Abstract
Background and Objectives
Subjects and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
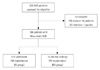 | Fig. 1Flow diagram of study patients. AVB: atrioventricular block, PM: pacemaker, ILR: implantable loop recorder, IB: irreversible block, RB: reversible block. |
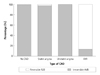 | Fig. 2Reversibility of AVB and CAD type. Reversibility of AVB was assessed on the aspect of CAD type. The proportion of reversible AVB was significantly higher in patients presented with AMI. AVB: atrioventricular block, CAD: coronary artery disease, AMI: acute myocardial infarction. |
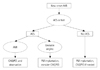 | Fig. 3Flow chart of management of new-onset AVB. AVB: atrioventricular block, ACS: acute coronary syndrome, AMI: acute myocardial infarction, CAG: coronary angiography, PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention, PM: pacemaker. |
Table 1

Classification of pathological coronary anatomy by Mosseri et al.2) AV: atrioventricular, LAD: left anterior descending coronary artery
Table 2
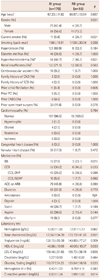
Values are mean±SD, or absolute number (%). *Hypercholesterolemia: known dyslipidemia or use of statin or total cholesterol >200 mg/dL, †Renal insufficiency: known chronic kidney disease or glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2. IB: irreversible block, RB: reversible block, CAD: coronary artery disease, SCD: sudden cardiac death, PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention, CABG: coronary artery bypass graft, BB: beta blocker, CCB: calcium channel blocker, DHP: dihydropyridine, NDHP: non-dihydropyridine, ACEi: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ARB: angiotensin receptor blocker, HDL-C: high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, LDL-C: low density lipoprotein-cholesterol
Table 3

Values are absolute number (%), or proportion of reversible AVB of each CAD types (%). *Proportion of reversible AVB among patients with CAD, †Proportion of reversible AVB among patients with RCA lesion, ‡Classification of coronary pathology by Mosseri et al.2) Values of this cell are absolute number (%), or proportion of reversible AVB of each CAD types (%), among patients with CAD, §Type II or IV vs. Type I or III. AVB: atrioventricular block, AMI: acute myocardial infarction, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval, CAD: coronary artery disease, RCA: right coronary artery, N/A: not applicable, MI: myocardial infarction
Table 4

*Multivariate logistic regression analysis to define factors associated with reversible AVB. All univariate variables of p<0.10 were entered for multivariate analysis. AVB: atrioventricular block, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval, CAD: coronary artery disease, AMI: acute myocardial infarction




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download