Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Mean angles of deviation at each postoperative time point in the bilateral lateral rectus recession (BLR) group and the unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection (RR) group treated for basic-type intermittent exotropia. (A) The mean angle of deviation at distant fixation was more exotropic in the RR group than in the BLR group through the entire follow-up period, except for postoperative year 3. (B) The mean deviation at near fixation was also more exotropic in the RR group than in the BLR group through the entire follow-up period, except postoperative year 3. *p <0.05 by independent t-test. |
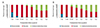 | Fig. 2The proportions of each surgical outcome type at distant fixation for each postoperative time point in the bilateral lateral rectus recession (BLR) group (A) and in the unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection (RR) group (B) for basic-type intermittent exotropia. Surgical outcomes at postoperative month 6 (p = 0.045) and year 1 (p = 0.040) differed significantly between the groups, demonstrating a higher success rate in the BLR group than in the RR group. *p <0.05 by Pearson's chi-square test. |
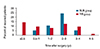 | Fig. 3The percentages of recurrence at distant fixation for each postoperative time point in the bilateral lateral rectus recession (BLR) group and the unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection (RR) group for basic-type intermittent exotropia. Analysis showed that recurrence was most common between postoperative years 2 and 3 in the BLR group, whereas it was most common within 6 months postoperatively in the RR group with continuous recurrences after surgery. |
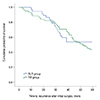 | Fig. 4Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for recurrence of exophoria/tropia more than 8 prism diopters in the bilateral lateral rectus recession (BLR) group and the unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection (RR) group for basic-type intermittent exotropia. The analysis showed no statistically significant difference in the cumulative probability of survival between the two groups (p = 0.531, log-rank test). |
Table 1
Patient characteristics

Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
BLR = bilateral lateral rectus muscle recession; RR = unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection; SE = spherical equivalent; OD = right eye; OS = left eye.
*Statistics by Fisher exact test; †Statistics by independent t-test; ‡Preoperative spherical equivalent measured by cycloplegic refraction.
Table 2
Postoperative angles of deviation for distant and near fixation in the BLR group and the RR group treated for basic-type intermittent exotropia
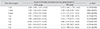
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The positive numbers represent exodeviation, and the negative numbers represent esodeviation.
BLR = bilateral lateral rectus muscle recession; RR = unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection.
*The mean deviations at each postoperative time point were calculated, including the angles in patients who underwent further operations; †Statistics by independent t-test.
Table 3
Postoperative surgical outcomes at distant fixation in the BLR group and the RR group treated for basic-type intermittent exotropia

Values are presented as number (%).
BLR = bilateral lateral rectus muscle recession; RR = unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection; Δ = prism diopters.
*Overcorrection = esophoria/tropia >8Δ at a distance; success = esophoria/tropia ≤8Δ to exophoria/tropia ≤8Δ at a distance; undercorrection/recurrence = exophoria/tropia >8Δ at a distance. All patients who underwent reoperation for a recurrence of exotropia were also included in “Recurrence” category; †Statistics by Pearson's chi-square test; ‡Statistics by Fisher exact test.
Table 4
Success rates and reoperation rates in the BLR group and RR group treated for basic-type intermittent exotropia at postoperative year 5

Table 5
Stereoacuity values of the BLR group and the RR group treated for basic-type intermittent exotropia

Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
BLR = bilateral lateral rectus muscle recession; RR = unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection.
*Statistics by independent t-test; †Stereopsis was measured at near distance using the Titmus stereo test; ‡Stereoacuity at postoperative year 5.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download