INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture of mouse podocytes
Treatment conditions
Immunofluorescence staining
Immunoblotting analysis for p130Cas
RESULTS
Ang II relocates p130Cas in podocytes
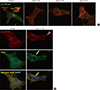 | Fig. 1Effects of Ang II on the localization of p130Cas in podocytes. p130Cas stainings are located in the cytoplasm of cultured podocytes diffusely, whereas, F-actin fibers are distributed in peripheral cytoplasm and run over nucleus, apart from p130Cas. (A) Ang II reduces and re-localizes the immunofluorescent intensities of p130Cas in internal cytoplasm and peri- and intra-nuclear areas of podocytes with concentrations. Such changes by Ang II are associated with disrupted F-actin fibers. (B) Ang II (10-6 M) also decreases and concentrates the immunofluorescent intensities of FAK (arrow) in internal cytoplasm and peri-nuclear areas of podocytes, which become to be separated partially from p130Cas (arrow head). Magnification, × 1,000. |
Ang II reduces the amount of p130Cas protein
 | Fig. 2Effects of Ang II on the p130Cas protein assayed by Western blotting. (A) The bands for p130Cas protein at 130 kDa are reduced by 10-7 M Ang II in a time-dependent manner. Such changes are further aggravated by compound C, a potent AMPK inhibitor. (B) At 24 hours, the density values for p130Cas decreased significantly at doses of 10-7 M and 10-6 M Ang II, respectively, compared to control (without Ang II) after correcting for β-tubulin levels. Data on the densitometric analysis of p130Cas/β-tubulin ratio are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Control (100%); the value of no Ang II conditions. *P < 0.05 and †
P < 0.01 vs. control. |
AICAR and metformin recover the changes of p130Cas induced by Ang II
 | Fig. 3Effects of AMPK activators on the distributional changes of p130Cas induced by Ang II. (A) AMPK activators, metformin and AICAR, restore the mal-localized p130Cas, whereas, AMPK inhibitor, compound C further aggravates the distributional changes of p130Cas (arrowheads). (B) AICAR also restores the mal-localized p130Cas (arrowheads) and FAK (arrows) induced by Ang II. Magnification, × 1,000. |
 | Fig. 4Effects of AMPK activators on the changes of p130Cas protein induced by Ang II. Ang II suppresses p130Cas protein significantly in a time-dependent manner. (A) Compound C further exaggerates the reduced p130Cas protein significantly (all P < 0.01, not denoted) at all experiment times. (B) Concerning the concentration of 10-7 M Ang II at 24 hours, Ang II suppresses p130Cas protein significantly, which is also reversed by AICAR and metformin. Compound C further aggravates the changes of p130Cas. Data on the densitometric analysis of p130Cas/β-tubulin ratio are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Control (100%); the value of no Ang II conditions.
*P < 0.05 and †
P < 0.01 vs. control. ‡
P < 0.05 and §
P < 0.01 vs. Ang II-treated groups.
|
The changes of p130Cas induced by Ang II are mediated via AT1R
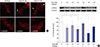 | Fig. 5Suppression of p130Cas by Ang II via AT1R. AT1R antagonist, losartan, ameliorates the mal-localized p130Cas (arrowheads, A) and reverses the suppression of p130Cas induced by high doses (10-7 M and 10-6 M) of Ang II (B). Data on the densitometric analysis of p130Cas/β-tubulin ratio are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Control (100%); the value of no Ang II conditions.
*P < 0.05 and †
P < 0.01 vs. control. ‡
P < 0.05 vs. Ang II-treated groups.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download