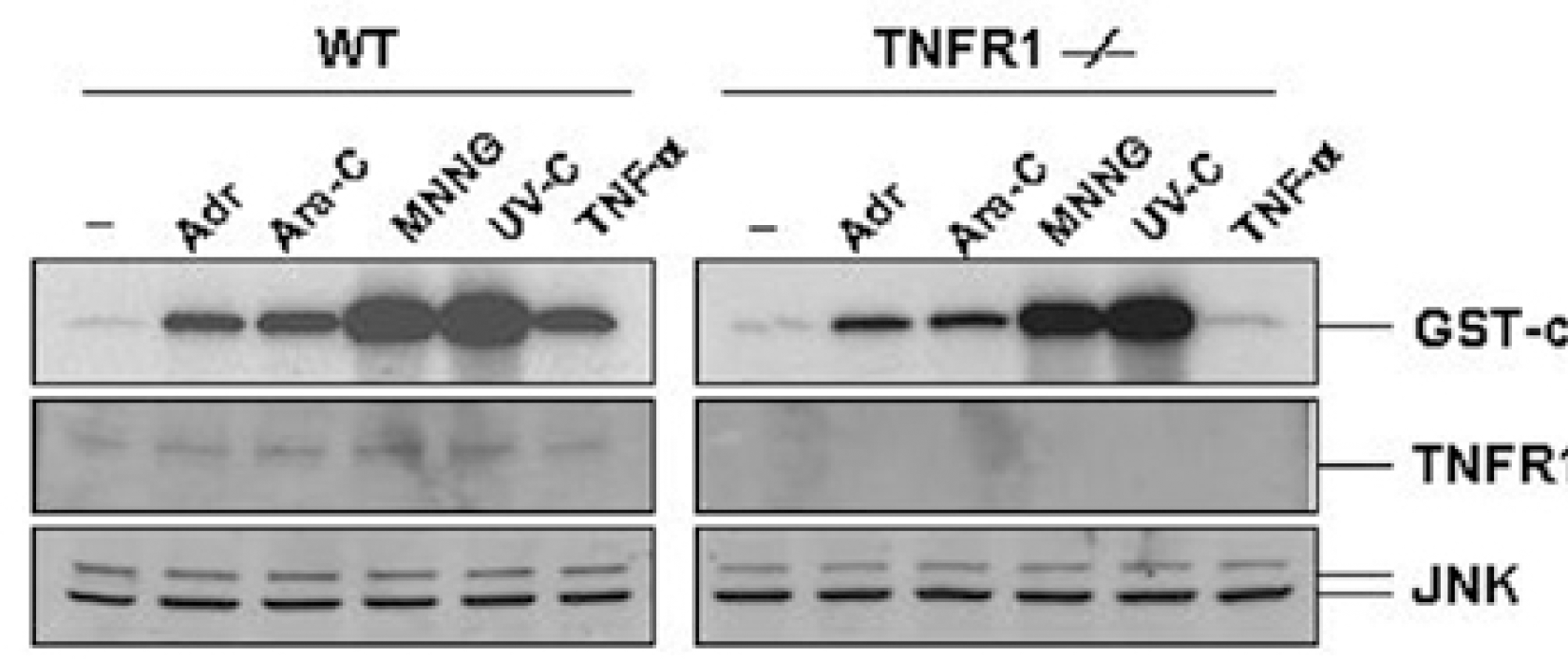 | Fig. 3.Genotoxic stress-induced JNK activation is independent of TNF receptor 1 signaling. Wild-type (WT) and TNFR1-/- fibroblasts were left untreated (–) or treated with Adr (10μg/ml) and Ara-C (50μM) for 12 hrs, MNNG (100μM) for 30 min or TNF-α (15 ng/ml) for 15 min and exposed to UV (20 J/m2) for 30 min. JNK activity (top) was measured as described in the legend of Fig 1. The same cell lysates were also analyzed for the expression of TNFR1 (middle) and JNK (bottom) by Western blotting with corresponding anti-TNFR1 and anti-JNK antibodies. |
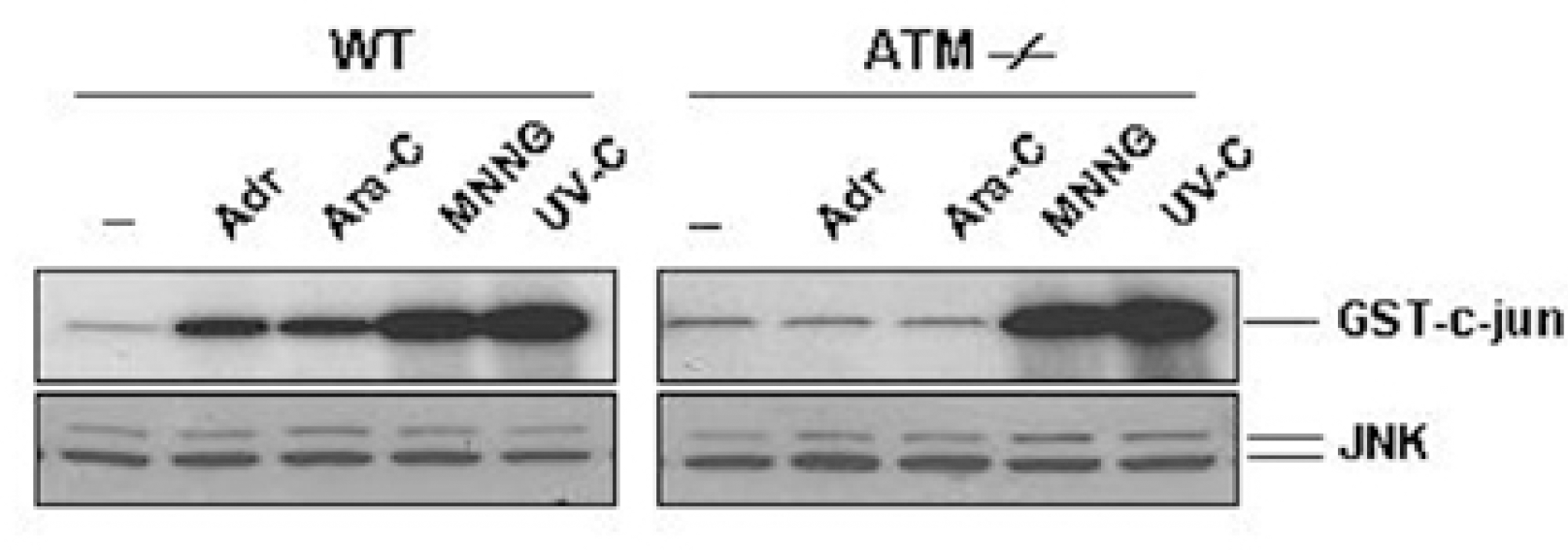 | Fig. 4.ATM is required for JNK activation by Adr and Ara-C, but not by MNNG and UV-C. Wild-type (WT) and ATM-/- fibroblasts were left untreated (–) or treated with Adr (10μg/ml) and Ara-C (50μM) for 12 hrs or MNNG (100μM) for 30 min, and exposed to UV (20 J/m2) for 30 min. JNK activity and expression were measured as described in the legend of Fig. 1. |
 | Fig. 5.Duration of JNK activation has an important role in DNA damage-induced cell death. (A) Long term activation of JNK is associated in the Adr-induced cell death. Wild-type (WT) fibriblasts were pretreated with SP-600125 (20μM) for 30 min and then treated with various doses of Adr as indicated on the figure. At 24 hrs after treatment, the percentage of cell death was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay, as described under “Materials and Methods”. Each bar shows mean±SE of at least three independent experiments. ∗p<0.05, when compared with Adr-treated group. (B) SP-600125 abrogates the Adr-induced JNK activation. WT fibriblasts were pretreated with SP-600125 (20μM) for 30 min and treated with Adr (10μg/ml) for 12 hrs. JNK activity and expression were measured as described in the legend of Fig. 1. (C) Rapid and short term activation of JNK is not associated with the MNNG- induced cell death. (WT) fibriblasts were pretreated with SP-600125 (20μM) for 30 min and treated with various doses of MNNG as indicated on the figure. At 24 hrs after treatment, the percentage of cell death was determined as described in (A). (D) WT fibriblasts were pretreated with SP-600125 (20μM) for 30 min and then treated with MNNG (100μM) for 30 min, and JNK activity was determined as described in (B). |
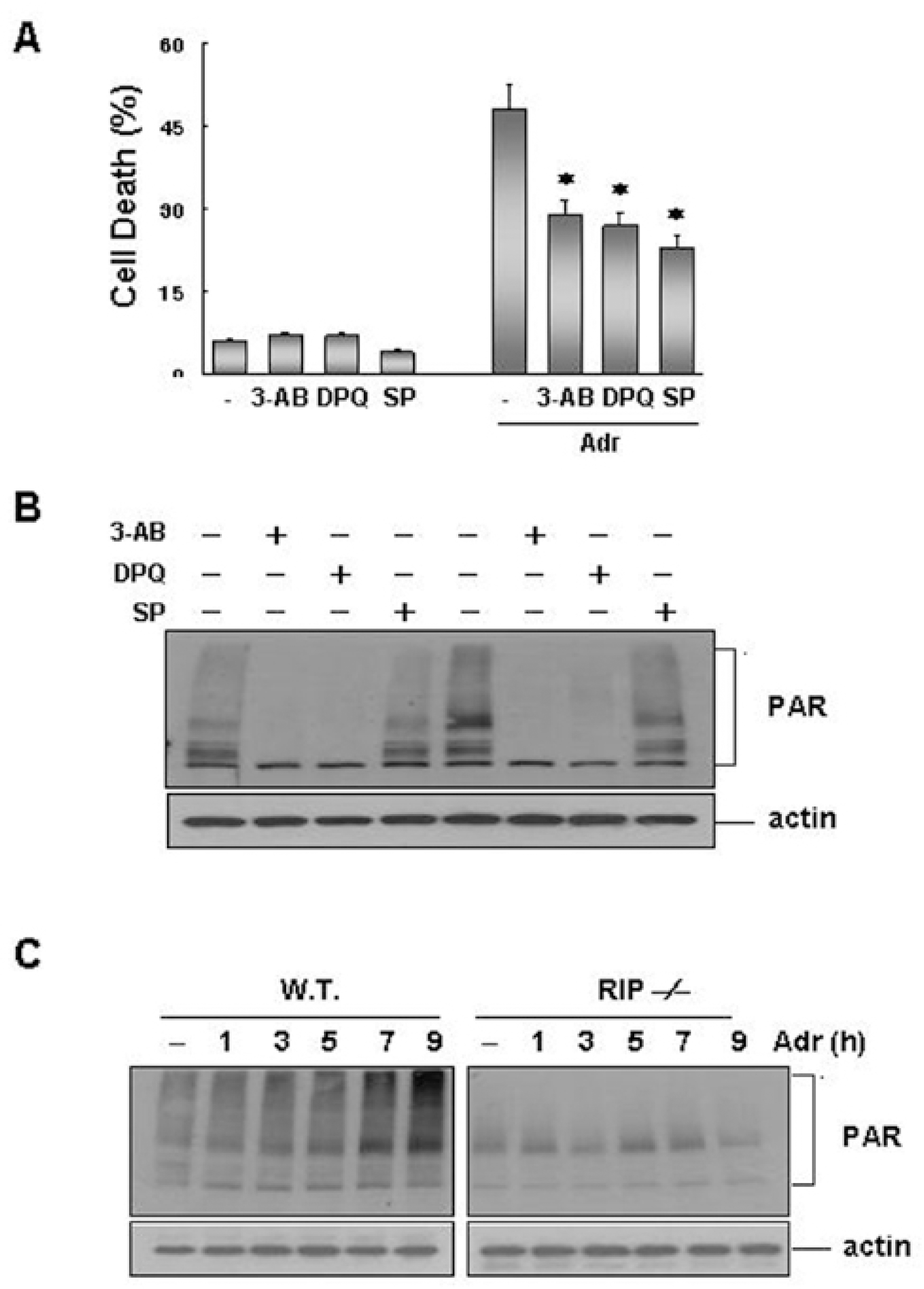 | Fig. 6.JNK plays as an upstream effector of DNA damage-induced PARP activation. (A) Wild-type (WT) fibriblasts were pretreated with either SP-600125 (20 μM) or PARP inhibitors (1 mM 3-AB or 30 μM DPQ). They were then treated with Adr (10 μ g/ml) for 24 hrs, and cell death was then quantified by trypan blue exclusion assay, as described in the legend of Fig 5A. Each bar shows mean ±SE of at least three independent experiments. ∗p<0.05, when compared with Adr-treated group. (B) Wild-type (WT) fibriblasts were treated with Adr (10 μ g/ml) for 12 hrs in the absence or presence of SP-600125 or PARP inhibitors (1 mM 3-AB or 30 μM DPQ), as indicated. Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against PAR and β-actin. (C) Wild-type and RIP-/- cells were treated with Adr (10 μ g/ml) for various times, as indicated. Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against PAR and β-actin. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download