INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines and cell culture
Reagents
HCC tissues and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis
Western blot analysis
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Cell viability assay
Colony formation assay
Cell cycle analysis
Cell migration assay
Mouse xenograft HCC models
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
OTX1 is highly expressed in clinical HCC tissues
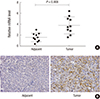 | Fig. 1OTX1 is highly expressed in clinical HCC tissues. (A) qRT-PCR analysis showed that the average mRNA level of OTX1 in the tumor tissues were approximately two-fold increased compared with the paired non-cancerous tissues (P = 0.008). (B) Protein level of OTX1 was analyzed by IHC in a subset of 128 HCC tissues and the paired adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Staining result for each slide was graded as negative (−), weakly positive (+), moderate positive (++), and strongly positive (+++) according to the stain density. OTX1 was shown to be mainly located in the membrane and cytoplasm. The representative images that showed the markedly higher level of OTX1 in tumor tissues than non-cancerous tissues were provided. Magnification 400 ×. |
Expression of OTX1 is positively correlated with metastasis status and TNM staging
Table 1
Correlation between the expression of OTX1 and clinicopathological variables in hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 128)
Knockdown of OTX1 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation in vitro
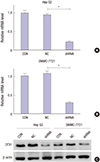 | Fig. 2Knockdown efficiency of OTX1 shRNA was assessed in vitro. Initially, effects of transfection of the shRNA against OTX1 (shOTX1) on mRNA level of OTX1 were assessed in Hep G2 cells (A) and SMMC-7221 cells (B). shOTX1, instead of the scrambled shRNA significantly knocked the mRNA level of OTX1 down in both cell lines. The protein level of OTX1 was accordingly decreased after transfection of shOTX1 in both cell lines (C). *
P < 0.01. |
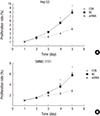 | Fig. 3Effects of OTX1 knockdown on cell viability. Knockdown of OTX1 by shRNA caused significantly lower proliferation rate in both Hep G2 cells (A) and SMMC-7221 cells (B). The proliferation rate was approximately half of the control cells by day 5. *
P < 0.01. |
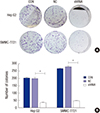 | Fig. 4Knockdown of OTX1 impairs the colony formation ability in vitro. (A) Fewer colonies were visually observed in shOTX1-transfected Hep G2 cells and SMMC-7221 cells. (B) Quantification of the colony numbers showed that only average 30 colonies were formed in shOTX1-transfected Hep G2 cells (15% of the controls). About 50 colonies were formed in shOTX1-transfected SMMC-7221 cells, accounting for only 19% of the controls. *
P < 0.01. |
Knockdown of OTX1 induces cell cycle arrest in S phase
 | Fig. 5Knockdown of OTX1 induces cell cycle arrest in S phase. Flow cytometry was employed to analyze the cell cycle distribution. Cell proportion in S phase was significantly increased, whereas cell proportion in G2/M phase was significantly decreased in shOTX1-transfected Hep G2 cells and SMMC-7221 cells. *
P < 0.01. |
Knockdown of OTX1 inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model
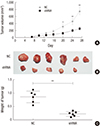 | Fig. 6Knockdown of OTX1 inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. A mouse model bearing the hepatic cancer was initially established using shOTX1-transfected Hep G2 cells (shRNA group) or negative control shRNA-transfected Hep G2 cells (NC group). (A) Periodic monitor of tumor dimensions in both the NC group and shRNA group. Average tumor volume from shRNA group was only 25% of control group by day 27. (B) Tumors were dissected and presented on day 27. (C) All tumor weights were determined and averaged for each group. The average tumor weight from the shRNA group was approximately 33% of the control group. *
P < 0.05, †
P < 0.01. |
Knockdown of OTX1 inhibits cell migration ability in vitro
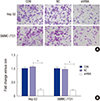 | Fig. 7Knockdown of OTX1 inhibits cell migration ability in vitro. Both Hep G2 cells and SMMC-7221 cells with distinct treatments were allowed to migrate in the upper chamber of a transwell for 12 hours. (A) After 12 hours, the under-surface of the upper chamber was stained with crystal violet. The stained cells were observed and photographed under a light microscopy. (B) Quantification of the migrated cell numbers showed that shOTX1-transfected cells exhibited significantly lower migration ability in both cell lines. Approximately 78% migration ability was decreased after knockdown of OTX1 in both Hep G2 and SMMC-7221 cells. *
P < 0.01. |
Deregulation of ERK/MAPK pathway is associated with silencing of OTX1
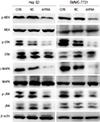 | Fig. 8Deregulation of ERK/MAPK pathway is associated with knockdown of OTX1. Knockdown of OTX1 caused the according decreases of phosphorylated MEK, ERK, MAPK and JNK without affecting the total MEK, ERK MAPK and JNK levels. ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase. MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase. MEK, a MAPK kinase, also known as MAP2K, or dual-specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download