1. Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron. 2003; 39:889–909.
2. Mandel S, Grünblatt E, Riederer P, Gerlach M, Levites Y, Youdim MB. Neuroprotective strategies in Parkinson’s disease : an update on progress. CNS Drugs. 2003; 17:729.
3. Kriks S, Shim JW, Piao J, Ganat YM, Wakeman DR, Xie Z, Carrillo-Reid L, Auyeung G, Antonacci C, Buch A, et al. Dopamine neurons derived from human ES cells efficiently engraft in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature. 2011; 480:547–551.
4. Hayashi T, Wakao S, Kitada M, Ose T, Watabe H, Kuroda Y, Mitsunaga K, Matsuse D, Shigemoto T, Ito A, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons function in parkinsonian macaques. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:272–284.
5. Swijnenburg RJ, Schrepfer S, Govaert JA, Cao F, Ransohoff K, Sheikh AY, Haddad M, Connolly AJ, Davis MM, Robbins RC, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy mitigates immunological rejection of human embryonic stem cell xenografts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008; 105:12991–12996.
6. de Wert G, Mummery C. Human embryonic stem cells: research, ethics and policy. Hum Reprod. 2003; 18:672–682.
7. Wang Y, Chen S, Yang D, Le WD. Stem cell transplantation: a promising therapy for Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2007; 2:243–250.
8. Lizier NF, Kerkis A, Gomes CM, Hebling J, Oliveira CF, Caplan AI, Kerkis I. Scaling-up of dental pulp stem cells isolated from multiple niches. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e39885.
9. Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, Robey PG, Shi S. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000; 97:13625–13630.
10. Khanna-Jain R, Vanhatupa S, Vuorinen A, Sandor GK, Suuronen R, Mannerstrom B, Miettinen S. Growth and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells maintained in fetal bovine serum, human serum and serum-free/xeno-free culture media. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012; 2:1.
11. Miura M, Gronthos S, Zhao M, Lu B, Fisher LW, Robey PG, Shi S. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100:5807–5812.
12. Zhang W, Walboomers XF, Shi S, Fan M, Jansen JA. Multilineage differentiation potential of stem cells derived from human dental pulp after cryopreservation. Tissue Eng. 2006; 12:2813–2823.
13. Nosrat IV, Smith CA, Mullally P, Olson L, Nosrat CA. Dental pulp cells provide neurotrophic support for dopaminergic neurons and differentiate into neurons in vitro; implications for tissue engineering and repair in the nervous system. Eur J Neurosci. 2004; 19:2388–2398.
14. Klein C, Fishell G. Neural stem cells: progenitors or panacea? Dev Neurosci. 2004; 26:82–92.
15. Guo L, Yin F, Meng HQ, Ling L, Hu-He TN, Li P, Zhang CX, Yu S, Duan DS, Fan HX. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into dopaminergic neuron-like cells in vitro. Biomed Environ Sci. 2005; 18:36–42.
16. Sanchez-Ramos J, Song S, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Hazzi C, Stedeford T, Willing A, Freeman TB, Saporta S, Janssen W, Patel N, et al. Adult bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neural cells in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2000; 164:247–256.
17. Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, Black IB. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000; 61:364–370.
18. Katayama M, Ishii K. 2-Mercaptoethanol-independent survival of fetal mouse brain neurons cultured in a medium of human serum. Brain Res. 1994; 656:409–412.
19. Ishii K, Katayama M, Hori K, Yodoi J, Nakanishi T. Effects of 2-mercaptoethanol on survival and differentiation of fetal mouse brain neurons cultured in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1993; 163:159–162.
20. Sun Y, Zigmond RE. Involvement of leukemia inhibitory factor in the increases in galanin and vasoactive intestinal peptide mRNA and the decreases in neuropeptide Y and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in sympathetic neurons after axotomy. J Neurochem. 1996; 67:1751–1760.
21. Bauer S, Patterson PH. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes neural stem cell self-renewal in the adult brain. J Neurosci. 2006; 26:12089–12099.
22. Kawasaki H, Mizuseki K, Nishikawa S, Kaneko S, Kuwana Y, Nakanishi S, Nishikawa SI, Sasai Y. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity. Neuron. 2000; 28:31–40.
23. Bez A, Corsini E, Curti D, Biggiogera M, Colombo A, Nicosia RF, Pagano SF, Parati EA. Neurosphere and neurosphere-forming cells: morphological and ultrastructural characterization. Brain Res. 2003; 993:18–29.
24. Wang J, Wang X, Sun Z, Wang X, Yang H, Shi S, Wang S. Stem cells from human-exfoliated deciduous teeth can differentiate into dopaminergic neuron-like cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010; 19:1375–1383.
25. Trzaska KA, Kuzhikandathil EV, Rameshwar P. Specification of a dopaminergic phenotype from adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2007; 25:2797–2808.
26. Ye W, Shimamura K, Rubenstein JL, Hynes MA, Rosenthal A. FGF and Shh signals control dopaminergic and serotonergic cell fate in the anterior neural plate. Cell. 1998; 93:755–766.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



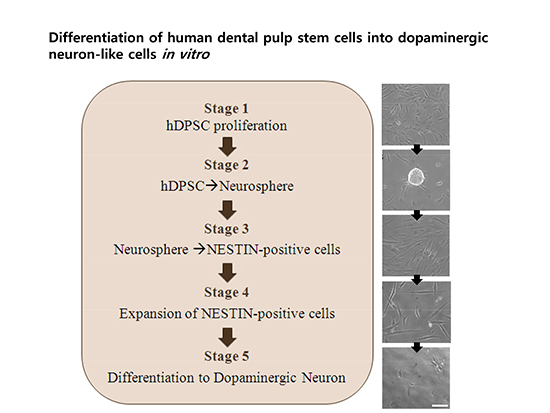

 XML Download
XML Download