Abstract
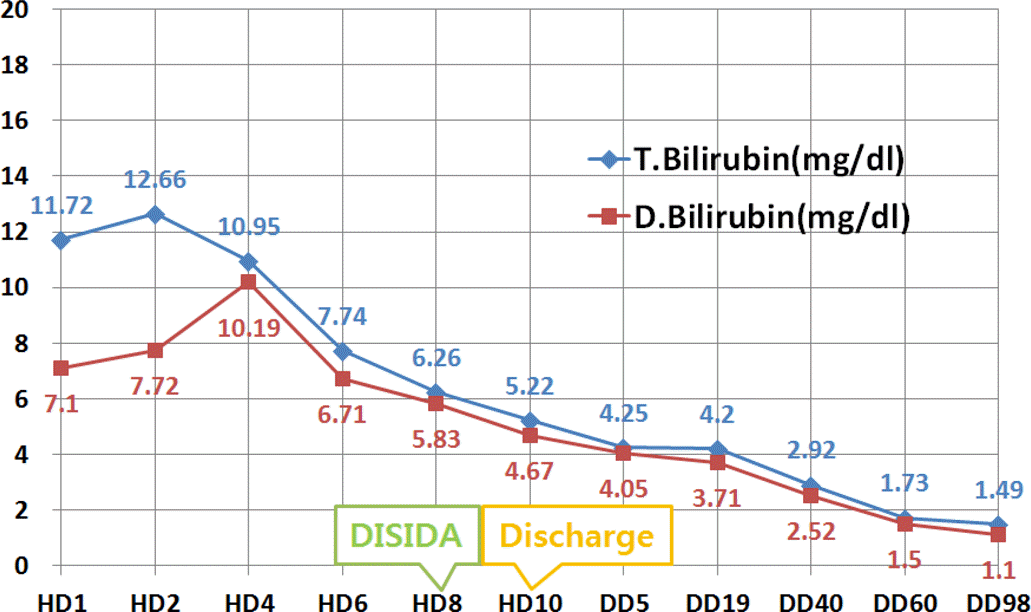
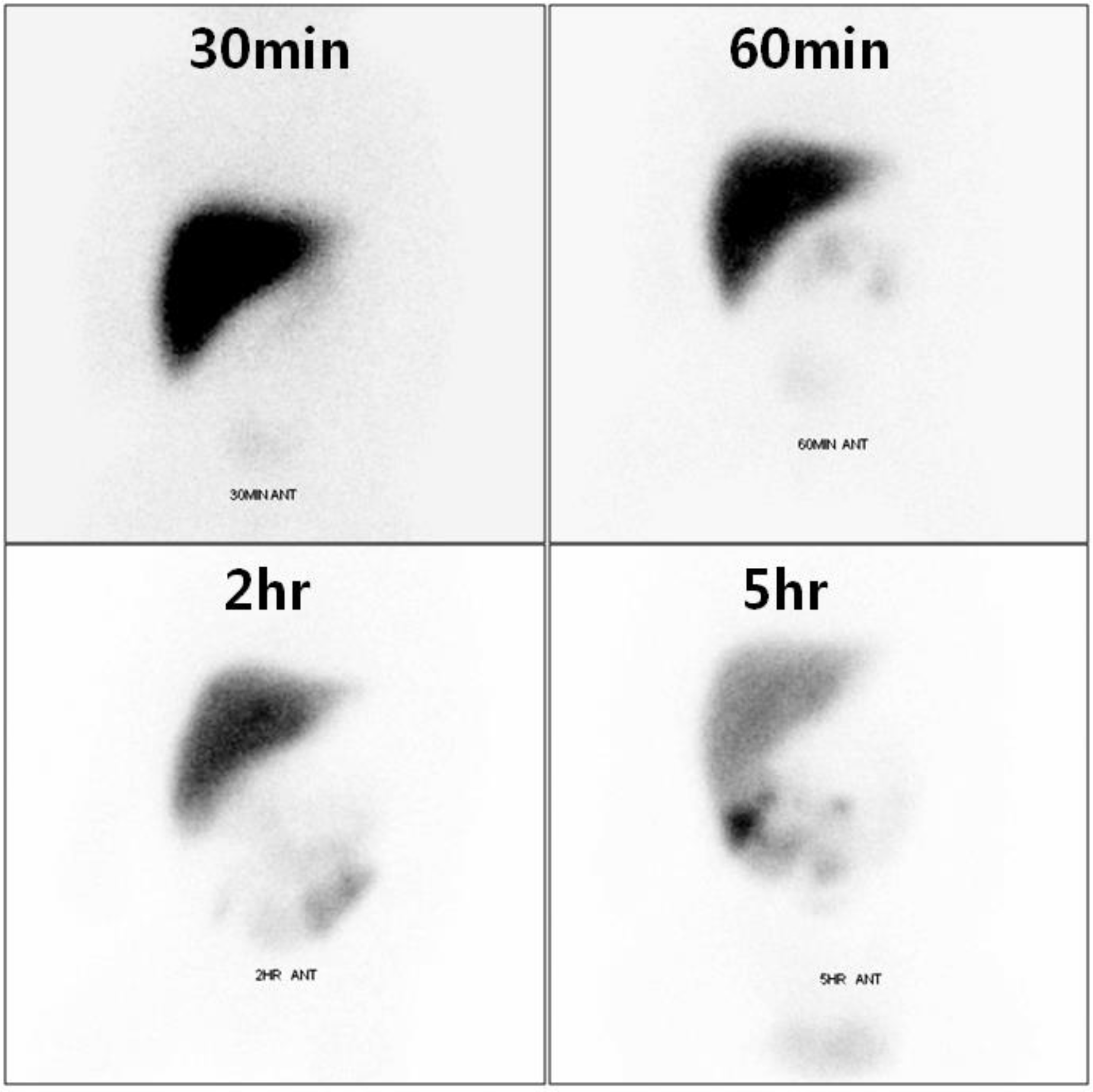
Rotavirus is the most common cause of infectious gastroenteritis in infants and young children and estimated to cause more than 111 million cases of diarrhea annually. Most patients show no specific symptom or experience mild fever, vomiting, non-bloody diarrhea and symptoms often resolve within several days. However, some of patients suffer from severe complication such as necrotizing enterocolitis, intussusception, seizure, encephalitis, and cholestasis. We report a neonatal case of rotavirus infection presenting with reversible direct hyperbilirubinemia with a brief review of associated literatures.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
3). Moon HH., Kim DS., Park SH., Kim H. Clinical characteristics and genotype of rotavirus infection in newborn infants. Korean J Perinatol. 2012. 23:266–72.
4). Sugata K., Taniguchi K., Yui A., Miyake F., Suga S., Asano Y, et al. Analysis of rotavirus antigenemia and extraintestinal manifestations in children with rotavirus gastroenteritis. Pediatrics. 2008. 122:392–7.

5). Kim DK., Jeong DS., Kim CR., Oh SH., Moon SJ. Clinical and epidemiologic features of rotavirus outbreak in a nursery. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2003. 10:208–17.
6). Rodriguez WJ., Kim HW., Brandt CD., Schwartz RH., Gardner MK., Jeffries B, et al. Longitudinal study of rotavirus infection and gastroenteritis in families served by a pediatric medical practice: clinical and epidemiologic observations. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987. 6:170–6.
7). de Villiers FP., Steele AD., Driessen M. Central nervous system involvement in neonatal rotavirus infection. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2003. 23:309–12.

8). Saulsbury FT., Winkelstein JA., Yolken RH. Chronic rotavirus infection in immunodeficiency. J Pediatr. 1980. 97:61–5.

9). Sızmaz E., Satar M., Ozlü F., Yaman A., Yıldızdaş HY., Ozcan K. The coincidence of necrotizing enterocolitis and rotavirus infections and potential associations with cytokines. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2012. 23:e103–5.

10). Konno T., Suzuki H., Kutsuzawa T., Imai A., Katsushima N., Sakamoto M, et al. Human rotavirus and intussusception. N Engl J Med. 1977. 297:945.
11). Takahashi S., Oki J., Miyamoto A., Koyano S., Ito K., Azuma H, et al. Encephalopathy associated with haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following rotavirus infection. Eur J Pediatr. 1999. 158:133–7.

12). Riepenhoff-Talty M., Gouvea V., Evans MJ., Svensson L., Hoffenberg E., Sokol RJ, et al. Detection of group C rotavirus in infants with extrahepatic biliary atresia. J Infect Dis. 1996. 174:8–15.

13). Sanghai SR., Shah I., Bhatnagar S., Murthy A. Incidence and prognostic factors associated with biliary atresia in western India. Ann Hepatol. 2009. 8:120–2.
15). Naini BV., Lassman CR. Total parenteral nutrition therapy and liver injury: a histopathologic study with clinical correlation. Hum Pathol. 2012. 43:826–33.

16). Hertel PM., Estes MK. Rotavirus and biliary atresia: can causation be proven? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. 28:10–7.
17). Shivakumar P., Sabla GE., Whitington P., Chougnet CA., Bezerra JA. Neonatal NK cells target the mouse duct epithelium via Nkg2d and drive tissue-specific injury in experimental biliary atresia. J Clin Invest. 2009. 119:2281–90.

18). St-Jules DE., Watters CA., Iwamoto LM. Use of fish oil-based lipid emulsions in infants with intestinal failure-associated liver disease: a case series. Infant Child Adolesc Nutr. 2014. 6:6–13.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download