Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to examine the drug adherence and treatment effect of the paliperidone long acting injection (LAI) in patients with schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders.
Methods
We reviewed the medical charts of patients who were prescribed paliperidone LAI from January 2010 to April 2014. Date of each injection, last observation, and first admission after use of the drug were obtained. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used for calculation of drug adherence. The dose of paliperidone LAI, concurrent oral antipsychotics, and anticholinergic agent was also obtained. Antipsychotics dose was calculated as olanzapine equivalent dose.
Results
The drug adherence of the paliperidone LAI on day 365 was 65%. The reasons for all cause discontinuation were follow-up loss, no effect, poor insight, rejection, extrapyramidal symptom, pain, etc. A total dose of 9.1 mg of oral antipsychotics was decreased, while the dose of anticholinergic agent was increased.
Figures and Tables
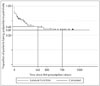 | Fig. 1The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing drug adherence of the paliperidone long acting injection. |
References
1. Fatemi SH, Folsom TD. The neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia, revisited. Schizophr Bull. 2009; 35:528–548.

2. Lieberman JA, Perkins DO, Jarskog LF. Neuroprotection: a therapeutic strategy to prevent deterioration associated with schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2007; 12:3 Suppl 4. 1–13. quiz 14.
3. Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, Sajatovic M, Scott J, Carpenter D, Ross R, et al. Strategies for addressing adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness: recommendations from the expert consensus guidelines. J Psychiatr Pract. 2010; 16:306–324.

4. Lambert M, Conus P, Cotton S, Robinson J, McGorry PD, Schimmelmann BG. Prevalence, predictors, and consequences of long-term refusal of antipsychotic treatment in first-episode psychosis. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2010; 30:565–572.

5. Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, Sajatovic M, Scott J, Carpenter D, Ross R, et al. The expert consensus guideline series: adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009; 70:Suppl 4. 1–46. quiz 47-48.
6. Bhanji NH, Chouinard G, Margolese HC. A review of compliance, depot intramuscular antipsychotics and the new long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic risperidone in schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004; 14:87–92.

7. Kishimoto T, Nitta M, Borenstein M, Kane JM, Correll CU. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mirror-image studies. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013; 74:957–965.
8. Fleischhacker WW. Second-generation antipsychotic long-acting injections: systematic review. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2009; 52:S29–S36.

9. Hill CL, Phadke D, Boyce KM. Four-week iloperidone depot injectable: safety and pharmacokinetic profile in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. In : Proceedings of the 161st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 3-8; Washington, DC. Washington, DC: APA;2008. New Research Abstracts 169 (NR4-022).
10. Citrome L. Olanzapine pamoate: a stick in time? A review of the efficacy and safety profile of a new depot formulation of a second-generation antipsychotic. Int J Clin Pract. 2009; 63:140–150.
11. Pandina GJ, Lindenmayer JP, Lull J, Lim P, Gopal S, Herben V, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and safety of 3 doses of paliperidone palmitate in adults with acutely exacerbated schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2010; 30:235–244.

12. Gopal S, Hough DW, Xu H, Lull JM, Gassmann-Mayer C, Remmerie BM, et al. Efficacy and safety of paliperidone palmitate in adult patients with acutely symptomatic schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2010; 25:247–256.

13. Kramer M, Litman R, Hough D, Lane R, Lim P, Liu Y, et al. Paliperidone palmitate, a potential long-acting treatment for patients with schizophrenia. Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy and safety study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010; 13:635–647.

14. Hough D, Gopal S, Vijapurkar U, Lim P, Morozova M, Eerdekens M. Paliperidone palmitate maintenance treatment in delaying the time-torelapse in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2010; 116:107–117.

15. Alphs L, Bossie CA, Sliwa JK, Ma YW, Turner N. Onset of efficacy with acute long-acting injectable paliperidone palmitate treatment in markedly to severely ill patients with schizophrenia: post hoc analysis of a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2011; 10:12.

16. Lee JS, Kim CY. Efficacy and tolerability of paliperidone palmitate in asian patients with schizophrenia. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2011; 22:Suppl 2. S49–S56.
17. Kim BR, Lee TJ, Woo JM, Park JI, Kwon JS. Cost-utility analysis of paliperidone palmitate long acting injection (plai) versus oral atypical antipsychotics in non-adherent schizophrenia patients in South Korea. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2012; 23:17–27.
18. Gardner DM, Murphy AL, O'Donnell H, Centorrino F, Baldessarini RJ. International consensus study of antipsychotic dosing. Am J Psychiatry. 2010; 167:686–693.

19. Attard A, Olofinjana O, Cornelius V, Curtis V, Taylor D. Paliperidone palmitate long-acting injection--prospective year-long follow-up of use in clinical practice. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2014; 130:46–51.

20. Taylor DM, Young C, Patel MX. Prospective 6-month follow-up of patients prescribed risperidone long-acting injection: factors predicting favourable outcome. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006; 9:685–694.

21. Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:1209–1223.

22. Moritz S, Hünsche A, Lincoln TM. Nonadherence to antipsychotics: the role of positive attitudes towards positive symptoms. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014; 24:1745–1752.

23. Gopal S, Liu Y, Alphs L, Savitz A, Nuamah I, Hough D. Incidence and time course of extrapyramidal symptoms with oral and long-acting injectable paliperidone: a posthoc pooled analysis of seven randomized controlled studies. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013; 9:1381–1392.

24. Leo RJ, Regno PD. Atypical antipsychotic use in the treatment of psychosis in primary Care. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2000; 2:194–204.

25. Kim YS, Ahn YM, Jeong SH. Dosing and switching. In : Oh YC, editor. Principle and practice of long-acting injectable antipsychotics. Seoul: Seoul National University Press;2012. p. 256–262.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download