Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C in Gwangju-Jeonnam area. Eighty-four patients with detectable HCV RNA were eligible for the study. Genotype-non-1 patients were treated with peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg/week plus ribavirin 800 mg/day for 24 weeks and genotype-1 patients were treated with peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg/week plus ribavirin 1,000-1,200 mg/day for 48 weeks. The end of treatment virologic response (ETVR), the sustained virologic response (SVR), the end of treatment of biochemical response (ETBR), the sustained biochemical response (SBR) and the adverse events were analyzed. The overall ETVR was 95.8%; 64.1% in genotype-1 group and 96.4% in genotype-non-1 group (p=0.56). The overall SVR was 80.4%; 60.0% in genotype-1 group and 86.1% in non-1 group (p=0.087). The ETBR was 72.2% and the SBR was 95.7%. In genotype-non-1, body mass index had independent effect on the SVR (p=0.038). Eight patients (32.0%) in the genotype-1 group and 4 patients (6.8%) in the non-1 group dropped out at the end of treatment, and 7 (8.3%) of 84 patients discontinued due to adverse events. This study shows that combination therapy with peginterferon and ribavirin as an initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients in this area is safe and effective as compared with Western and other reports; and that the body mass index may be regarded as one of the significant factors influencing the SVR.
Figures and Tables
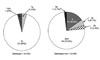
 | Fig. 2Patient flow diagram. EVR, early virologic response; ETVR, end of treatment virologic response; SVR, sustained virologic response; n, number. |
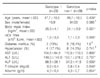
 | Fig. 3End of treatment virologic response (ETVR) and sustained virologic response (SVR) and end of treatment biochemical response (ETBR) and sustained biocemical response (SBR) according to the genotype of hepatitis C virus. ETVR and SVR was 95.8% and 80.4% and ETBR and SBR was 72.2% and 95.7%. There was not significantly different between patients with genotype 1 and those with genotype non-1 (ETVR, 94.1% vs. 96.4% p=0.56; SVR, 60.0% vs. 86.1% p=0.087; ETBR, 58.8% vs. 76.4%; p=0.112; SBR, 90.0% vs. 97.2% p=0.37). |
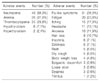
Table 2
Factors influencing on sustained virologic response in chronic hepatitis C caused by HCV genotype 1

References
2. Wasley A, Alter MJ. Epidemiology of hepatitis C: geographic differences and temporal trends. Semin Liver Dis. 2000. 20:1–16.

3. Armstrong GL, Alter MJ, McQuillan GK, Margolis HS. The past incidence of hepatitis C virus infection: implications for the future burden of chronic liver disease in the United States. Hepatology. 2000. 31:777–782.

4. Di Bisceglie AM. Natural history of hepatitis C: its impact on clinical management. Hepatology. 2000. 31:1014–1018.

5. Barrera JM, Bruguera M, Ercilla MG, Gil C, Celis R, Gil MP, et al. Persistent hepatitis C viremia after acute self-limiting posttransfusion hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1995. 21:639–644.

6. Kim YS, Pai CH, Chi HS, Kim DW, Min YI, Ahn YO. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus antibody among Korean adults. J Korean Med Sci. 1992. 7:333–336.

7. Strader DB, Seeff LB. The natural history of chronic hepatitis C infection. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996. 8:324–328.

8. Kim YS, Um SH, Ryu HS, Lee JB, Lee JW, Park DK, et al. The prognosis of liver cirrhosis in recent years in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:833–841.

9. Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2004. 39:1147–1171.
10. Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Arase Y, Chayama K, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, et al. Effect of interferon therapy on hepatocellular carcinogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis type C: a long-term observation study of 1,643 patients using statistical bias correction with proportional hazard analysis. Hepatology. 1999. 29:1124–1130.

11. Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, et al. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 140:346–355.

12. Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001. 358:958–965.

13. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL Jr, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:975–982.

14. Lee H, Choi MS, Paik SW, Kim JH, Kim DY, Lee JH, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:31–40.
15. Westin J, Hellstrand K, Alsio A, Ydreborg M, Ferrari C, Neumann AU, et al. Impact of disease severity on outcome of antiviral therapy in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2007. 45:1333–1334.

16. Manns MP, Wedemeyer H, Cornberg M. Treating viral hepatitis C: efficacy, side effects, and complications. Gut. 2006. 55:1350–1359.

17. Seeff LB, Hoofnagle JH. National institutes of health consensus development conference: management of hepatitis C: 2002. Hepatology. 2002. 36(5 Suppl 1):S1–S2.

18. Kuboki M, Iino S, Okuno T, Omata M, Kiyosawa K, Kumada H, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 KD) plus ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in Japanese patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:645–652.
19. Han KH, Yoon YH. Peginterferon-alpha and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2004. 10:81–87.
20. Weigand K, Stremmel W, Encke J. Treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 13:1897–1905.

21. Hwang SY, Lee HJ, Park KT, Kim KY, Lee SM, Park CW, et al. Effectiveness and complications of combination therapy with interferon alpha and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007. 49:166–172.
22. Shiffman ML, Suter F, Bacon BR, Nelson D, Harley H, Solá R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin for 16 or 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:124–134.

23. Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasp DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, et al. Dienstag JL, editor. Chronic hepatitis C. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2008. 17th ed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc;1963–1966.
24. Bressler BL, Guindi M, Tomlinson G, Heathcote J. High body mass index is an independent risk factor for nonresponse to antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003. 38:639–644.

25. Hickman IJ, Clouston AD, Macdonald GA, Purdie DM, Prins JB, Ash S, et al. Effect of weight reduction on liver histology and biochemistry in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 2002. 51:89–94.

26. National Institutes. National institutes of health consensus development conference statement: management of hepatitis C: 2002-June 10-12, 2002. Hepatology. 2002. 36(5 Suppl 1):S3–S20.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download