Abstract
Umbilical vein varix has diverse clinical features and an unpredictable course during the pregnancy and/or perinatal period. We report a rare case of isolated fetal varix of the intra-abdominal umbilical vein, which was associated with fetal cardiomegaly. After birth, the umbilical vein varix remained with continuous blood flow through the patent ductus venosus. In addition, persistent cardiomegaly was complicated with an atrial septal defect.
References
1. Sepulveda W, Mackenna A, Sanchez J, Corral E, Carstens E. Fetal prognosis in varix of the intrafetal umbilical vein. J Ultrasound Med. 1998; 17:171–5.

2. Valsky DV, Rosenak D, Hochner-Celnikier D, Porat S, Yagel S. Adverse outcome of isolated fetal intraabdominal umbilical vein varix despite close monitoring. Prenat Diagn. 2004; 24:451–4.

3. Fung TY, Leung TN, Leung TY, Lau TK. Fetal intraabdominal umbilical vein varix: what is the clinical significance? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 25:149–54.

4. Weissmann-Brenner A, Simchen MJ, Moran O, Kassif E, Achiron R, Zalel Y. Isolated fetal umbilical vein varix-prenatal sonographic diagnosis and suggested management. Prenat Diagn. 2009; 29:229–33.

5. Ismail H, Chang YL, Chang SD, Nusee Z. Fetal intraabdominal umbilical vein varix in monochorionic twins: is it significant? Malays J Med Sci. 2012; 19:69–73.
6. Bas-Lando M, Rabinowitz R, Samueloff A, Latinsky B, Schimmel MS, Chen O, et al. The prenatal diagnosis of isolated fetal varix of the intraabdominal umbilical vein is associated with favorable neonatal outcome at term: a case series. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013; 288:33–9.

7. Estroff JA, Benacerraf BR. Fetal umbilical vein varix: sonographic appearance and postnatal outcome. J Ultrasound Med. 1992; 11:69–73.

8. Navarro-Gonzalez T, Bravo-Arribas C, Fernandez-Pacheco RP, Gamez-Alderete F, de Leon-Luis J. Perinatal outcome after prenatal diagnosis of intraabdominal umbilical vein varix. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2013; 81:140–5.
Fig. 1.
Fetal intra-abdominal umbilical vein varix in a 28-week-old fetus. (A) transverse abdominal view of an obstetrical sonogram showing a hypoechoic tubular structure indicating an umbilical vein varix on the right side of the abdomen at the stomach level (identified on the left side of the abdomen without flow signals). (B) Four-chamber view of the fetus showing an enlarged fetal heart (fetal cardiomegaly), especially in the right atrium.
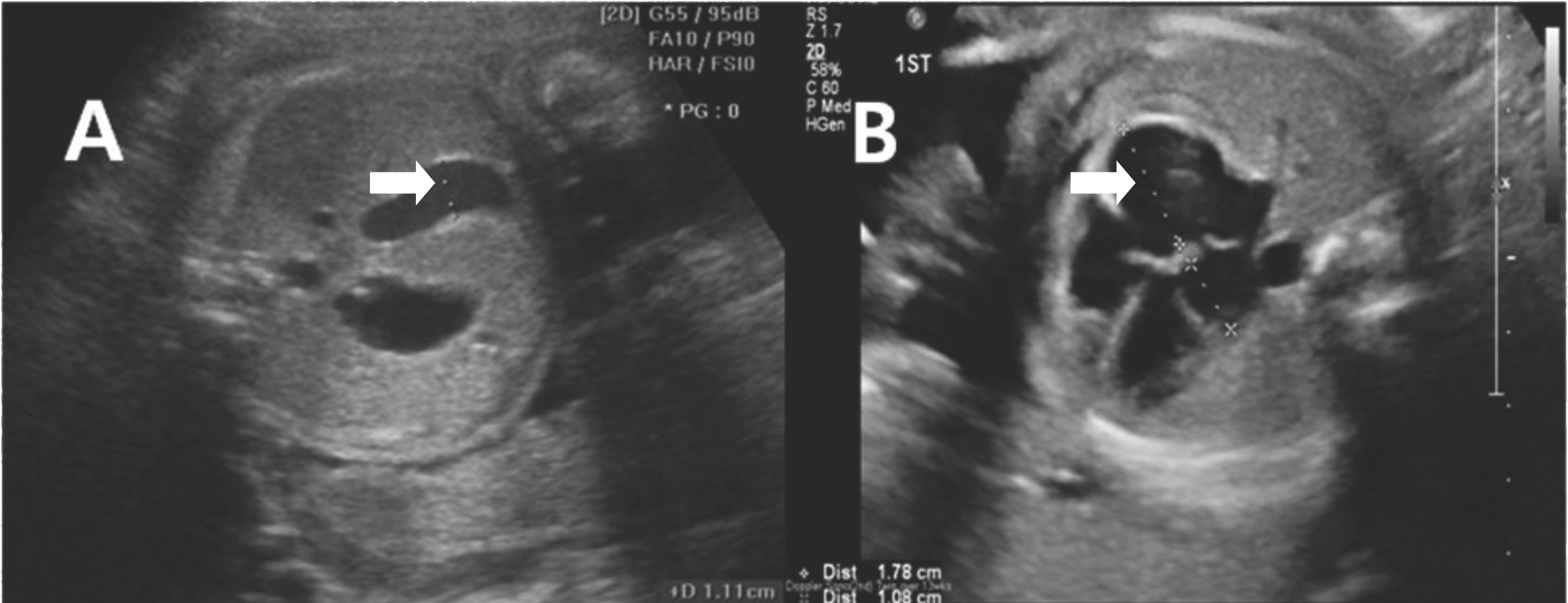
Fig. 2.
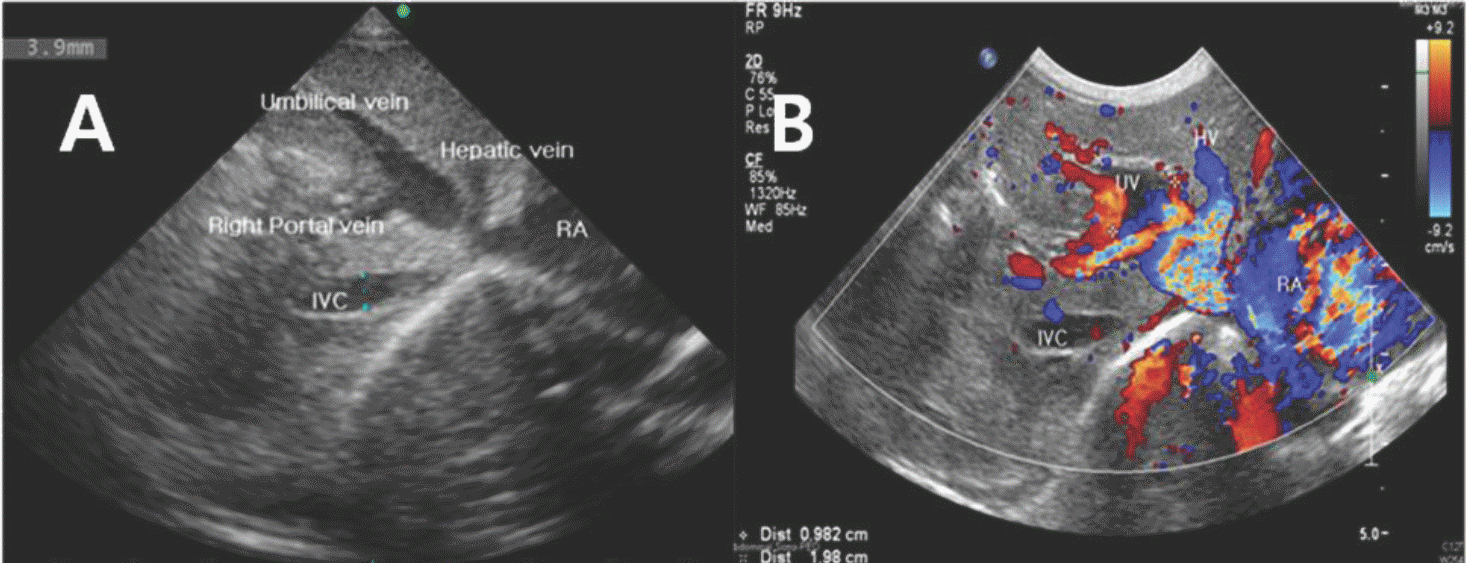
Remnant of intra-abdominal umbilical vein varix and persistent ductus venosus in a 12-day-old neonate. (A) Oblique view of an abdominal sonogram showing an unusual focally dilated vessel representing a remnant of intra-abdominal umbilical vein varix. (B) Color sonogram revealing continuous blood flow from the dilated vessel into the inferior vena cava just below the insertion of the hepatic veins through the persistent ductus venosus. Abbreviations: HV, hepatic vein; IVC, inferior vena cava; RA, right atrium; UV, umbilical vein.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download