Abstract
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) results from abnormal anatomic relationship between acetabulum and femoral head-neck junction, which causes secondary chondrolabral injury. FAI is the common cause of hip joint pain in young adults who have nearly normal hip joint structure. The pain usually progresses on hip flexion and internal rotation. Although it is still controversial whether FAI is one of the reason of secondary hip osteoarthritis or the contrary, instruments and surgical technique for treating FAI is continuing to improve. When we initially diagnosed with FAI, conservative treatment is recommended. But if the conservative treatment has no response, we can consider surgical intervention. The arthroscopic technique is one of the promising options, and it is the fastest growing fields for the treatment FAI.
Figures and Tables
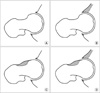 | Figure 2(A) Normal hip joint, (B) pincer type femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI) which shows decreased acetabular anteversion, (C) cam type FAI which shows decreased femoral head-neck offset, (D) mixed type FAI. |
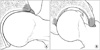 | Figure 3(A) Acetabular chondral injury caused deformed femoral head-neck anatomy in cam type femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI), but (B) in pincer type FAI, usually labrum injury precedes and sometimes following ipsilateral acetabular chondral injury is shown by lever-arm effect. |
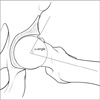 | Figure 4Alpha angle: the angle between the line from the femoral head center through the middle of the femoral neck and the line through a point where the contour of the femoral head-neck junction exceeds the radius of the femoral head. Normal alpha angle <50°. |
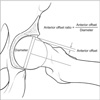 | Figure 5Anterior offset: the distance between the line from the femoral head center through the middle of the femoral neck and the parallel line which contact the femoral head anterior margin. Anterior offset ratio=anterior offset/femoral head diameter. |
References
1. Ito K, Leunig M, Ganz R. Histopathologic features of the acetabular labrum in femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (429):262–271.

2. Myers SR, Eijer H, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; (363):93–99.

3. Ganz R, Leunig M, Leunig-Ganz K, Harris WH. The etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip: an integrated mechanical concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:264–272.
4. Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (417):112–120.
5. Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1012–1018.
6. Cobb J, Logishetty K, Davda K, Iranpour F. Cams and pincer impingement are distinct, not mixed: the acetabular pathomorphology of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2143–2151.

8. Siebenrock KA, Kalbermatten DF, Ganz R. Effect of pelvic tilt on acetabular retroversion: a study of pelves from cadavers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (407):241–248.

9. Giori NJ, Trousdale RT. Acetabular retroversion is associated with osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (417):263–269.
10. Ochoa LM, Dawson L, Patzkowski JC, Hsu JR. Radiographic prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement in a young population with hip complaints is high. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2710–2714.

11. Reichenbach S, Jüni P, Werlen S, et al. Prevalence of camtype deformity on hip magnetic resonance imaging in young males: a cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62:1319–1327.

12. Hack K, Di Primio G, Rakhra K, Beaulé PE. Prevalence of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement morphology in asymptomatic volunteers. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:2436–2444.

13. Ahn T, Kim CH, Kim TH, et al. What is the prevalence of radiographic hip findings associated with femoroacetabular impingement in asymptomatic Asian volunteers? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474:2655–2661.

14. Gerhardt MB, Romero AA, Silvers HJ, Harris DJ, Watanabe D, Mandelbaum BR. The prevalence of radiographic hip abnormalities in elite soccer players. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:584–588.

15. Kapron AL, Anderson AE, Aoki SK, et al. Radiographic prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement in collegiate football players: AAOS Exhibit Selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:e111(1-10).
16. Ayeni OR, Farrokhyar F, Crouch S, Chan K, Sprague S, Bhandari M. Pre-operative intra-articular hip injection as a predictor of short-term outcome following arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:801–805.

17. Krych AJ, Griffith TB, Hudgens JL, Kuzma SA, Sierra RJ, Levy BA. Limited therapeutic benefits of intra-articular cortisone injection for patients with femoro-acetabular impingement and labral tear. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:750–755.

18. Emara K, Samir W, Motasem el H, Ghafar KA. Conservative treatment for mild femoroacetabular impingement. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011; 19:41–45.

19. Hunt D, Prather H, Harris Hayes M, Clohisy JC. Clinical outcomes analysis of conservative and surgical treatment of patients with clinical indications of prearthritic, intra-articular hip disorders. PM R. 2012; 4:479–487.

20. Guanche CA, Bare AA. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:95–106.

21. Parvizi J, Leunig M, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007; 15:561–570.

22. Laude F, Sariali E, Nogier A. Femoroacetabular impingement treatment using arthroscopy and anterior approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:747–752.

23. Clohisy JC, McClure JT. Treatment of anterior femoroacetabular impingement with combined hip arthroscopy and limited anterior decompression. Iowa Orthop J. 2005; 25:164–171.
24. Khan M, Habib A, de Sa D, et al. Arthroscopy up to date: hip femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32:177–189.

25. Kim PS, Hwang DS, Kang C, Lee JB, Lee WW, Han SC. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in young taekwondo players. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2011; 46:303–311.

26. Leunig M, Huff TW, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement: treatment of the acetabular side. Instr Course Lect. 2009; 58:223–229.
27. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic femoroplasty in the management of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:739–746.

28. Philippon MJ, Bolia I, Locks R, Utsunomiya H. Treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: labrum, cartilage, osseous deformity, and capsule. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2017; 46:23–27.
29. Khan M, Bedi A, Fu F, Karlsson J, Ayeni OR, Bhandari M. New perspectives on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016; 12:303–310.

30. Espinosa N, Rothenfluh DA, Beck M, Ganz R, Leunig M. Treatment of femoro-acetabular impingement: preliminary results of labral refixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:925–935.
31. Hwang DS, Kang C, Cha SM, Kim JH. Second-look hip arthroscopy after arthroscopic labrectomy of the hip: preliminary report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2009; 44:480–485.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


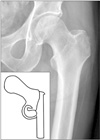
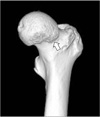
 XML Download
XML Download