Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effectiveness of internal fixation with a helical plate for displaced proximal humeral shaft fractures by analyzing the clinical outcomes of patients.
Materials and Methods
Fourteen displaced fractures of the proximal humeral shaft were treated by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) or by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) with the use of helical locking compression plates. We evaluated the adequacy of reduction, time-to-fracture healing, range of motion of the shoulder, and postoperative complications. The functional outcome of the shoulder was evaluated using a Constant-Murley shoulder score.
Results
Anatomical reduction of the fracture was obtained in nine cases treated by ORIF, and anatomical alignment was obtained in five cases treated by MIPO. All fractures were healed in an average of 14.9 weeks. The active range of motion of the shoulder was fully recovered in five cases, and restricted in nine cases, at around 12 months after surgery. The mean Constant-Murley shoulder score was 87.4 points, at around 12 months after surgery. There were no major complications, such as neurovascular injury, infection, loss of fixation, and nonunion.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
(A) A locking plate, PHILOS is contoured in a helical shape using the model of the humeurs. (B) A PHILOS was contoured on a helical plate. (C) A metaphyseal locking compression plate was contoured in a helical plate.
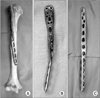
Figure 2
Case 12. (A) Initial anteroposterior radiograph of a 55-year-old woman shows a displaced simple spiral fracture of the proximal humeral shaft. (B) Radiographs after open reduction and internal fixation show anatomical reduction of the fracture fixed with lag screws and a helical plate made with PHILOS. (C) Radiographs 14 weeks after surgery show good fracture healing. (D) Eighteen months after surgery the plate and screws were removed due to shoulder pain by subacomical impingement.

Figure 3
Case 2. (A) Initial anteroposterior radiograph of a 44-year-old woman shows a complex fracture of the proximal humeral shaft. (B) Radiographs after minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis show anatomical alignment of the fracture fixed with a helical plate made with metaphyseal locking compression plate. (C) Radiographs 16 weeks after surgery show good fracture healing with callus formation. (D) Radiographs three years after surgery show consolidation of the callus with remodeling.

References
1. Sarmiento A, Zagorski JB, Zych GA, Latta LL, Capps CA. Functional bracing for the treatment of fractures of the humeral diaphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:478–486.
2. Zagorski JB, Latta LL, Zych GA, Finnieston AR. Diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. Treatment with prefabricated braces. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:607–601.
3. Modabber MR, Jupiter JB. Operative management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. Plate versus nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (347):93–104.
4. Rommens PM, McCormack R. Humerus, shaft. In : Rüedi TP, Buckley RE, Morgan CG, editors. AO principles of fracture management. 2nd ed. Stuttgart, New York: Thieme-Verlag;2007. p. 594–607.
5. McKee MD, Larsson S. Humeral shaft fractures. In : Bucholz RW, Court-Brown CM, Heckman JD, Torne P, editors. Rockwood and green's fractures in adults. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2010. p. 999–1038.
6. Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, Benca PJ. Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; 14:162–166.
7. McCormack RG, Brien D, Buckley RE, McKee MD, Powell J, Schemitsch EH. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82:336–339.
8. Ouyang H, Xiong J, Xiang P, Cui Z, Chen L, Yu B. Plate versus intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: an updated meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22:387–395.
9. Fernández Dell'Oca AA. The principle of helical implants. Unusual ideas worth considering. Injury. 2002; 33:Suppl 1. SA1–SA27.
10. Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Lorich DG. Helical plating of the proximal humerus. Injury. 2005; 36:1197–1200.
11. Tan JC, Kagda FH, Murphy D, Thambiah JS, Khong KS. Minimally invasive helical plating for shaft of humerus fractures: technique and outcome. Open Orthop J. 2012; 6:184–188.
12. Yang KH, Han DY, Park SJ, Yoo HW. Spiral plate fixation for treatment of proximal humerus fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2000; 35:71–76.
13. Byun YS, Shin DJ, Chang SA, Kwon DY. Inlay fibular autograft and helical LCP fixation for a segmental comminuted fracture of the osteoporotic proximal humerus: a case report. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:100–103.
14. Gill DR, Torchia ME. The spiral compression plate for proximal humeral shaft nonunion: a case report and description of a new technique. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:141–144.
15. Krishna KR, Sridhar I, Ghista DN. Analysis of the helical plate for bone fracture fixation. Injury. 2008; 39:1421–1436.
16. Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (214):160–164.
17. Jung SW. Indirect reduction maneuver and minimally invasive approach for displaced proximal humerus fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013; 5:66–73.
18. Gardner MJ, Lorich DG, Werner CM, Helfet DL. Second-generation concepts for locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2007; 36:460–465.
19. De Boer P. Diaphyseal fractures: principles. In : Rüedi TP, Buckley RE, Morgan CG, editors. AO principles of fracture management. 2nd ed. Stuttgart, New York: Thieme-Verlag;2007. p. 126–136.
20. Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, Kim JJ, Park KC. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; 29:189–194.
21. Ko SH, Lee SH, Cho BK. The treatment of humerus shaft simple fracture by MIPO technique. Clin Should Elbow. 2013; 16:27–32.
22. Oh CW, Byun YS, Oh JK, et al. Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98:54–60.
23. Shin SJ, Sohn HS, Do NH. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of humeral shaft fractures: a technique to aid fracture reduction and minimize complications. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:585–589.
24. Moon JG, Kwon HN, Biraris S, Shon WY. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a helical plate for metadiaphyseal complex fractures of the proximal humerus. Orthopedics. 2014; 37:e237–e243.
25. Bono CM, Grossman MG, Hochwald N, Tornetta P 3rd. Radial and axillary nerves. Anatomic considerations for humeral fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (373):259–264.
26. Smith J, Berry G, Laflamme Y, Blain-Pare E, Reindl R, Harvey E. Percutaneous insertion of a proximal humeral locking plate: an anatomic study. Injury. 2007; 38:206–211.
27. Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of proximal humeral fracture. Int Orthop. 2007; 31:657–664.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download