Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to identify the risk factors of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) in neonates with respiratory diseases.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 58 term newborn infants with respiratory diseases who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of the Seoul Eulji Hospital between January 2008 and July 2014 and required airway intubation and mechanical ventilation within 24 hours of admission. The infants were divided into a PPHN group and a non-PPHN group. Their clinical characteristics; diagnoses at admission; initial blood test results; and changes in vital signs, blood gas analysis results, and ventilator parameters that occurred within 48 hours of admission were investigated.
Results
There were 16 infants in the PPHN group and 42 infants in the non-PPHN group. The incidence of secondary PPHN was 27.6%. The incidence of PPHN was significantly higher in infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) associated with extrapulmonary air leakage and meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) with secondary RDS as the cause. Respiratory rate over 80 breaths/min (P=0.032, OR 11.3, 95%, CI 1.23–103.57) and FiO2 over 0.8 (P=0.013, OR 16.8, 95% CI 1.82–154.68), when measured 6 hours after admission, were found to be statistically significant risk factors.
References
1. Kim DY, Bae SY, Joo JW, Kim MJ, Song ES, Choi YY. Frequency and clinical outcome of the respiratory tract disease in fullterm infant. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2007; 14:199–205.
2. Son SB, Kim KA, Yun SY, Ko SY, Lee YK, Shin SM. Oral sildenafil in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2011; 18:124–9.

3. Delaney C, Cornfield DN. Risk factors for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pulm Circ. 2012; 2:15–20.

4. Puthiyachirakkal M, Mhanna MJ. Pathophysiology, management, and outcome of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: a clinical review. Front Pediatr. 2013; 1:23. doi:. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2013.00023.

5. Gibbs RS. Diagnosis of intraamniotic infection. Semin Perinatol. 1997; 1:71–7.
6. Leuthner SR, Das UG. Low Apgar scores and the definition of birth asphyxia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2004; 51:737–45.

7. Sweet DG, Carnielli V, Greisen G, Hallman M, Ozek E, Plavka R, et al. European consensus guidelines on the management of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants-2010 update. Neonatology. 2010; 97:402–17.
8. Fanaroff AA. Meconium aspiration syndrome: historical aspects. J Perinatol. 2008; 28(Suppl 3):S3–7.

9. Vergnano S, Sharland M, Kazembe P, Mwansambo C, Heath PT. Neonatal sepsis: an international perspective. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005; 90:F220–4.

11. Gersony WM, Duc GV, Sinclair JC. PFC syndrome. Circulation. 1969; 40(Suppl 3):87.
12. Jun YH. Pathophysiology of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Korean J Pediatr. 2004; 47:707–15.
13. Lee EC, Choi MG, Shim GH, Song YH, Chey MJ. Comorbid risk factors of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn in infants with meconium aspiration syndrome. Neonatal Med. 2014; 21:166–71.

14. Gouyon JB, Ribakovsky C, Ferdynus C, Quantin C, Sagot P, Gouyon B. Severe respiratory disorders in term neonates. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2008; 22:22–30.

15. Razzaq A, Iqbal Quddusi A, Nizami N. Risk factors and mortality among newborns with persistent pulmonary hypertension. Pak J Med Sci. 2013; 29:1099–104.

16. Hernández-Díaz S, Van Marter LJ, Werler MM, Louik C, Mitchell AA. Risk factors for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:e272–82.
17. Nair J, Lakshminrusimha S. Update on PPHN: mechanisms and treatment. Semin Perinatol. 2014; 38:78–91.

18. Cabral JE, Belik J. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment. J Pediatr(Rio J). 2013; 89:226–42.

19. Bendapudi P, Barr S. Diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Paediatr Child Health. 2014; 24:12–6.

20. Sharma M, Mohan KR, Narayan S, Chauhan L. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: a review. Med J Armed Forces India. 2011; 67:348–53.

21. Park HK, Lim JW, Jun NL, Kim EA, Kim KS, Pi SY. Comparison of treatment outcomes in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2003; 10:29–38.
Fig. 1.
Vital sign such as (A) Respiratory rate (B) Mean blood pressure (C) Heart rate according to time in PPHN group and Non-PPHN group. ∗P<0.05
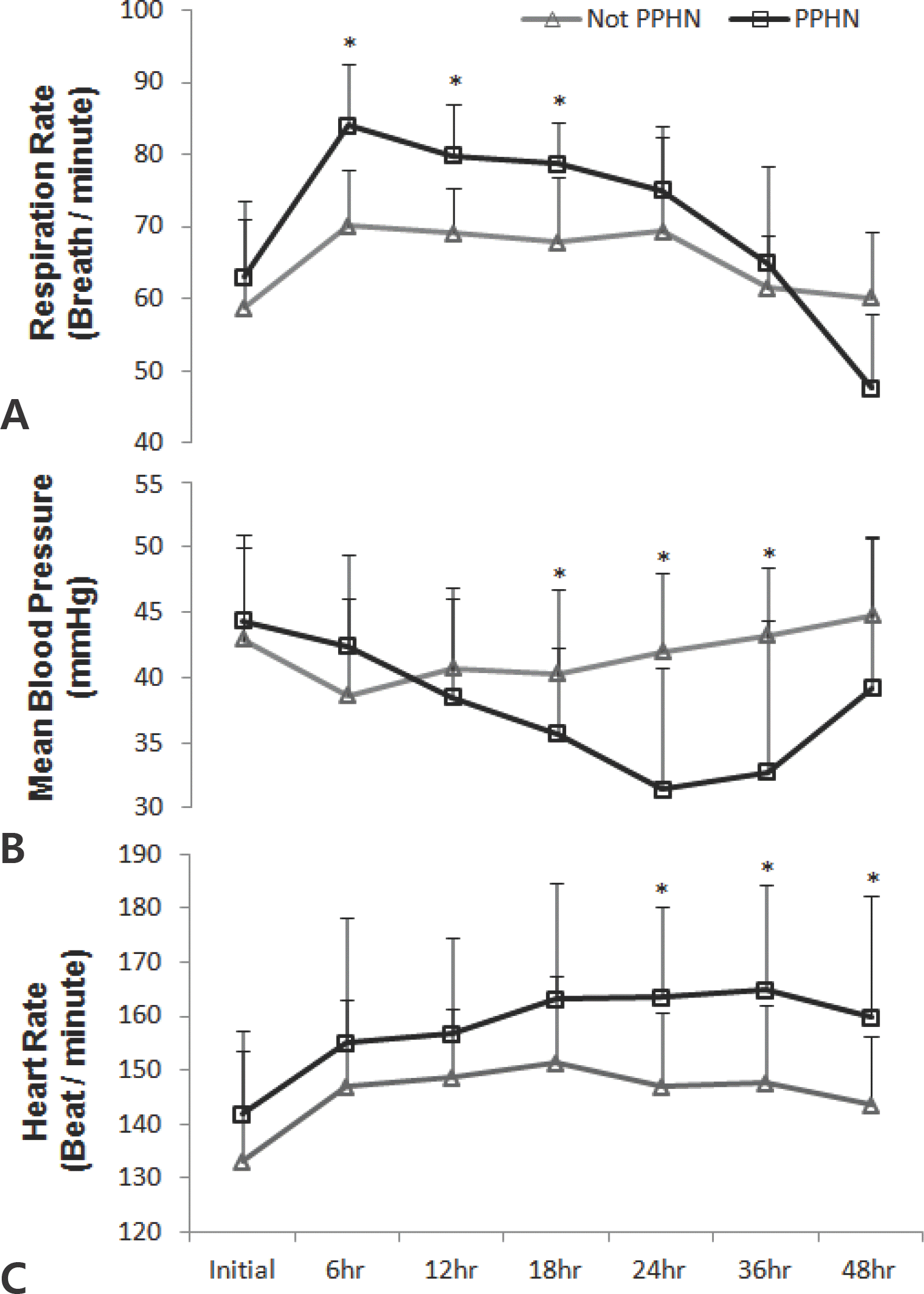
Fig. 2.
Blood gas analysis findings such as (A) pH (B) PCO2 (C) Base excess according to time in PPHN group and Non-PPHN group. ∗P<0.05
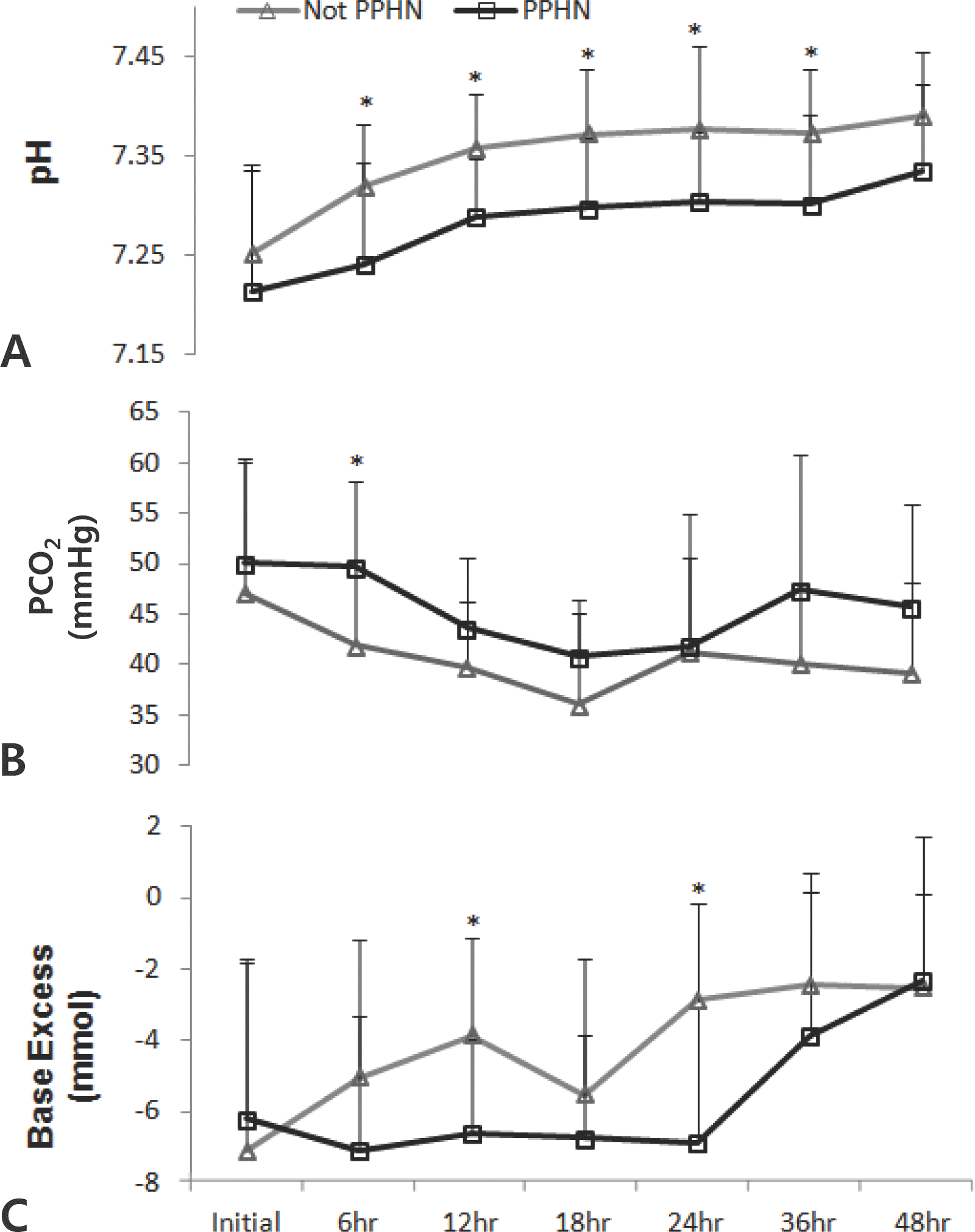
Fig. 3.
Ventilatory parameter such as (A) mean airway pressure (B) FiO2 according to time in PPHN group and Non-PPHN group. ∗P<0.05
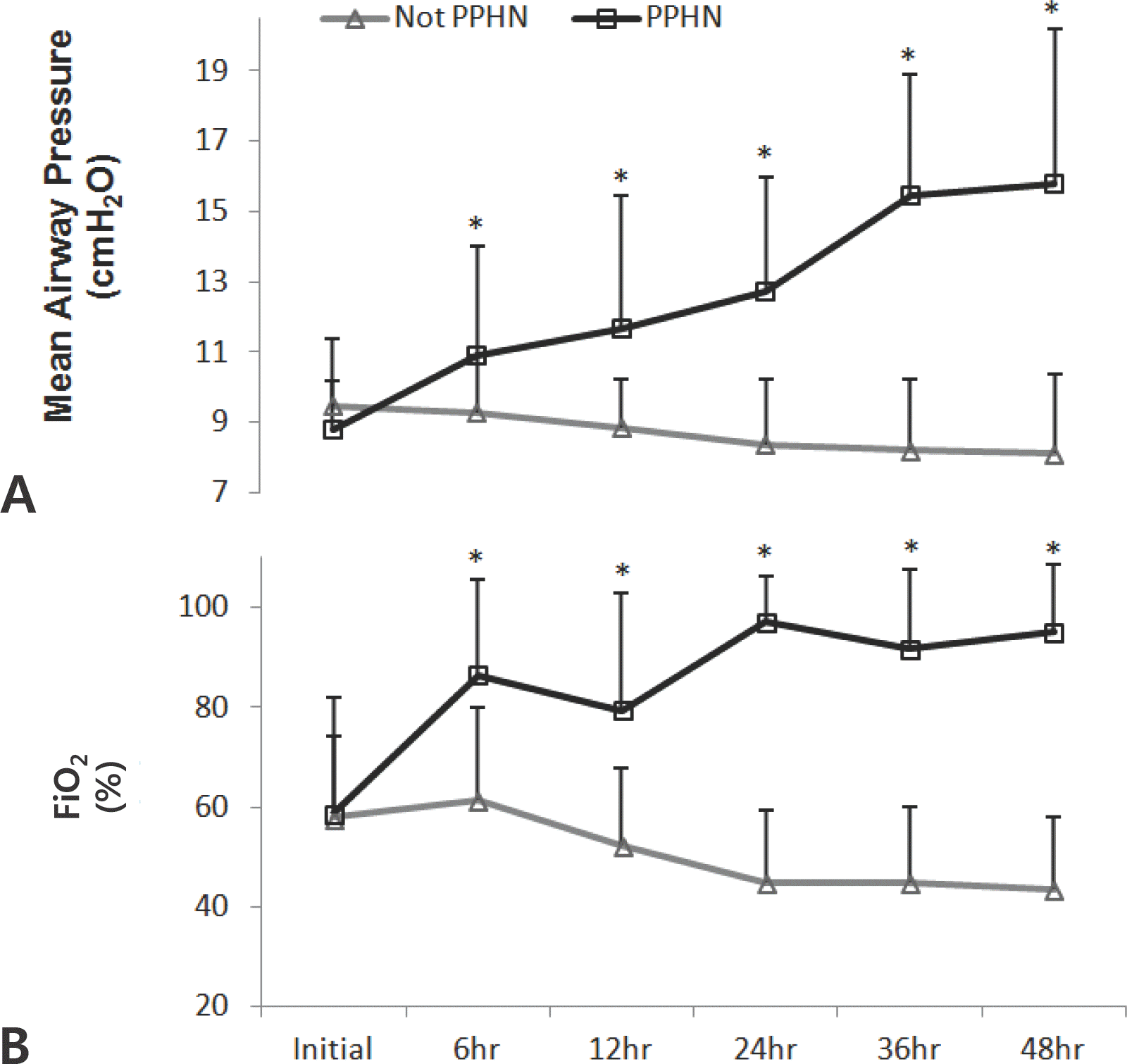
Table 1.
Clinical Characteristics of Study Subjects
Table 2.
Initial Diagnosis at Admission
Table 3.
Laboratory Findings at Admission




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download