Abstract
Figures and Tables
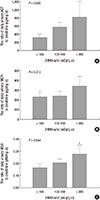 | Fig. 1Urinary cytokines to creatinine ratio among 24HUna/cr groups. (A) AGT, angiotensinogen. (B) MCP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. (C) MDA, malondialdehyde. 24HUna/cr, the ratio of 24-hr urine sodium to creatinine (mg/g creatinine). The P value was calculated by one-way ANOVA test. *Different from the group with 24HUna/cr<100 mEq/g cr. The bar means 95% confidence interval of each mean value. |
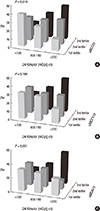 | Fig. 2The frequency of tertile groups of cytokines according to 24HUna/cr groups. The ratio of 24-hr urine sodium to creatinine (mg/g creatinine) by (A) uAGT/cr, urine angiotensinogen to creatinine ratio (pg/mg cr), (B) uMCP1/cr, urine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 to creatinine ratio (pg/mg cr), (C) uMDA/cr: urine malondialdehyde to creatinine ratio (pM/mg cr). |
 | Fig. 3The relationship between the changes of 24-hr urine cytokines to creatinine ratio and urine sodium to creatinine ratio during 16 weeks after ARB medication. Frequency of increase in cytokine level: Frequency of increase in 24-hr urinary cytokine to creatinine ratio at 16-week compared to 0-week 25% or more. Increased 24HUna/cr defined as increase of 24HUna/cr ratio 25% or more, Decreased 24HUna/cr defined as decrease of 24HUna/cr ratio 25% or more, and unchanged 24HUna/cr defined as the ratio of 24HUna/cr between -24.9% and 24.9%, at 16-week compared to 0-week. uAGT/Cr: 24-hr urine angiotensinogen to creatinine ratio (pg/mg cr), uMCP1/Cr: 24-hr urine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 to creatinine ratio (pg/mg cr), uMDA/Cr: 24-hr urine malondialdehyde to creatinine ratio (pM/mg cr). |
Table 1

*0-week, the period starting Olmesartan (40 mg per day) after a 8-wash out period of any ARB, ACEI, or aldosterone blocker. BMI, body mass index; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CVA, cerebrovascular accident including thrombotic cerebral infarction and intracranial hemorrhage; Number of HTN medications, number of medications to control hypertension; ACEI, angiotensin II converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin type I receptor blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; BB, beta-blocker; Anti-platelet agent, low dose aspirin, cilostazole, and clopidogrel; Lipid lowering agent, statins and fibrates; SBP, systolic blood pressure, DBP, diastolic blood pressure; GFR, glomerular filtration rate estimated using the original Modification of Diet in Renal Diease equation using serum creatinine values measured by the modified Jaffe reaction; 24HUcr, amount of daily urinary creatinine; 24HUna, amount of daily urinary sodium; 24HUna/cr, the ratio of 24-hr urine sodium to creatinine (mg/g creatinine); 24HUalb, amount of daily urinary albumin; 24HUalb/cr, the ratio of 24-hr urine albumin to creatinine (mg/g creatinine); uc, unable to calculate. P values were calculated using the One-way ANOVA test among 24-hr urinary sodium/cr groups.
Table 2

*24HUna/cr, 24-hr urine sodium to creatinine ratio. Each parameter was used in the multiple linear regression model adjusted with age and gender, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, height, serum cholesterol, hemoglobin, GFR, urine MCP-1 to creatinine ratio, and urine angiotensinogen to creatinine ratio, which were the factors related to the 24-hr albumin to creatinine ratio.
Table 3

*0 week, starting week for Olmesartan (40 mg per day) after a 8-wash out period of any ARB, ACEI, or aldosterone blocker; 24HUna/cr group: group according to the ratio of 24-hr urine sodium to creatinine with the criteria of 100 and 200 mEq/g cr; 24HUalb/cr: the ratio of 24-hr urine albumin to creatinine (mg/g creatinine); uAGT/cr: urine angiotensinogen to creatinine ratio (pg/mg cr); uMDA/cr: urine malondialdehyde to creatinine ratio (pM/mg cr); BB medication: beta-blocker medication; Linear regression for uAGT/cr was adjusted for age, gender, hemoglobin, 24-hr urine albumin to creatinine ratio, GFR, and group of 24HUna/cr, which were the factors related to the urine angiotensinogen to creatinine ratio at 0-week. Linear regression for uMDA/cr was adjusted for age, gender, beta-blocker, serum total CO2, and group of 24HUna/cr.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download