Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the correlated factors that may influence the length of stay in mental health related facilities.
Methods
We chose 2253 patients with mental illness using a stratified multi-stage cluster sampling from 48 psychiatric hospitals, twelve psychiatric clinics, five psychiatric welfare facilities, and five mental rehabilitation facilities. The investigation involved psychiatrists, psychology practitioners, and social workers, and lasted from August 1, 2008 to November 15, 2008. Assessment and investigation of diverse factors was performed using one-way analysis of variance in order to examine their influence on length of stay.
Results
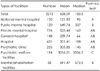
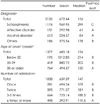
Factors showing significant correlation with length of stay included the types of mental health related facilities, age, marital status, socioeconomic status, type of medical security, familial support, type of admission, diagnosis, age of onset of the illness, number of admissions, severity of psychiatric symptoms, daily living and social function, GAF score, prominent thought/perception disability, memory/orientation disturbance, odd behavior/prominent regression, personal hygiene, communication/personal relationship, management of money, and public transportation/facility utilization.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Suh TW, Lee YM, Kim Y, Lim JK, Kim DJ. Study on the Program and Profiles of Patients in Mental Health Facilities in Korea. 1999. Seoul: Korean Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
2. Lee YM, Kim Y, Lee MS, Lee JS, Park JI, Kang SK, et al. Annual Report 2010. 2010. Seoul: The National Mental Health Commission.
3. OECD. Policy Brief: Mental Health in OECD Countries. OECD 2008. Available from www.oecd.org/publications/Policybriefs.
4. Wing JK, Brown G. Institutionalism and Schizophrenia. 1970. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
5. Suh TW. Length of stay of psychiatric inpatients by sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, and type of facilities. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2002. 41:1174–1184.
6. Thornicroft G, Bebbington P, Leff J. Outcomes for long-term patients one year after discharge from a psychiatric hospital. Psychiatr Serv. 2005. 56:1416–1422.

7. Weisbrod BA, Test MA, Stein LI. Alternative to mental hospital treatment. II. Economic benefit-cost analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980. 37:400–405.
8. Andrews G, Sanderson K, Corry J, Issakidis C, Lapsley H. Cost-effectiveness of current and optimal treatment for schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 2003. 183:427–435.

9. Caton CL, Gralnick A. A review of issues surrounding length of psychiatric hospitalization. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1987. 38:858–863.

10. Mezzich JE, Coffman GA. Factors influencing length of hospital stay. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1985. 36:1262–1264.

11. Taube C, Lee ES, Forthofer RN. Diagnosis-related groups for mental disorders, alcoholism, and drug abuse: evaluation and alternatives. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1984. 35:452–455.

12. Kiesler CA, Simpkins C, Morton T. Predicting length of hospital stay for psychiatric inpatients. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1990. 41:149–154.

13. Durbin J, Goering P, Pink G, Murray M. Classifying psychiatric inpatients: seeking better measures. Med Care. 1999. 37:415–423.
14. Lee HY, Lee YM, Chung YK, Kim BH. The Study about Reclassification of Mentally Disability and Development of Metal Health Medical Facility Standard. 1994. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Social Welfare.
15. Lee YM, Kim JH, Lee HY, Jeong YK, Lim KY, Lee JH, et al. Length of stay in the mental health facilities in Korea. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1998. 37:83–94.
16. Suh T, Lee YM, Hong JP, Cho SJ, Lee JY, Lee SY, et al. Influencing factors on length of stay of psychiatric patients in mental health-related facilities. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2003. 42:761–770.
17. Cho SJ, Lee BJ, Cho MJ, Kim YI, Suh T, Jung IK. Length of stay of psychiatric patient and its correlate in mental health-related facilities. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2006. 45:372–381.
18. Suh SK, Kim Y, Park JI, Lee MS, Jang HS, Lee SY, et al. [Medical care utilization status and associated factors with extended hospitalization of psychiatric patients in Korea]. J Prev Med Public Health. 2009. 42:416–423.

19. Seo JS, Bhang S, Kim S, Cho E, Park JI, Suh T, et al. Factors influencing on length of stay in a psychiatric open ward of a general hospital. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2003. 42:749–754.
20. Chung S, Bahk WM, Kwon JS, Park JH, Ahn JH, Goh J, et al. Symptom remission and functional outcomes in patients with recent-onset schizophrenia: a one-year prospective observational study. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2007. 46:480–491.
21. Kim JY, Kang SH, Kim SJ, Kwak KH, Kim CY. The validity and reliability of brief rating scales for the assessment of symptoms and functions in patients with psychosis. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2007. 46:492–498.
22. Mattes JA. The optimal length of hospitalization for psychiatric patients: a review of the literature. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1982. 33:824–828.

23. Lave JR, Frank RG. Effect of the structure of hospital payment on length of stay. Health Serv Res. 1990. 25:327–347.
24. Goodpastor WA, Hare BK. Factors associated with multiple readmissions to an urban public psychiatric hospital. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1991. 42:85–87.

25. Huntley DA, Cho DW, Christman J, Csernansky JG. Predicting length of stay in an acute psychiatric hospital. Psychiatr Serv. 1998. 49:1049–1053.

26. Talbott JA. Oldham JM, Ribci M, editors. Fifty years of psychiatric services: Changes in treatment of chronically mentally ill patients. Review of Psychiatry. 1994. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press;93–120.
27. Citrome L, Green L, Fost R. Length of stay and recidivism on a psychiatric intensive care unit. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1994. 45:74–76.

28. Nieminen P, Isohanni M, Winblad I. Length of hospitalization in an acute patients' therapeutic community ward. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1994. 90:466–472.

29. Jakubaschk J, Waldvogel D, Wurmle O. Differences between long-stay and short-stay inpatients and estimation of length of stay. Berne, Switzerland: Psychiatric Clinic of Berne University;Accepted: November 19, 1992.
30. Frank RG, Lave JR. The psychiatric DRGs. Are they different? Med Care. 1985. 23:1148–1155.
31. Chang G, Brenner L, Bryant K. Variables predicting inpatient length of stay in a CMHC. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1991. 42:853–855.
32. Heiman EM, Shanfield SB. Length of stay for patients in one city's ho-spitals with psychiatric units. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1980. 31:632–634.

33. Oiesvold T, Saarento O, Sytema S, Christiansen L, Göstas G, Lönnerberg O, et al. The Nordic Comparative Study on Sectorized Psychiatry--length of in-patient stay. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1999. 100:220–228.

34. Lehmann HE, Cancro R. Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ, editors. Schizophrenia: Clinical Features. Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry IV. 1985. Vol I. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;709–713.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download