Abstract
Background and Objectives
Subjects and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
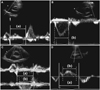 | Fig. 1Measurement of right ventricular Tei index (RTX) by (A and B) the conventional flow Doppler method (RTXCFD), (C) the dual pulsed-wave Doppler method (RTXDPD), and by (D) tissue Doppler echocardiography (RTXTDE). RTX was defined as [(a)-(b)]/(b), where (a) is the time from tricuspid valve inflow cessation to onset for RTXCFD and RTXDPD and time from the end of A'TV to the onset of E'TV for RTXTDE, and (b) is the pulmonary ejection time for RTXCFD and RTXDPD or the duration of S'TV for RTXTDE. A'TV: late diastolic tricuspid annular velocity, E'TV: early diastolic tricuspid annular velocity, S'TV: systolic tricuspid annular velocity. |
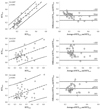 | Fig. 2Correlation (left column) and Altman-Bland plots (right column) between right ventricular Tei indexes (RTX) using conventional flow Doppler (CFD) and dual pulsed-wave Doppler (DPD; upper row); RTX using CFD and tissue Doppler (TDE; mid-row); and RTX using the DPD and TDE methods. |
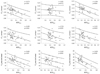 | Fig. 3Correlation plots of the right ventricular Tei index (RTX) vs. the S'TV (upper row), E'TV (mid-row), and maximal exercise capacity (lower row). Horizontal axes in the leftmost column represent RTX values determined using conventional flow Doppler (RTXCFD); the middle column represents RTX values determined using tissue Doppler echocardiography (RTXTDE); and the right column RTX values determined using the dual pulsed-wave Doppler method (RTXDPD). S'TV: systolic tricuspid annular velocity, E'TV: early diastolic tricuspid annular velocity. |
Table 1

Data are presented as the means±SD or as numbers (%). *p were calculated using an independent t-test or Chi-squared test between groups A and B. Fisher,s exact tests were used when applicable. One-way analysis of variance with post-hoc analysis using the Bonferroni correction method was also used for comparison of the parameters between three groups, †p<0.05 compared with the healthy control group in post-hoc analysis, ‡Patients that developed chronic pulmonary regurgitation after surgical treatment of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). RVSP: right ventricular systolic pressure, ASD: atrial septal defect, PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension, RVOT: right ventricular outflow tract
Table 2

Data are presented as the means±SD or as numbers (%). *p calculated using the independent t-test or one-way analysis of variance with posthoc analysis by the Bonferroni correction method, †p<0.05 compared with the healthy control group, ‡p<0.05 compared with group B. RVSP: right ventricular systolic pressure, LV: left ventricle, E: early diastolic mitral inflow velocity, E'MV: early diastolic mitral annular velocity, E/E'MV: E to E'MV ratio, RV: right ventricle, S'TV: peak systolic tricuspid annular velocity, E'TV: peak early diastolic tricuspid annular velocity, A'TV: peak late diastolic tricuspid annular velocity, RTX: RV Tei index, CFD: conventional flow Doppler, TDE: tissue Doppler echocardiography, DPD: dual pulsed-wave Doppler, VO2 max: peak oxygen consumption rate, METS: metabolic equivalents
Table 3
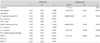
N=41, dependent variable as METS. R2=0.79, Adjusted R2=0.75, standard error of the estimate=1.32. The backward stepwise approach was used to select best model fits to predict the METS. *RTXCFD and RTXTDE were excluded for the multiple regression model in this table (see text for details). LV: left ventricle, E'MV: early diastolic mitral annular velocity, E/E'MV: E to E'MV ratio, RV: right ventricle, S'TV: systolic tricuspid annular velocity, E'TV: early diastolic tricuspid annular velocity, RTX: RV Tei index, DPD: dual pulsed-wave Doppler, CFD: conventional flow Doppler, TDE: tissue Doppler echocardiography




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download