Abstract
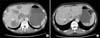
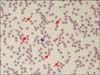
Oxaliplatin is widely used as a chemotherapeutic agent for treating unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal tract cancer, such as gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. The toxic effects commonly associated with oxaliplatin include neuropathy, myelosuppression, hypersensitivity reactions, and chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity. However, oxaliplatin-induced hemolytic anemia has rarely been reported in the medical literature. Herein, we describe a case of oxaliplatin-induced autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a patient with metastatic gastric cancer who received biweekly oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy that included fluorouracil and folinic acid. He presented with acute-onset anemia and acute renal failure shortly after the 25th course of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. A positive direct and indirect Coombs test and a good response to steroid therapy suggested the diagnosis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Afterwards, the patient was switched to an oral 5-fluorouracil agent, TS-1, for further treatment.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Lévi F, Metzger G, Massari C, Milano G. Oxaliplatin: pharmacokinetics and chronopharmacological aspects. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000. 38:1–21.
2. Thomas RR, Quinn MG, Schuler B, Grem JL. Hypersensitivity and idiosyncratic reactions to oxaliplatin. Cancer. 2003. 97:2301–2307.

3. Polyzos A, Tsavaris N, Gogas H, Souglakos J, Vambakas L, Vardakas N, et al. Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: a 10-year experience. Oncology. 2009. 76:36–41.

4. Sørbye H, Bruserud Y, Dahl O. Oxaliplatin-induced haematological emergency with an immediate severe thrombocytopenia and haemolysis. Acta Oncol. 2001. 40:882–883.

5. Earle CC, Chen WY, Ryan DP, Mayer RJ. Oxaliplatin-induced Evan's syndrome. Br J Cancer. 2001. 84:441.

6. Dold FG, Mitchell EP. Sudden-onset thrombocytopenia with oxaliplatin. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 139:E156.

7. Cobo F, De Celis G, Pereira A, Latorre X, Pujadas J, Albiol S. Oxaliplatin-induced immune hemolytic anemia: a case report and review of the literature. Anticancer Drugs. 2007. 18:973–976.

8. Desrame J, Broustet H, Darodes de Tailly P, Girard D, Saissy JM. Oxaliplatin-induced haemolytic anaemia. Lancet. 1999. 354:1179–1180.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download