Abstract
Stress fractures of the tibia are relatively common in military and young people. However, stress fracture of the proximal tibia is rare in elderly patients, but has been reported in association with osteoporosis, Paget disease, rheumatoid arthritis, pyrophosphate arthropathy, and knee deformities. We experienced a 65-year-old patient who did not have a chronic disease, with a stress fracture with primary degenerative knee osteoarthritis with varus deformity, which occurred at the proximal tibia, and we report on this unusual case with a literature review.
Figures and Tables
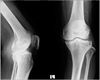 | Figure 1Proximal tibial fracture is missed on the initial radiologic evaluation in other hospital because plain radiographs do not include enough of the fracture site. |
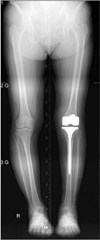
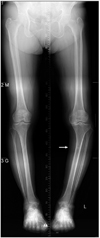 | Figure 2Orthoradiogram shows varus knee alignment with degenerative medial compartmental osteoarthritis of the knee joints at left (arrow). |
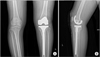
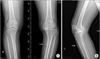 | Figure 3On initial radiographs, knee anteroposterior (A; arrow) and knee lateral (B; arrow), tibial stress fracture was apparent. An intracortical fracture was observed at the medial aspect of the proximal tibia with callus formation, suggesting a stress fracture at left. |
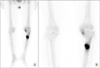 | Figure 4On bone scan (A) and (B), intense focal radioactive uptake in the left proximal tibial shaft, suggesting a fracture. Focally increased radioactive uptake in the medial compartment of the left knee suggests osteoarthritis. |
References
1. Devas M. Stress fractures. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;1975.
2. Resnick D, Guerra J Jr. Stress fractures associated with adjacent osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1981; 8:161–164.
Grundy M. Fractures of the femur in paget's disease of bone. Their etiology and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970. 52:252–263.
4. Young A, Kinsella P, Boland P. Stress fractures of the lower limb in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981; 63:239–243.

5. Ross DJ, Dieppe PA, Watt I, Newman JH. Tibial stress fracture in pyrophosphate arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983; 65:474–477.

6. Reynolds MT. Stress fractures of the tibia in the elderly associated with knee deformity. Proc R Soc Med. 1972; 65:377–380.
7. Kelly JM. Stress fractures in the tibia associated with knee deformities. J Ir Med Assoc. 1974; 67:97–99.
8. Sourlas I, Papachristou G, Pilichou A, Giannoudis PV, Efstathopoulos N, Nikolaou VS. Proximal tibial stress fractures associated with primary degenerative knee osteoarthritis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009; 38:120–124.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download