Abstract
Background and Objectives
Subjects and Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
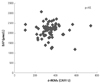 | Fig. 1Relationship between derivatives of reactive oxidative metabolites (d-ROMs) and biological antioxidant potential (BAP) before cardiac rehabilitation in patients with cardiovascular diseases (n=69). CARR U: carratelli unit, NS: not significant. |
 | Fig. 2Relationships between derivatives of reactive oxidative metabolites (d-ROMs), and the percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2peak (%V̇O2peak; n=96) (A), the percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2 at the anaerobic threshold (%V̇O2 AT; n=96) (B), and plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP; n=94) (C) before cardiac rehabilitation in patients with cardiovascular diseases. CARR U: carratelli unit. |
 | Fig. 3Time-dependent effects of cardiac rehabilitation on the derivatives of reactive oxidative metabolites (d-ROMs) (A), biological antioxidant potential (BAP) (B), and BAP/d-ROMs, the antioxidative/oxidative stress ratio (C). *p<0.05, †p<0.01, ‡p<0.005, §p=0.001. CARR U: carratelli unit, ANOVA: analysis of variance. |
 | Fig. 4Time-dependent effects of cardiac rehabilitation on the percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2peak (%V̇O2peak) (A), the percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2 at the anaerobic threshold (%V̇O2 AT) (B), and plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) (C). *p<0.001. ANOVA: analysis of variance. |
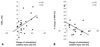 | Fig. 5Relationship between the % changes of V̇O2 at the anaerobic threshold (V̇O2 AT) and the % changes of biological antioxidant potential/derivatives of reactive oxidative metabolites, the antioxidative/oxidative stress ratio (n=23) (A), and the relationship between the % changes of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and the % changes of the antioxidative/oxidative stress ratio (n=17) (B) from pre-CR to 6 months after CR, respectively. CB: cardiac rehanilitation. |
Table 1

Mean±SD. LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction, BMI: body mass index, CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting, LAD: left anterior descending artery, LCX: left circumflex artery, RCA: right coronary artery, NYHA: New York Heart Association, ACEI: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ARB: angiotensin receptor blocker, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, HDL-C: high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c, BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide, %V̇O2peak: percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2 peak, V̇O2 AT: V̇O2 at the anaerobic threshold, %V̇O2 AT: percentage of the predicted values of V̇O2 AT, d-ROMs: derivatives of reactive oxidative metabolites, BAP: biological antioxidant potential, CARR U: carratelli unit




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download