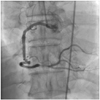
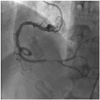
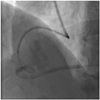
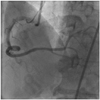
A 61-year-old man was admitted for progressively accelerating chest pain during 12 hours. An electrocardiogram showed ST segment elevation of about 2 mm in leads II, III, and aVF. Left coronary angiogram showed normal coronary arteries. Right coronary angiogram showed distal right coronary artery (RCA) "culprit" lesion just before the posterodescending and posterolateral bifurcation, but the mid RCA showed severe tortuosity (Fig. 1). Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed using a 6 Fr XBRCA guide catheter (Cordis, Warren, NJ, USA) and a Runthrough NS (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) guide wire. Predilation of culprit lesion was performed using 2×20 mm balloon inflated up to 8 atmospheres (Fig. 2). Attempted delivery of a coronary stent was unsuccessful due to excessive tortuosity of the mid RCA. We changed the guiding catheter to a 7 Fr Amplatz Right 1 (Cordis, Warren, NJ, USA), but stent passage failed again, despite use of a buddy wire technique. Finally, we used a Choice PT Extra Support guide wire (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) with a 7 Fr Judkins Right (JR4) (Cordis, Warren, NJ, USA) guiding catheter and performed an extra deep intubation using a Terumo 5 Fr Heartrail guiding catheter (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan). The tip of this catheter passed easily into the mid RCA, allowing distal delivery of the 3×24 mm Taxus Liberte monorail stent (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) without resistance. This was deployed successfully at the culprit lesion (Fig. 3). After stenting, slow flow was developed, but coronary flow was restored gradually after administration of intracoronary nitroglycerin. The final angiogram showed an acceptable result (Fig. 4).
The Terumo "five-in-six" system involves insertion of an extra length, 5 Fr Terumo guiding catheter (Heartrail; Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) into a standard 6 Fr guide catheter.1) A Heartrail 5 Fr catheter is 120 cm in length, whereas the standard guiding catheter is 100 cm long. A 5 Fr Heartrail catheter has a very soft 13 cm end portion, which can easily negotiate the tortous coronary artery with minimal damage and which can be subsequently inserted more deeply into the artery.2) We used a 7 Fr guiding catheter instead of a 6 Fr guiding catheter to increase backup support, enabling stent delivery against the tortuous coronary artery.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download