Abstract
The stent has been a key part of percutaneous coronary intervention. The advent of drug-eluting stents has further expanded the indication for this technology with a lower overall rate of restenosis. However, the limitations of the current generation stent platforms have become more apparent as more complex are being treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. Coronary stenting sometimes results in a suboptimal outcome for challenging lesion subsets such as tortuous, calcified, bifurcating and multiple and long lesions. In this review, novel stent systems that have been developed to overcome the challenges surrounding current stent designs will be discussed.
References
1. Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1773–80.

2. Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, et al. A polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:221–31.

3. Seung KB. Drug eluting stent and percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. 2003; 33:857–60.

4. Park JS, Kim YJ, Shin DG, et al. Clinical and angiographic outcome of sirolimus-eluting stent for the treatment of very long lesions. Korean Circ J. 2006; 36:490–4.

5. Lohavanichbutr K, Webb JG, Carere RG, et al. Mechanisms, management, and outcome of failure of delivery of coronary stents. Am J Cardiol. 1999; 83:779–81.

6. Ferrer Gracia MC, Moreno R, Perez Vizcayno MJ, et al. Failure in the implantation of drug eluting stents: frequency and related factors. Med Intensiva. 2007; 31:423–7.
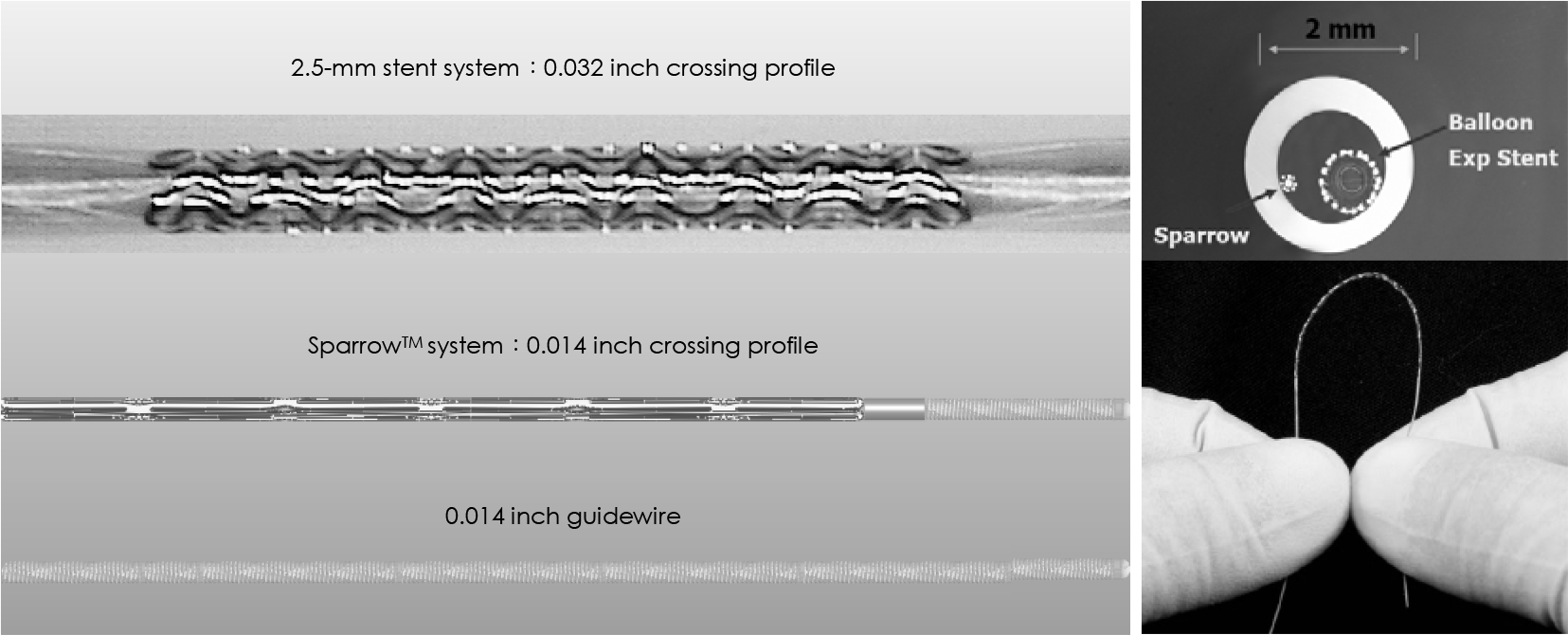
7. Yamasaki M, Ako J, Honda Y, et al. Novel guidewire-based stent delivery system: examination by intravascular ultrasound. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008; 72:47–51.
8. Evans LW, Doran P, Marco P. XTENT® Custom NXTM drug eluting stent systems. EuroInterv. 2007; 3:158–61.
9. Grube E, Sievert H, Hauptmann KE, et al. Novel drug eluting stent system for customised treatment of coronary lesions: CUSTOM I feasibility trial 24 months results. EuroInterv. 2008; 4:71–8.
10. Kim W, Kim YJ, Lee WJ, et al. Lesion location: its impacts on the procedural and postprocedural outcomes of unprotected left main coronary stenting. Korean Circ J. 2007; 37:419–24.

11. Tanabe K, Hoye A, Lemos PA, et al. Restenosis rates following bifurcation stenting with sirolimus-eluting stents for de novo narrowings. Am J Cardiol. 2004; 94:115–8.

12. Lemos PA, Hoye A, Goedhart D, et al. Clinical, angiographic, and procedural predictors of angiographic restenosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation in complex patients: an evaluation from the rapamycin-eluting stent evaluated at Rotterdam Cardiology Hospital (RESEARCH) study. Circulation. 2004; 109:1366–70.

13. Colombo A, Moses JW, Morice MC, et al. Randomized study to evaluate sirolimus-eluting stents implanted at coronary bifurcation lesions. Circulation. 2004; 109:1244–9.

14. Lefevre T, Ormiston J, Guagliumi G, et al. The FRONTIER Stent Registry: safety and feasibility of a novel dedicated stent for the treatment of a bifurcation coronary artery lesions. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 46:592–8.
15. Laborde JC, Borenstein N, Behr L, Ramcharitar S. Stentys coronary bifurcation stent. EuroInterv. 2007; 3:162–5.
16. Onuma Y, Muller R, Ramcharitar S, et al. Tryton I, First-In-Man (FIM) study: six month clinical and angiographic outcomes, analysis with new quantitative coronary angiography dedicated for bifurcation lesions. EuroInterv. 2008; 3:546–52.
17. Grube E, Wijns W, Schofer J, Shmulewitz A, Steckel MG, Leon MB. FIM results of Cappella Sidegruard for treatment of coronary bifurcations. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 100:18L. Abstract.
18. Grube E, Buellesfeld L, Neumann FJ, et al. Six-month clinical and angiographic results of a dedicated drug-eluting stent for the treatment of coronary bifurcation narrowings. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 99:1691–7.

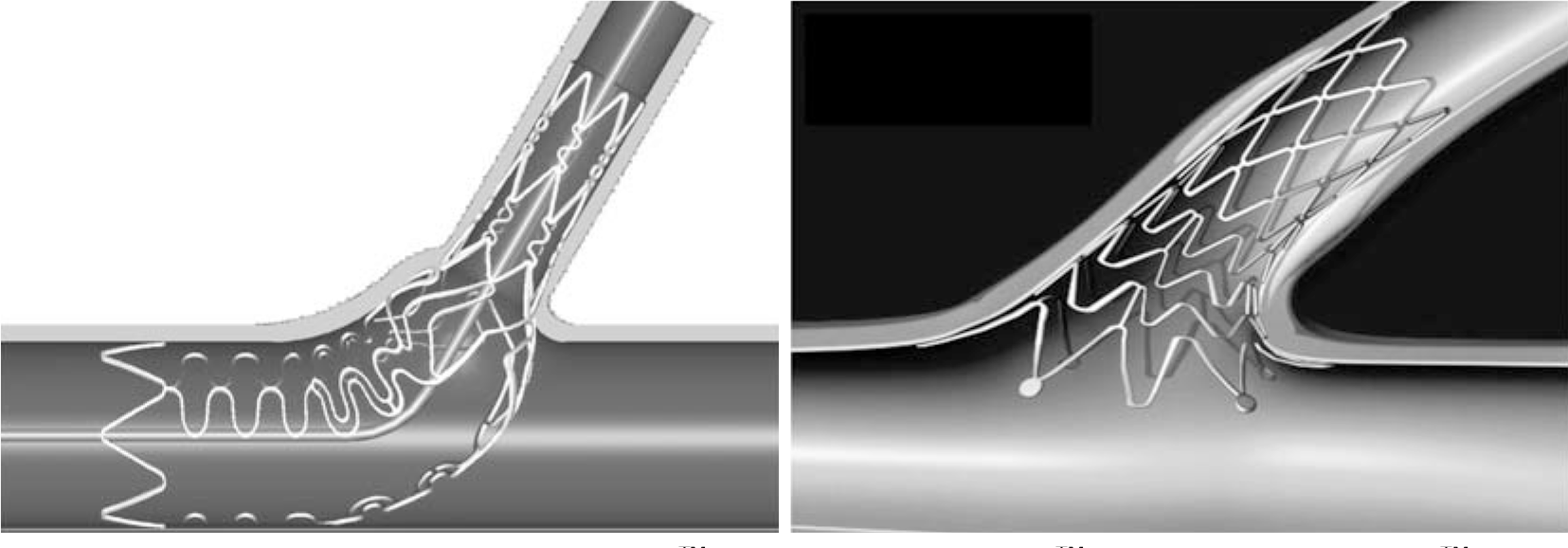
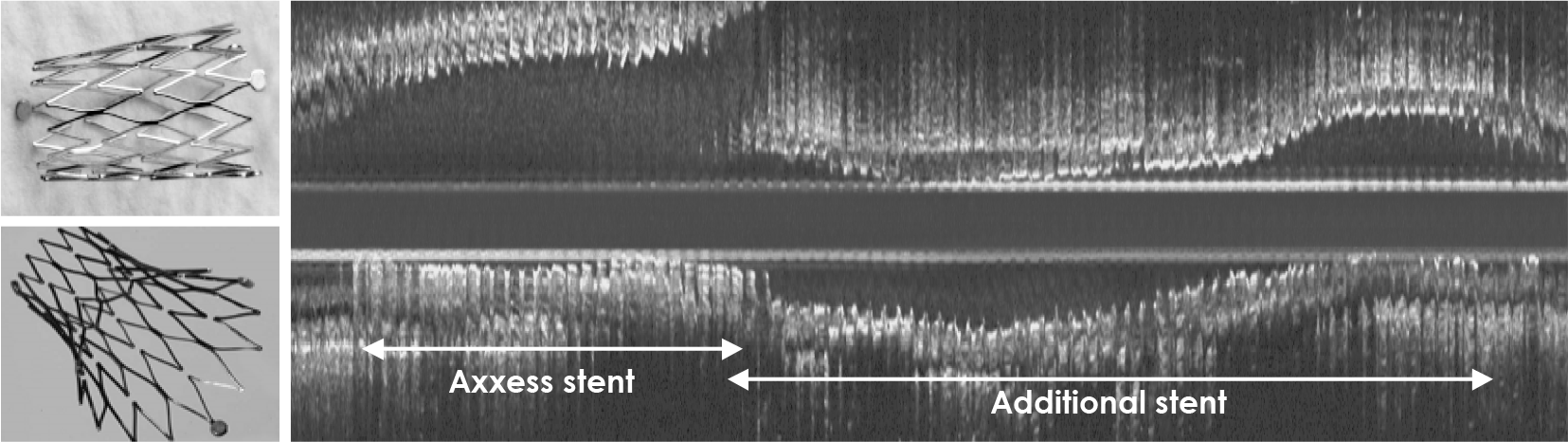
19. Hasegawa T, Ako J, Miyazawa A, et al. Analysis of left main coronary bifurcation lesions treated with Biolimus-eluting Devax Axxess plus nitinal self-expanding stent: Intravascular ultrasound results of the AXXENT trial. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 100:18L. Abstract.
Fig. 2.
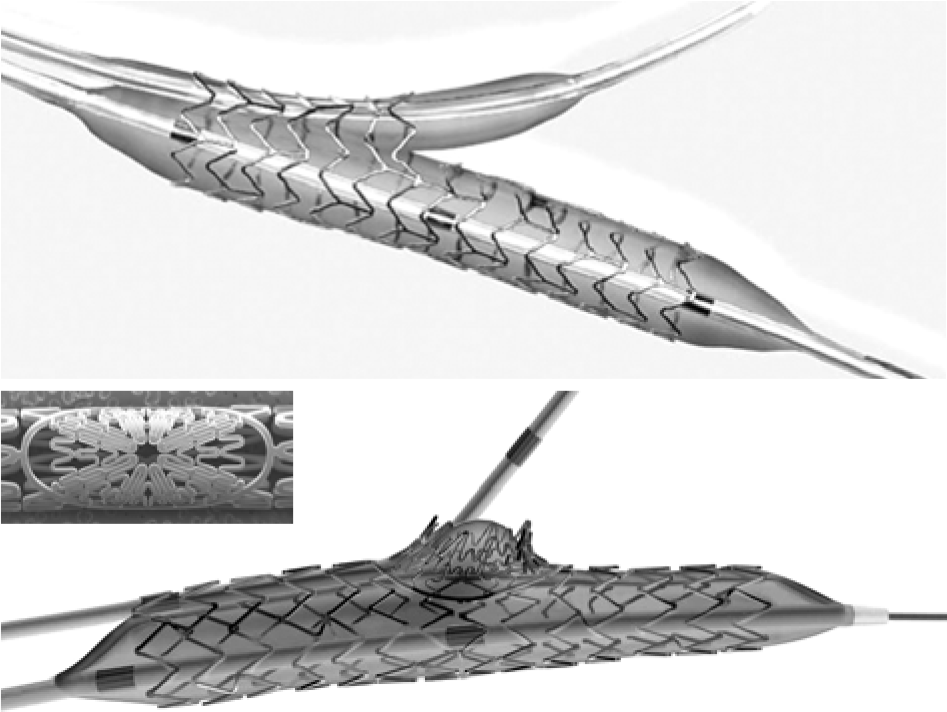
The interdigitating stent design of the Custom NX®DES system. Manipulation of the switch on the handle (Right) activates the separation of the interdigitated segment at a desired location; therefore, the operator can customize the stent length.

Fig. 4.
Angiographic and intravascular ultrasound results of a bifurcation lesion treated with an AntaresTM stent. The ostial preservation structure (arrow) covers the side branch ostium to provide scaffolding.
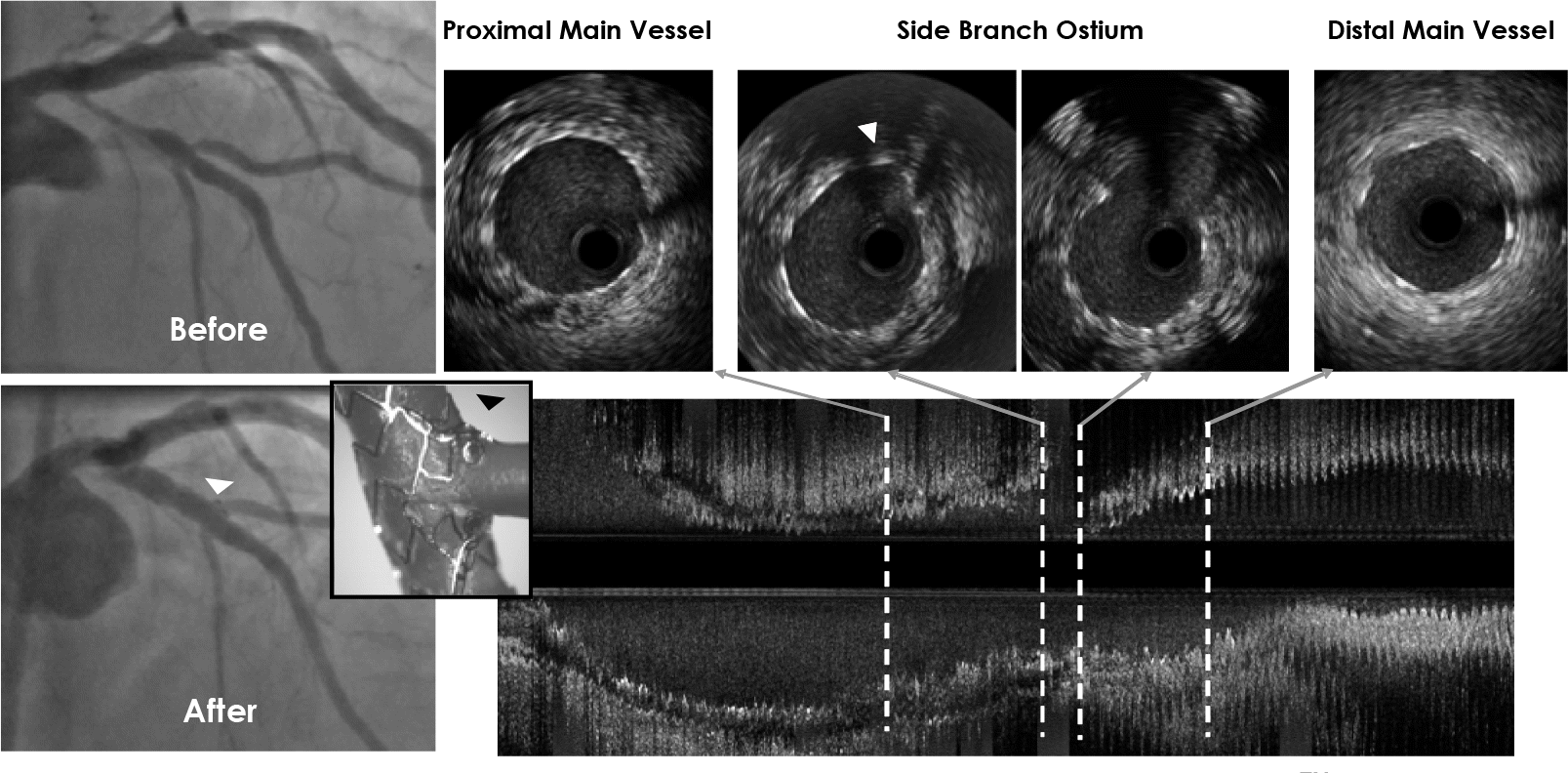
Fig. 5.
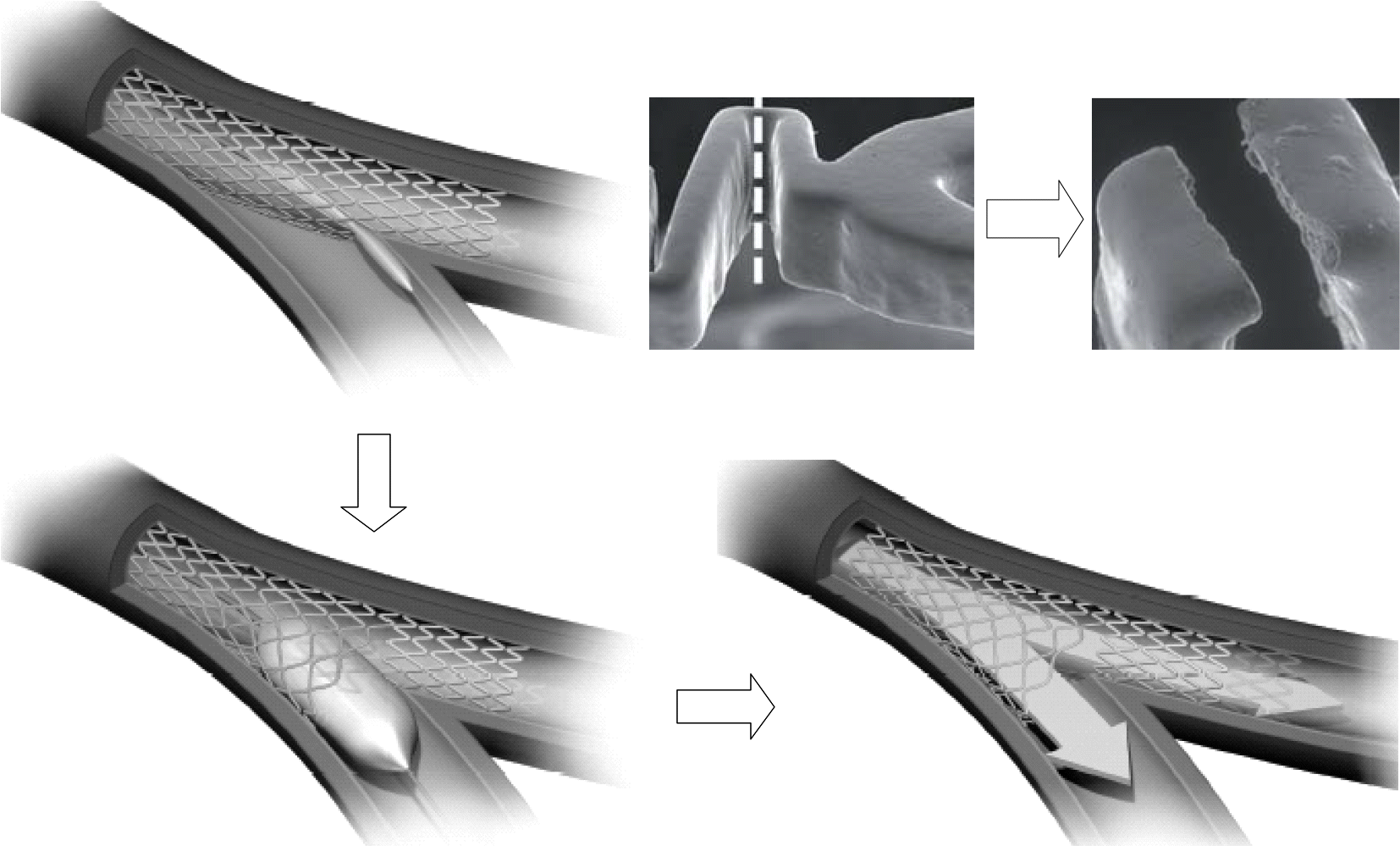
The StentysTM coronary bifurcation stent. The struts can be disconnected using an angioplasty balloon to create side branch access and to achieve side branch ostial scaffolding as the struts are linked by small interconnections.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download