INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data sources and study population
Treatment pattern and operational definition
Outcome variables and statistical analysis
RESULTS
Characteristics of the study population
Table 1
Basic characteristics of study population

Treatment pattern and annual trends
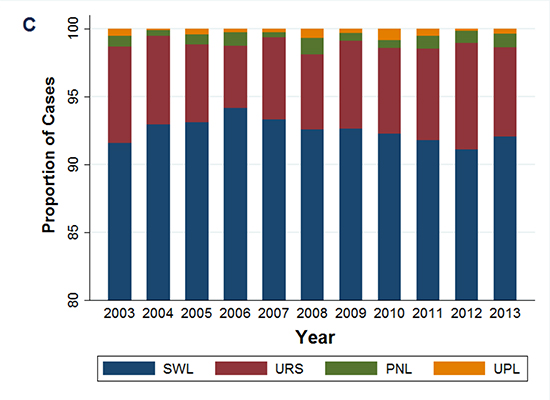
 | Fig. 1Time trends of upper urinary tract calculi in Korea’s primary treatment (A) and all treatment cases (B) for Time trends for the relative proportions of primary treatments (C) and all treatment cases (D) are also shown.
SWL = shock wave lithotripsy, URS = ureteroscopic surgery, PNL = percutaneous nephrolithotomy, UPL = uretero/pyelolithotomy.
|
Association between sociodemographic factors and treatment modality choice
Table 2
Association of sociodemographic factors with primary treatment modality for upper urinary tract calculi (compared to SWL Group)

Stone recurrence after initial treatment
DISCUSSION
Table 3
Summary of published studies that investigated treatment patterns for urinary lithiasis and time trends

| References | Year | Nation | Subjects | Study period | Main findings of the study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matlaga et al. (8) | 2009 | USA | UUTC (data from American Board of Urology) | 2003–2008 | *Provider specific attributes affect treatment choice. |
| Scales et al.(9) | 2011 | USA | UUTC (Medicare 5% sample) | 1997–2007 | *Nonclinical factors are associated with the use of URS or SWL. |
| Lee and Bariol (10) | 2011 | Australia | UUTC (Medicare Australia and Australian Institute of Health and Welfare databases) | 1995–2010 | An increase in URS, Steady use of SWL. |
| Turney et al. (11) | 2012 | UK | UUTC (data from the Hospital Episode Statistics website) | 2000–2010 | An increase in both SWL and URS use. |
| Seklehner et al. (12) | 2014 | USA | Ureter calculi only (5% Medicare Public Use Files) | 2001, 2004, 2007, and 2010 | The use of URS increased over time, while the use of SWL declined. |
| Oberlin et al. (13) | 2015 | USA | UUTC (data from American Board of Urology) | 2003–2012 | An increase in URS and a corresponding decrease in SWL over time. |
| Present study | - | Korea | UUTC (2% random sample from Korean National Health Insurance database) | 2003–2013 | Dominant use of SWL remained steady. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download