Abstract
Hip arthroscopy has been useful for resolving unexplained pains of the hip joint, despite its clinical applicability came after many other joints. Surgical indications have been increasing recently. Moreover, additional surgical techniques allow both the anatomy and function to return to its normal state. Recently, the concepts and treatments for extra-articular pathologies, such as deep gluteal syndrome, ischiofemoral impingement, subspinal impingement and iliopsoas impingement as well as classic indication, such as femoroacetabular impingement, acetabular labral tear, loose bodies, and synovial osteochondromatosis have been introduced. We present a diagnosis and treatment for diverse indications of hip arthroscopy, preoperative considerations, surgical technique and postoperative rehabilitation.
Figures and Tables
Figure 2
Radiographic evaluation for hip arthroscopy. (A) Simple radiography. (B) Three-dimensional computed tomography of the hip. The angle in femoral head is alpha angle. Increased alpha angle is a evidence of cam impingement. (C) Magnetic resonance arthrography. (D) Ultrasonography. A, acetabulum; L, labrum; FH, femoral head.
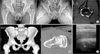
Figure 5
Iatrogenic injury in establishing portals. (A) Labral injury: the obturator cannula perforated the labrum (L). (B) Scuffing: iatrogenic chondral injury (arrow) in the femoral head. A, acetabulum; FH, femoral head.
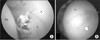
Figure 7
Serial fluoroscopic images of the classic portal insertion method in the central compartment. (A) Vacuum seal shadow due to negative intraarticular pressure is created by distraction of the joint. (B) Needle is inserted and the stylet is removed, then break the seal. (C) As obturator is inserted into the joint, the operator can identify successful insertion of the spinal needle by the shape of the spinal needle under fluoroscopy. (D) After check of intraarticular pin insertion, arthroscopy is inserted.
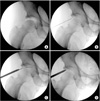
Figure 8
Paralabral space (PS; white arrow). A, acetabular bone; AC, acetabuar cartilage; L, labrum.
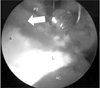
Figure 9
Methods of acetabular labral repair. (A) Looped repair or rolling repair: The fiber of suture anchor rolls up the torn labrum (L). In looped repair, eversion of L may be occurred after procedure. (B) Through or basement repair: The suture line is passed through the substance of the L and can fix the base area of the L. After the repair, the anatomical shape of the L may be preserved. A, acetabulum; AC, acetabular cartilage.
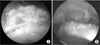
Figure 10
Acetabular labral reconstruction using autologous iliotibial band. (A) Labral defect by previous labral resection. (B) Harvest of iliotibial band from ipsilateral hip. (C) Harvested autogenous iliotibial band (triangle). (D) Arthroscopic labral reconstruction was performed. The harvested iliotibial band (triangle) was transferred and repaired on acetabular margin for labral defect. (E) Identification of a successful reconstructed labrum at 2nd look arthroscopy. Triangle is harvested iliotibial band. A, acetabulum; AC, acetabular cartilage; AL, anterolateral portal; HS, Harvest site; FH, femoral head.
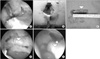
Figure 11
Motions of ligamentum teres according to hip rotation. While ligamentus teres is relaxed on internal rotation (IR), it is tensed on external rotation (ER) of the hip. FH, femoral head; LT, ligamentum teres; AF, acetabular fossa.

Figure 12
Arthroscopic femoroplasty. (A) Subchondral bone of the femoral head (FH)-neck junction was exposed for decompression. (B) After femoroplasty (arrow), the operator has to check the relationship between labrum (L) and FH.

Figure 13
Ischiofemoral impingement occurred at the ischiofemoral space (IS) between the ischium and lesser trochanter of femur (F). The quadratus femoris muscle was injured and high signal intensity (white arrow) was shown in magnetic resonance imaging. IT, ischial tuberosity.
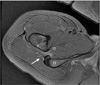
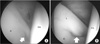
Figure 14
Acetabular labral tear by iliopsoas impingement is located more anteriorly than that by femoroacetabular impingement. (A) Spinal needle is located at 1 o'clock from the anterior portal and labral tear (white arrow) at the far anterior position. (B) Labral tear (white arrow) is found at 3 o'clock of acetabulum. A, acetabulum; FH, femoral head; L, labrum.
References
1. Konan S, Rayan F, Meermans G, Witt J, Haddad FS. Validation of the classification system for acetabular chondral lesions identified at arthroscopy in patients with femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:332–336.

2. Philippon MJ, Maxwell RB, Johnston TL, Schenker M, Briggs KK. Clinical presentation of femoroacetabular impingement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007; 15:1041–1047.

3. Kamegaya M, Saisu T, Nakamura J, Murakami R, Segawa Y, Wakou M. Drehmann sign and femoro-acetabular impingement in SCFE. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011; 31:853–857.

4. Kivlan BR, Martin RL, Sekiya JK. Response to diagnostic injection in patients with femoroacetabular impingement, labral tears, chondral lesions, and extra-articular pathology. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:619–627.

5. Ross JR, Bedi A, Stone RM, et al. Intraoperative fluoroscopic imaging to treat cam deformities: correlation with 3-dimensional computed tomography. Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42:1370–1376.
6. Eriksson E, Arvidsson I, Arvidsson H. Diagnostic and operative arthroscopy of the hip. Orthopedics. 1986; 9:169–176.

7. Brumback RJ, Ellison TS, Molligan H, Molligan DJ, Mahaffey S, Schmidhauser C. Pudendal nerve palsy complicating intramedullary nailing of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992; 74:1450–1455.

8. Aprato A, Giachino M, Masse A. Arthroscopic approach and anatomy of the hip. Muscles ligaments tendons J. 2016; 6:309–316.

9. Byrd JW, Pappas JN, Pedley MJ. Hip arthroscopy: an anatomic study of portal placement and relationship to the extra-articular structures. Arthroscopy. 1995; 11:418–423.

10. Robertson WJ, Kelly BT. The safe zone for hip arthroscopy: a cadaveric assessment of central, peripheral, and lateral compartment portal placement. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:1019–1026.

11. Dienst M, Kohn D. Hip arthroscopy. Minimal invasive diagnosis and therapy of the diseased or injured hip joint. Unfallchirurg. 2001; 104:2–18.
12. Jackson TJ, Stake CE, Trenga AP, Morgan J, Domb BG. Arthroscopic technique for treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthrosc Tech. 2013; 2:e55–e59.

13. Dandachli W, Najefi A, Iranpour F, Lenihan J, Hart A, Cobb J. Quantifying the contribution of pincer deformity to femoro-acetabular impingement using 3D computerised tomography. Skeletal Radiol. 2012; 41:1295–1300.

14. Blankenbaker DG, De Smet AA, Keene JS, Fine JP. Classification and localization of acetabular labral tears. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:391–397.

15. Redmond JM, El Bitar YF, Gupta A, Stake CE, Vemula SP, Domb BG. Arthroscopic acetabuloplasty and labral refixation without labral detachment. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43:105–112.

16. Lertwanich P, Ejnisman L, Torry MR, Giphart JE, Philippon MJ. Defining a safety margin for labral suture anchor insertion using the acetabular rim angle. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39:Suppl. 11S–16S.

17. Degen RM, Poultsides L, Mayer SW, et al. Safety of hip anchor insertion from the midanterior and distal anterolateral portals with a straight drill guide: a cadaveric study. Am J Sports Med. 2017; 45:627–635.

18. Philippon MJ, Nepple JJ, Campbell KJ, et al. The hip fluid seal: part I: the effect of an acetabular labral tear, repair, resection, and reconstruction on hip fluid pressurization. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:722–729.
19. Jackson TJ, Hammarstedt JE, Vemula SP, Domb BG. Acetabular labral base repair versus circumferential suture repair: a matched-paired comparison of clinical outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31:1716–1721.

20. Chahla J, Soares E, Bhatia S, Mitchell JJ, Philippon MJ. Arthroscopic technique for acetabular labral reconstruction using iliotibial band autograft. Arthrosc Tech. 2016; 5:e671–e677.

21. Nepple JJ, Larson CM, Smith MV, et al. The reliability of arthroscopic classification of acetabular rim labrochondral disease. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:2224–2229.

22. Stafford GH, Bunn JR, Villar RN. Arthroscopic repair of delaminated acetabular articular cartilage using fibrin adhesive. Results at one to three years. Hip Int. 2011; 21:744–750.

23. Marquez-Lara A, Mannava S, Howse EA, Stone AV, Stubbs AJ. Arthroscopic management of hip chondral defects: a systematic review of the literature. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32:1435–1443.

24. de SA D, Phillips M, Philippon MJ, Letkemann S, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR. Ligamentum teres injuries of the hip: a systematic review examining surgical indications, treatment options, and outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:1634–1641.

25. Kulcu DG, Naderi S. Differential diagnosis of intraspinal and extraspinal non-discogenic sciatica. J Clin Neurosci. 2008; 15:1246–1252.

26. Coppieters MW, Alshami AM, Babri AS, Souvlis T, Kippers V, Hodges PW. Strain and excursion of the sciatic, tibial, and plantar nerves during a modified straight leg raising test. J Orthop Res. 2006; 24:1883–1889.

27. Martin HD, Kelly BT, Leunig M, et al. The pattern and technique in the clinical evaluation of the adult hip: the common physical examination tests of hip specialists. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:161–172.

28. Meknas K, Kartus J, Letto JI, Christensen A, Johansen O. Surgical release of the internal obturator tendon for the treatment of retro-trochanteric pain syndrome: a prospective randomized study, with long-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17:1249–1256.

29. Benson ER, Schutzer SF. Posttraumatic piriformis syndrome: diagnosis and results of operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:941–949.
30. Dezawa A, Kusano S, Miki H. Arthroscopic release of the piriformis muscle under local anesthesia for piriformis syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2003; 19:554–557.

31. Martin HD, Shears SA, Johnson JC, Smathers AM, Palmer IJ. The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:172–181.

32. Hwang DS, Kang C, Lee JB, Cha SM, Yeon KW. Arthroscopic treatment of piriformis syndrome by perineural cyst on the sciatic nerve: a case report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18:681–684.

34. Johnson KA. Impingement of the lesser trochanter on the ischial ramus after total hip arthroplasty. Report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977; 59:268–269.

35. Viala P, Vanel D, Larbi A, Cyteval C, Laredo JD. Bilateral ischiofemoral impingement in a patient with hereditary multiple exostoses. Skeletal Radiol. 2012; 41:1637–1640.

36. Nakano N, Yip G, Khanduja V. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of extra-articular hip impingement syndromes. Int Orthop. 2017; 41:1321–1328.

37. Siebenrock KA, Steppacher SD, Haefeli PC, Schwab JM, Tannast M. Valgus hip with high antetorsion causes pain through posterior extraarticular FAI. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:3774–3780.

38. Tannast M, Hanke M, Ecker TM, Murphy SB, Albers CE, Puls M. LCPD: reduced range of motion resulting from extra- and intraarticular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:2431–2440.

39. Patti JW, Ouellette H, Bredella MA, Torriani M. Impingement of lesser trochanter on ischium as a potential cause for hip pain. Skeletal Radiol. 2008; 37:939–941.

40. Safran M, Ryu J. Ischiofemoral impingement of the hip: a novel approach to treatment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:781–785.

41. Jones CW, Biant LC, Field RE. Dislocation of a total hip arthroplasty following hip arthroscopy. Hip Int. 2009; 19:396–398.

42. de Sa D, Alradwan H, Cargnelli S, et al. Extra-articular hip impingement: a systematic review examining operative treatment of psoas, subspine, ischiofemoral, and greater trochanteric/pelvic impingement. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:1026–1041.

43. Hetsroni I, Poultsides L, Bedi A, Larson CM, Kelly BT. Anterior inferior iliac spine morphology correlates with hip range of motion: a classification system and dynamic model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:2497–2503.

44. Pan H, Kawanabe K, Akiyama H, Goto K, Onishi E, Nakamura T. Operative treatment of hip impingement caused by hypertrophy of the anterior inferior iliac spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:677–679.

45. Larson CM, Kelly BT, Stone RM. Making a case for anterior inferior iliac spine/subspine hip impingement: three representative case reports and proposed concept. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:1732–1737.

46. Hapa O, Bedi A, Gursan O, et al. Anatomic footprint of the direct head of the rectus femoris origin: cadaveric study and clinical series of hips after arthroscopic anterior inferior iliac spine/subspine decompression. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:1932–1940.

48. Alpert JM, Kozanek M, Li G, Kelly BT, Asnis PD. Cross-sectional
analysis of the iliopsoas tendon and its relationship to the acetabular labrum: an anatomic study. Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37:1594–1598.
49. Domb BG, Shindle MK, McArthur B, Voos JE, Magennis EM, Kelly BT. Iliopsoas impingement: a newly identified cause of labral pathology in the hip. HSS J. 2011; 7:145–150.

50. Cobb JP, Davda K, Ahmad A, Harris SJ, Masjedi M, Hart AJ. Why large-head metal-on-metal hip replacements are painful: the anatomical basis of psoas impingement on the femoral head-neck junction. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:881–885.
51. Browne JA, Polga DJ, Sierra RJ, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME. Failure of larger-diameter metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty resulting from anterior iliopsoas impingement. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:978978.e5–978.e8.

52. Piggott RP, Doody O, Quinlan JF. Iliopsoas tendon rupture: a new differential for atraumatic groin pain post-total hip arthroplasty. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015:bcr2014208518.

53. Winston P, Awan R, Cassidy JD, Bleakney RK. Clinical examination and ultrasound of self-reported snapping hip syndrome in elite ballet dancer. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:118–126.
54. Ilizaliturri VM Jr, Villalobos FE Jr, Chaidez PA, Valero FS, Aguilera JM. Internal snapping hip syndrome: treatment by endoscopic release of the iliopsoas tendon. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:1375–1380.

55. Ilizaliturri VM Jr, Buganza-Tepole M, Olivos-Meza A, Acuna M, Acosta-Rodriguez E. Central compartment release versus lesser trochanter release of the iliopsoas tendon for the treatment of internal snapping hip: a comparative study. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:790–795.
56. Nelson IR, Keene JS. Results of labral-level arthroscopic iliopsoas tenotomies for the treatment of labral impingement. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:688–694.

57. Tey M, Alvarez S, Ríos JL. Hip labral cyst caused by psoas impingement. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:1184–1186.

58. Zaltz I, Kelly BT, Larson CM, Leunig M, Bedi A. Surgical treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: what are the limits of hip arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. 2014; 30:99–110.

59. Matsuda DK. Protrusio acetabuli: contraindication or indication for hip arthroscopy? And the case for arthroscopic treatment of global pincer impingement. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:882–888.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download