Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated firstly the change of intraocular pressure (IOP) after injection of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) for the treatment of macular edema and secondly the factors that influence these changes.
Methods
A prospective, non-comparative study was performed in 60 patients at Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital from October 2003 to September 2004. All the patients received 4-mg IVTA injection.
Results
Mean IOP was elevated from the day after injection and peaked at 20.5 mmHg after 2 months (p=0.000). Twenty-six eyes (43.3%) showed significant IOP elevation. IOP was not controlled despite full glaucoma medication in 7 (11.7%) eyes. Two eyes underwent filtering surgery. Younger age was a statistically significant predictive factor for IOP elevation (p=0.009).
REFERENCES
1. Graham RO, Peyman GA. Intravitreal injection of dexamethasone. Treatment of experimentally induced endophthalmitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974; 92:149–54.
2. Beer PM, Bakri SJ, Singh RJ, et al. Intraocular concentration and pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide after a single injection. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:681–6.
3. Jonas JB. Intraocular availability of triamcinolone acetonide after intravitreal injection. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:560–2.

4. Danis RP, Ciulla TA, Pratt LM, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2000; 20:244–50.

5. Gillies MC, Simpson JM, Luo W, et al. A randomized clinical trial of a single dose of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: One-year results. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:667–73.
6. Jonas JB, Keissig I, Hugger P, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for exudative age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:462–8.

7. Jonas JB, Sofker A. Intraocular injection of crystalline cortisone as adjunctive treatment of diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:425–7.

8. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Sofker A, et al. Intravitreal injection of triamcinolone for diffuse diabetic macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:57–61.

9. Martidis A, Duker JS, Greenberg PB, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:920–7.

10. Greenberg PB, Martidis A, Rogers AH, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for macular edema due to central retinal vein occlusion. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:247–8.

11. Ip MS, Kumar KS. Intravitreous triamcinolone acetonide as treatment for macular edema from central retinal vein occlusion. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120:1217–9.

12. Antcliff RJ, Spalton DJ, Stanford MR, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for uveitic cystoid macular edema: an optical coherence tomography study. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:765–72.

13. Martidis A. Duker JS, Puliafito CA. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory cystoid macular edema secondary to birdshot retinochoroidopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:1380–3.
14. Young S, Larkin G. Branley M, et al. Safety and efficacy of intravitreal triamcinolone for cystoid macular edema in uveitis. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2001; 29:2–6.
15. Conway MD, Canakis C, Livir-Rallatos C, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for refractory chronic pseudophakic cystoid macular edema. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:27–33.

16. Benhamou N, Massin P, Haouchine B, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory pseudophakic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:246–9.

17. Shields MB. Textbook Of Glaucoma. 4th ed.Philadelphia: LIPPINCOTT WILLIAMS & WILKINS;1997. p. 323–8.
18. Lee J, Lee JH. The Effect of Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide on cystoid Macular Edema. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:413–8.
19. Kreissig I, Degenring RF, Jonas JB. Diffuse diabetic macular edema intraocular pressure after intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide. Der Ophthalmologe. 2004. 13.
20. Wingate RJ, Beaumont PE. Intravitreal triamcinolone and elevated intraocular pressure. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1999; 27:431–2.
21. Bakri SJ, Beer PM. The effect of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide on intraocular pressure. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2003; 34:386–90.

22. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Degenring R. Intraocular pressure after intravitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:24–7.

23. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Degenring R. Secondary chronic open-angle glaucoma after intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:729–30.

24. Singh IP, Ahmad SI, Yeh D, et al. Early rapid rise in intra ocular pressure after intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:286–7.
25. Kaushik S, Gupta V, Gupta A, et al. Intractable glaucoma following intravitreal triamcinolone in central retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:758–60.

26. IN YS, Kim JH, Uhm KB. The effect of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide on intraocular pressure. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1075–80.
27. Savage H, Roh M. Safety and efficacy of intravitreal triamcinolone. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:1083.

28. Gillies MC, Simpson JM, Billson FA, et al. Safety of an intravitreal injection of triamcinolone: results from randomized clinical trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004; 122:336–40.
29. Jaissle GB, Szurman P, Bartz-Schmidt KU. Ocular side effects and complication of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection. Ophthalmologe. 2004; 101:121–8.
30. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Degenring RF. Retinal complications of intravitreal injections of triamcinolone acetonide. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2004; 242:184–5.

32. Floman N, Zor U. Mechanism of steroid action in ocular inflammation: inhibition of prostaglandin production. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 16:69–73.
Fig. 1.
Distribution of mean intraocular pressure (IOP) after 4-mg intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection in 60 patients, 60 eyes. A: group of patients with normal IOP (N=34). B: group of patients with postoperative IOP elevation (N=26).
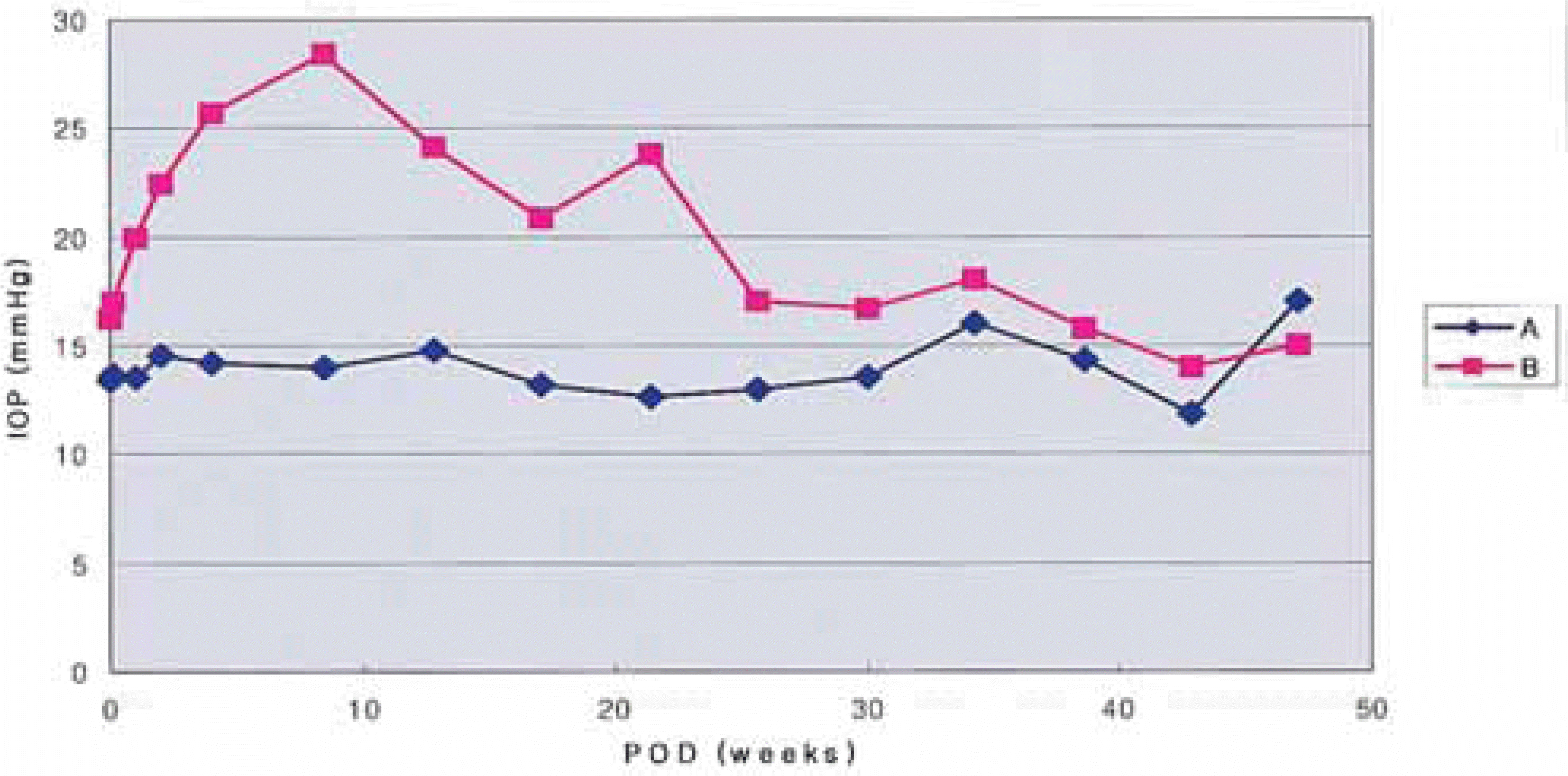
Fig. 2.
Distribution of intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with uncontrolled IOP (N=7). a,b: recovered to normal range of IOP during the long term follow-up period. c,d: were lost during the follow-up period and further observation was not available. e.f: showed persistent ocular hypertension despite full glaucoma medication and required filtering surgery to control IOP. After conventional penetrating glaucoma surgery, IOP was normalization. g: even though topical glaucoma medication was performed due to IOP elevation, IOP fluctuation continued for several months and the patient was still on follow-up at the time of writing. (number): patients age, ◇: date of trabeculectomy
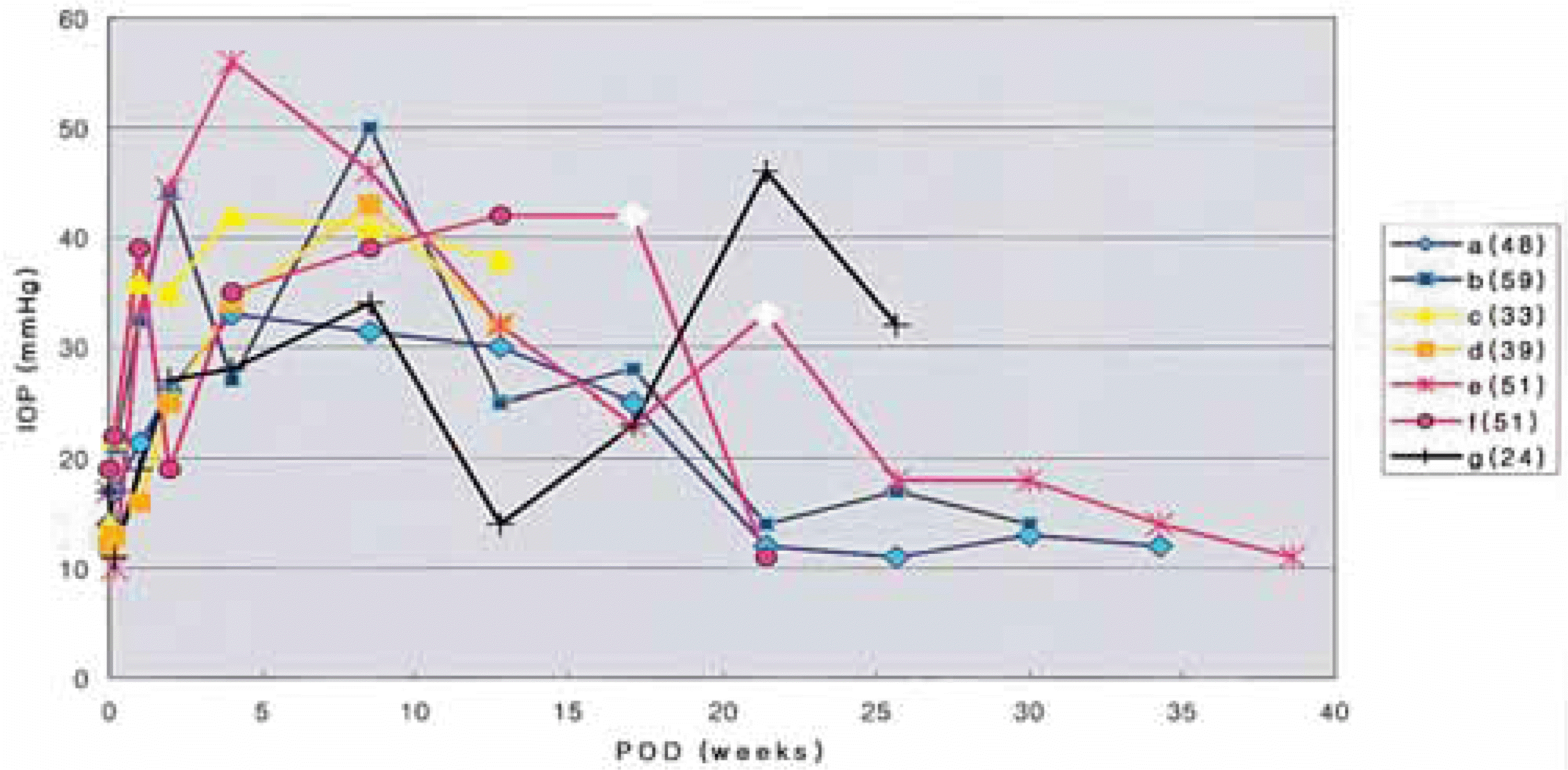
Table 1.
Intraocular pressure (IOP) before and after 4-mg intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection
Table 2.
Factors affecting intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation
| Factors | Group A vs. B |
|---|---|
| p-value | |
| Mean Age | 0.009∗ |
| Sex | 0.602 |
| Past Medical History | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 0.651 |
| Hypertension | 0.171 |
| Ophthalmologic operation History | |
| Phaco. + PCL | 0.020† |
| Vitrectomy | 0.208 |
| Mean Refractive Error | 0.117 |
Table 3.
Time at elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP) in the patients who underwent intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection twice
There was no IOP elevation in one patient (patient 4). In two cases (patients 2 and 6) IOP elevation occurred after the first injection but not after the second injection. In the other cases, significant IOP elevation occurred after both injections. POD: post-operation days, IOP: intraocular pressure, IVTA: intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download