Abstract
Postoperative gas-forming bacterial infection is very rare. However, it can be a life threatening problem if not properly addressed. Authors treated a patient who was infected with gas forming Escherichia coli after both knee arthroplasty with incision and drainage, as well as arthroscopic synovectomy and antibiotics. Herein, we report a case of postoperative gas-forming bacterial infection with literature review.
Figures and Tables
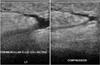 | Figure 2Duplex sonogram shows intramuscular or intermuscular space airfoaming abscess around the knee joints. LT, left. |
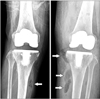
 | Figure 3(A) Computed tomography (CT) scan shows diffuse wall thickening with intramural air bubbles (arrows) in the bladder, (B) CT scan shows intermuscular abscess (arrows) in both legs—thigh to lower leg. |
References
1. Kumar A, Turney JH, Brownjohn AM, McMahon MJ. Unusual bacterial infections of the urinary tract in diabetic patients: rare but frequently lethal. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001; 16:1062–1065.
2. Nabi Z, Almukdad H, Alnassri A, Adli K, Adie E. Gas-forming urinary tract infection. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008; 18:652–654.
3. Kim YS, Woo YK, Lee KJ, Boo KH, Kwon SY. Deep infection caused by gas-forming bacteria after total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Hip Soc. 2009; 21:275–277.

4. Chun CH, Park JY, Kim JW, Kim JY. Total knee arthroplasty in diabetic patients. J Korean Knee Soc. 2005; 17:105–111.
5. Aghasi MK, Halperin N, Axer A. Unusual gas-forming infection with Escherichia coli. Injury. 1981; 12:288–290.

6. Chiari H. Non-clostridial gas infection in diabetes mellitus. Prague Med Wochenschr. 1893; 18:1.
7. Hitschmann E, Linderthal O. Ein weiterer Beitrag zur Pathologie und Aetiologie der Gangrene foudroyante, Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1900; 13:1057–1067.
8. Garg P, Patel R, Taraporvala FJ, Pispati A. Impact of urinary tract infection in primary joint replacement surgery. Sch J App Med Sci. 2015; 3:1612–1614.
9. Back MS, Hur JM, Jo KK, et al. A case of emphysematous cystitis due to E.coli and Candida albicans; successful management by appropriate antibiotics and adequate urinary drainage. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1997; 21:200–204.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download