Abstract
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Decreased activation in OCD patients before and after treatment compared to the controls (for illustrative purpose, P < 0.005 uncorrected, cluster level > 30). Activation in ventral frontal regions in OCD was normalized after treatment. However, dysfunctional activation in dorsal frontal regions persisted regardless of treatment. |
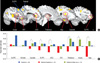 | Fig. 2The different activations between OCD patients at baseline and controls and between pre- and post-treatment in patients. (A) Dysfunctional activation pattern was sustained in the dorsal frontoparietal regions, indicated by the blue line circle, while the ventral frontal, striatal and limbic/paralimbic regions, indicated by the red line circle, were partially normalized after treatment. (B) Mean percent signal change for task-switch minus task-repeat of the controls, pre-treatment and post-treatment OCD patients in the ROIs. The significant differences in regional activity between pre- and post-treatment in OCD patients are presented in *P < 0.05, using LSD post hoc test. DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; VLPFC, ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; rACC, rostral anterior cingulate cortex; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; Hipp, Hippocampus. |
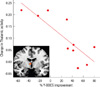 | Fig. 3The correlation of percent (%) Y-BOCS improvement and longitudinal change in left thalamus activation. The correlation coefficient was -0.82 (< 0.006; corrected P value = 0.05/9). |
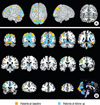 | Fig. 4Activation maps showing the results of fixed effects analyses in patients before and after treatment separately. Although fixed effects results cannot be generalized beyond the samples studies, these results are presented to emphasize the similarities and the differences in task-switching-related brain regions in patients with OCD before and after treatment. Both patients before and after treatment showed the similar activation patterns in the DLPFC and parietal cortex, while different activation patterns in the OFC, ACC, and caudate were observed. (A) Surface rendering of fixed effects results. (B) Multislice coronal view of fixed effects results. |
Table 1

Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; †χ2 test comparing OCD patients at baseline versus controls; ‡Independent t-test comparing OCD patients at baseline versus controls; §Paired t-test comparing OCD patients at baseline versus OCD patients at follow-up. SD, standard deviation; Y-BOCS, Yale-Brown Obsessive-compulsive Scale; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; BAI, Beck Anxiety Inventory.
Table 2

Table 3

All activations at P < 0.005 uncorrected at the voxel level with P < 0.05 at the cluster level or at *P < 0.005 uncorrected with a cluster of more than 30 for regions of a priori interest based on our previous study (3). L, Left; R, Right; BA, Brodmann's area; MNI, Montreal Neurological Institute.
Table 4
All activations at P < 0.005 uncorrected at the voxel level with P < 0.05 at the cluster level or at *P < 0.005 uncorrected with a cluster of more than 30 for regions of a priori interest based on our previous study (3). L, Left; R, Right; BA, Brodmann's area.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Notes
This work was supported by World Class University program through the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (R32-10142) and a grant (2009K001270) from the Brain Research Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download