Abstract
Background and Objectives
Subjects and Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
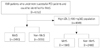 | Fig. 1Patient flow chart. A total of 6352 AMI patients who had successful PCI and could be identified for MetS between November 2005 and January 2008 at 51 hospitals participating in the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry were divided into 2 groups according to the presence of MetS: the MetS group versus the Non-MetS group. Among them, 4049 AMI patients who had high LDL-C levels (more than 100 mg/dL) were divided into the MetS group versus the Non-MetS group. AMI: acute myocardial infarction, PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention, MetS: metabolic syndrome, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol. |
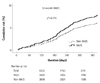 | Fig. 2Twelve-month MACE in the overall population. In the overall population, 12-month MACE rates were higher in the MetS group than in the Non-MetS group, but there was no significant difference between the 2 groups. MACE: major adverse cardiac events, MetS: metabolic syndrome, p*: adjusted p. |
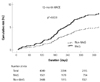 | Fig. 3Twelve-month clinical outcomes in the high LDL-C population. In the high LDL-C population, 12-month MACE rates were higher in the MetS group than in the Non-MetS group, and there was a significant difference between the 2 groups. LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, MACE: major adverse cardiac events, MetS: metabolic syndrome, p*: adjusted p. |
Table 1

Data are presented as the n (%) of patients or mean±SD. *Values are expressed as the median (interquartile range). MetS: metabolic syndrome, CAD: coronary artery disease, SBP: systolic blood pressure, LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction, STEMI: ST elevation myocardial infarction, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, HDL-C: high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, CrCl: creatinine clearance, CK-MB: creatine kinase-MB, hsCRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide, Gp2b3aI: glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor, ACEI: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ARB: angiotensin receptor blockers, CCB: calcium channel blocker
Table 2

Data are presented as the n (%) of patients or mean±SD. MetS: metabolic syndrome, LAD: left anterior descending artery, LCX: left circumflex artery, RCA: right coronary artery, ACC/AHA: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association, PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention, TIMI: Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction
Table 3

Values are n (%). All comparisons were made using the chi-square test. P was calculated by log rank analysis, and p* was calculated by multivariate Cox regression analysis. Major adverse cardiac events included cardiac deaths, recurrent myocardial infarction, and target vessel revascularization. p*: adjusted p, MetS: metabolic syndrome, MI: myocardial infarction, TVR: target vessel revascularization, MACE: major adverse cardiac event(s)
Table 4

Values are n (%). All comparisons were made using the chi-square test. P was calculated by log rank analysis, and p* was calculated by multivariate Cox regression analysis. Major adverse cardiac events included cardiac deaths, recurrent myocardial infarction, and target vessel revascularization. p*: adjusted p, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, MetS: metabolic syndrome, MI: myocardial infarction, TVR: target vessel revascularization, MACE: major adverse cardiac event(s)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download