Abstract
Objectives
Social cognition plays an important role in psychiatric symptoms and prognosis in patients with schizophrenia. Diagnostic scales are predominantly text-based or intended for the evaluation of theoretical concepts, with limited usefulness in clinical settings. We therefore developed a video based social cognition scale.
Methods
Our scale consists of 20 video clips portraying frequently experienced social interactions in real life. Patients were asked which interactions were socially unnatural and the reasons for lies told by actors. Our scale was validated and social cognition and its relationship with symptoms was evaluated using item response theory.
Results
A total of 209 participants (schizophrenia, 101 ; bipolar disorder, 49 ; healthy controls 59) were enrolled. Our scale showed high reliability and concurrent validity compared with the order subtest of the short form of the Weschler Adult Intelligence scale. Internal validity also was high (Cronbach's alpha=0.904). Most items were easy to answer and highly discriminative. The test information curve showed our scale to be more informative in patients with low social cognition ability.
Figures and Tables
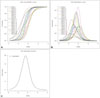 | Fig. 2Item characteristics curves, item information curves, and test information function. A : Item characteristic curves of each item. The relationship between the probability of correct response to each item and the participant's ability. B : Item informative curves of each item. The amount of item information (estimated participants' ability) is plotted against ability. C : Test informative curve. The sum of all item informative curves in the test. |
References
1. Green MF, Schooler NR, Kern RS, Frese FJ, Granberry W, Harvey PD, et al. Evaluation of functionally meaningful measures for clinical trials of cognition enhancement in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2011; 168:400–407.

2. Schiffman J, Walker E, Ekstrom M, Schulsinger F, Sorensen H, Mednick S. Childhood videotaped social and neuromotor precursors of schizophrenia: a prospective investigation. Am J Psychiatry. 2004; 161:2021–2027.

3. Gibson CM, Penn DL, Prinstein MJ, Perkins DO, Belger A. Social skill and social cognition in adolescents at genetic risk for psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2010; 122:179–184.

4. Bearden CE, Shih VH, Green MF, Gitlin M, Sokolski KN, Levander E, et al. The impact of neurocognitive impairment on occupational recovery of clinically stable patients with bipolar disorder: a prospective study. Bipolar Disord. 2011; 13:323–333.

5. Green MF, Bearden CE, Cannon TD, Fiske AP, Hellemann GS, Horan WP, et al. Social cognition in schizophrenia, part 1: performance across phase of illness. Schizophr Bull. 2012; 38:854–864.

6. Eack SM, Mermon DE, Montrose DM, Miewald J, Gur RE, Gur RC, et al. Social cognition deficits among individuals at familial high risk for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2010; 36:1081–1088.

7. Hans SL, Auerbach JG, Asarnow JR, Styr B, Marcus J. Social adjustment of adolescents at risk for schizophrenia: the Jerusalem Infant Development Study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2000; 39:1406–1414.

8. Amodio DM, Frith CD. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006; 7:268–277.

9. Park JY, Park HJ, Kim DJ, Kim JJ. Positive symptoms and water diffusivity of the prefrontal and temporal cortices in schizophrenia patients: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2014; 224:49–57.

10. Seidman LJ, Rosso IM, Thermenos HW, Makris N, Juelich R, Gabrieli JD, et al. Medial temporal lobe default mode functioning and hippocampal structure as vulnerability indicators for schizophrenia: a MRI study of non-psychotic adolescent first-degree relatives. Schizophr Res. 2014; 159:426–434.

11. Kuperberg G, Heckers S. Schizophrenia and cognitive function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000; 10:205–210.

12. Green MF, Penn DL, Bentall R, Carpenter WT, Gaebel W, Gur RC, et al. Social cognition in schizophrenia: an NIMH workshop on definitions, assessment, and research opportunities. Schizophr Bull. 2008; 34:1211–1220.

13. Pinkham AE, Penn DL, Green MF, Buck B, Healey K, Harvey PD. The Social Cognition Psychometric Evaluation study: results of the expert survey and RAND panel. Schizophr Bull. 2014; 40:813–823.

14. Goh JG, Hyun MH, Kim CY. The assessment of social cognitive ability for schizophrenia. Korean J Health Psychol. 2008; 13:461–480.

15. Jang J. Relation of social cognition and psychosocial function in chronic schizophrenia patients [dissertation]. Ulsan: University of Ulsan;2007.
16. Segal HG, Westen D, Lohr NE, Silk KR. Clinical assessment of object relations and social cognition using stories told to the picture arrangement subtest of the WAIS-R. J Pers Assess. 1993; 61:58–80.

17. Sung T. Understanding and application of item response theory. Seoul: KyoYookBook;2001.
18. Couture SM, Penn DL, Roberts DL. The functional significance of social cognition in schizophrenia: a review. Schizophr Bull. 2006; 32:Suppl 1. S44–S63.

19. Gard DE, Fisher M, Garrett C, Genevsky A, Vinogradov S. Motivation and its relationship to neurocognition, social cognition, and functional outcome in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009; 115:74–81.

20. Burns T, Patrick D. Social functioning as an outcome measure in schizophrenia studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2007; 116:403–418.

21. Sergi MJ, Green MF, Widmark C, Reist C, Erhart S, Braff DL, et al. Social cognition [corrected] and neurocognition: effects of risperidone, olanzapine, and haloperidol. Am J Psychiatry. 2007; 164:1585–1592.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download