Abstract
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical results between 2.2 mm micro-coaxial cataract surgery (MCCS) and 2.8 mm small incision cataract surgery (SICS). Seventy-five patients (75 eyes) were divided into the MCCS (33 eyes) and SICS (42 eyes) groups. AcrySof IQ intraocular lenses were implanted into all patients. Effective phacoemulsification time, CDE (cumulative dissipated energy), and total amount of balanced salt solution (BSS) during cataract surgery were measured in the two groups. Visual acuity, spherical equivalent, intraocular pressure (IOP), endothelial cell count, corneal thickness, and surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) were analyzed preoperatively and postoperatively at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. There were no statistically significant differences in effective phacoemulsification time, CDE, amount of BSS, visual acuity, spherical equivalent, IOP, endothelial cell count and corneal thickness, or SIA between the two groups. In conclusion, the clinical results of the 2.2 mm MCCS group and 2.8 mm SICS group revealed no significant differences.
Figures and Tables
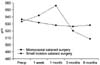 | Fig. 1Postoperative changes in corneal thickness (µm) in microcoaxial and small incision cataract surgery. |
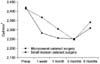 | Fig. 2Postoperative changes in corneal endothelial cell count (cell/mm2) in microcoaxial and small incision cataract surgery. |
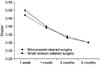 | Fig. 3Postoperative changes in surgically induced astigmatism (Diopter) in microcoaxial and small incision cataract surgery. |
References
1. Shepherd JR. Induced astigmatixm in small incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1989. 15:85–88.
2. Linebarger EJ, Hardten DR, Shah GK, Lindstrom RL. Phacoemulsification and modern cataract surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 1999. 44:123–147.

3. Tsuneoka H, Shiba T, Takahashi Y. Ultrasonic phacoemulsification using 1.4 mm incision: clinical results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002. 28:81–86.
4. Martin RG, Snaders DR, Miller JD, Cox CC 3rd, Ballew C. Effect of cataract wound incision size on acute changes in corneal topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993. 19:Suppl. 170–177.

5. Lundström M. Endophtahlmitis and incision construction. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006. 17:68–71.
6. Herretes S, Stark WJ, Pirouzmanesh A, Reyes JM, Mcdonnel PJ, Behrens A. Inflow of ocular surgace fluid into the anterior chamber after phacoemulsification through sutureless corneal cataract wounds. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 140:737–740.

7. Taban M, Sarayba MA, Ignacio TS, Behrens A, Mcdonnell PJ. Ingress of india ink into the anterior chamber through sutureless clear corneal cataract wounds. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005. 123:643–648.

8. Alió J, Rodríquez-Prats JL, Galai A, Ramzy M. Outcomes of microincision cataract surgery versus coaxial phacoemulsification. Ophthamol. 2005. 112:1997–2003.

9. Stratas BA. Clear corneal paracentesis: a case of chronic wound leakage in a patient having bimanual phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. 31:1075.

10. Weikert MP. Update on bimanual microincisional cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006. 17:62–67.

11. Cavallini GM, Campi L, Masini C, Pelloni S, Pupino A. Bimanual microphacoemulsification vs coaxial miniphacoemulsification: prospective study. J Cataract Refractive Surg. 2007. 33:387–392.

12. Berdahl JP, DeStafeno JJ, Kim T. Corneal wound architecture and integrity after phacoemulsification evaluation of coaxial, microincision coaxial, and microincision bimanual techniques. J Cataract Refractive Surg. 2007. 33:510–515.
13. Holladay JT, Cravy TV, Koch DD. Calculating the surgically induced refractive change following ocular surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992. 18:429–443.

14. Kahraman G, Amon M, Franz C, Prinz A, Abela-Formanek C. Intraindividual comparison of surgical trauma after bimanual microincision and conventional small-incision coaxial phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007. 33:618–622.

15. Lee DS, Joo CK. Effect of incision length on visual recovery and astigmatism in no-suture cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992. 33:470–475.
16. Hu YJ, Jo CK. Surgicallly induced astigmatism after temporal clear corneal incision in sutureless cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998. 39:2622–2627.
17. Agarwal A, Agarwal A, Agarwal S, Narang P, Narang S. Phakonit: phacoemulsification through 0.9 mm corneal incision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001. 27:1548–1552.
18. Tsuneoka H, Shiba T, Takahashi Y. Feasibility of ultrasound cataract surgery with a 1.4 mm incision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001. 27:934–940.

19. Elkady B, Piñero D, Alió JL. Corneal incision quality: Microincision cataract surgery versus microcoaxial phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. 35:466–474.

20. Hayashi K, Yoshida M, Hayashi H. Postoperative corneal shape changes: microincision versus small-incision coaxial cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. 35:233–239.

21. Dosso AA, Cottet L, Burgener ND, Di Nardo S. Outcomes of coaxial microincision cataract surgery versus conventional coaxial cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:284–288.

22. Masket S, Wang L, Belani S. Induced astigmatism with 2.2- and 3.0-mm coaxial phacoemulsification incisions. J Refract Surg. 2009. 25:21–24.

23. Moon SC, Mohamed T, Fine IH. Comparison of surgically induced astigmatisms after clear corneal incisions of different sizes. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2007. 21:1–5.

24. Lee KM, Kwon HG, Joo CK. Microcoaxial cataract surgery outcomes: Comparison of 1.8 mm system and 2.2 mm system. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. 35:874–880.

25. Choi JA, Chung SK, Kim HS. Comparative study of microcoaxial cataract surgery and coventinoal cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008. 49:904–910.

26. Jee DH, Lee PY, Joo CK. The comparision of astigmatism according to the incision size in cataract operation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:594–598.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download