Abstract
Figures and Tables
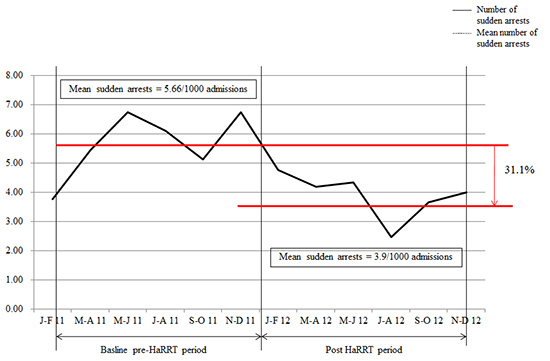
Fig. 1

Table 2

*CVR, critical value results: composed of abnormal results of electrolytes, blood gas profile, and glucose results, which were discussed with the Department of Clinicopathology, the Q.I. department and the E-RRS. The criteria of the CVR were revised three times to achieve a higher sensitivity of screening. E-RRS, extended rapid response system; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; CVR, critical value results; Q.I., quality improvement; ICU, intensive care unit.
Table 3

Values are mean value±standard deviation. Note that some cases required multiple actions (e.g., patients with septic shock due to pneumonia required multiple procedures such as intubation, C-line insertion, EGDT, oxygen supplement and ICU arrangement). *Emergent consultation before regular consultation including correcting electrolyte imbalance, early use of antibiotics, early anticoagulation for pulmonary thromboembolism, correcting fluid overload, dehydration and treatment of pulmonary congestion, ventilator care of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and treatment of arrhythmia (using defibrillator or medication). †Including low-flow oxygen supplement and high-flow nasal oxygen therapy. BMI, body mass index; ICU, intensive care unit; SBP, systolic blood pressure; MEWS, modified early warning score; DNR, do not resuscitate; C-line, central venous line.
Table 4

"Reported cases" mean symptoms or signs that were found when patients were screened for all causes. "Calls from primary physician" means a call from the primary physician due to the screening criteria (symptoms or signs). "Cases that triggered advanced management" means actions that triggered advanced managements such as intubation, C-line insertion, EGDT, ICU arrangement, or supplementation with high-flow nasal oxygen therapy. For example, a patient was screened due to 'mental change', but we also found shock and chest pain at the same time, and intubation and C-line insertion was performed; the "reported cases" included three items (mental change, shock, and chest pain). The "calls from primary physician" is 'mental change' only, and "triggered advances management" is intubation and C-line insertion (2 items). *All cases of 'call from primary physician' is reported as systolic blood pressure <70 mmHg. †We set up the 'critical value results from the clinicopathology department' in August 2012, and the criteria were modified twice in December 2012 and in December 2013. The data were collected for only half of the year. ‡Many of cases had more than two overlapping criteria. Twenty-four of these patients had more than two laboratory findings that fell under the E-RRS criteria. §Patients undergoing operation under general anesthesia who were deemed high-risk were screened with consultations from cardiology and respirology (from January 2012), as well as daily calls from the Department of Anesthesiology (from August 2012). ¶There were no calls related to abnormal findings of pH, lactate, or electrolyte imbalances. These findings were from critical value results of the clinicopathology department. ICU, intensive care unit; SBP, systolic blood pressure; EGDT, early goal-directed therapy; C-line, central venous line.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download