Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of arthroscopic debridement with continuous irrigation in patients with septic arthritis of the knee after failed primary arthroscopic treatment.
Materials and Methods
Among 69 patients undergoing arthroscopic debridement for septic arthritis of the knee from March 2008 to March 2013, 14 patients (5 male, 9 female; mean age, 68.9±11.3 years) with failed arthroscopic debridement for septic arthritis of the knee were reviewed retrospectively (mean follow-up period, 49.2±23.2 months). All 14 patients underwent re-do of the arthroscopic debridement, then continuous irrigation. Continuous irrigation following arthroscopic debridement was maintained for a mean 8.4±2.5 days. For clinical evaluation, Lysholm knee score and visual analogue scale (VAS) were used at 1 month, 3 months, and 12 months after surgery. During the entire follow-up period, recurrence of infection and operation-related complication were also assessed.
Results
Symptom improvement was observed in 12 cases (85.7%) of the 14 cases. Lysholm knee score was improved from 36.1±7.9 to 84.2±9.2 at 12 months after surgery (p<0.05). VAS was improved from 8.9±1.3 to 2.1±1.2 at 12 months after surgery (p<0.05). Synovial fluid cultures yielded positive findings in 9 of the 14 cases with the same bacteria in primary surgery. During the follow-up period, septic arthritis relapsed in 2 of the 5 cases with negative finding of cultures. After reoperation was performed in those 2 cases, no recurrence was observed to final follow-up. There was no complication related operation in any cases.
Figures and Tables
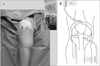 | Figure 1Establishment of a continuous irrigation system of the knee joint. (A) Continuous irrigation system after arthroscopic debridement for septic arthritis of the left knee. (B) Positioning of the drains in the knee. |
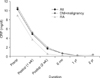 | Figure 2Changing pattern of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the patients with failed septic arthritis of the knee. Preop, preoperative; Postop, postoperative; DM, diabetes mellitus; RA, rheumatoid arthritis. |
References
1. Broy SB, Schmid FR. A comparison of medical drainage (needle aspiration) and surgical drainage (arthrotomy or arthroscopy) in the initial treatment of infected joints. Clin Rheum Dis. 1986; 12:501–522.

2. Jarrett MP, Grossman L, Sadler AH, Grayzel AI. The role of arthroscopy in the treatment of septic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981; 24:737–739.

3. Stutz G, Kuster MS, Kleinstück F, Gächter A. Arthroscopic management of septic arthritis: stages of infection and results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2000; 8:270–274.

4. Armstrong RW, Bolding F, Joseph R. Septic arthritis following arthroscopy: clinical syndromes and analysis of risk factors. Arthroscopy. 1992; 8:213–223.

5. Montgomery SC, Campbell J. Septic arthritis following arthroscopy and intra-articular steroids. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989; 71:540.

7. Vincent GM, Amirault JD. Septic arthritis in the elderly. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 251:241–245.

9. Tsumura H, Ikeda S, Torisu T. Debridement and continuous irrigation for the treatment of pyogenic arthritis caused by the use of intra-articular injection in the osteoarthritic knee: indications and outcomes. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2005; 13:52–57.

10. Kuo CL, Chang JH, Wu CC, Shen PH, Wang CC, Lin LC, et al. Treatment of septic knee arthritis: comparison of arthroscopic debridement alone or combined with continuous closed irrigation-suction system. J Trauma. 2011; 71:454–459.

11. Shukla A, Beniwal SK, Sinha S. Outcome of arthroscopic drainage and debridement with continuous suction irrigation technique in acute septic arthritis. . J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2014; 5:1–5.

12. Baek SH, Kim SS. Arthroscopic management for pyogenic arthritis with positive culture in the knee joint. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2012; 16:167–174.
13. Lee DC, Shon OJ, Kong BS. Arthroscopic treatment of septic knee arthritis in old aged group: prognostic factor. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2010; 14:114–119.
14. Bauer TW, Parvizi J, Kobayashi N, Krebs V. Diagnosis of periprosthetic infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:869–882.

15. Birmingham P, Helm JM, Manner PA, Tuan RS. Simulated joint infection assessment by rapid detection of live bacteria with real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:602–608.

16. The Korean Orthopaedic Association. Orthopaedics. 7th ed. Seoul: Choishineuihaksa;2013. p. 355.
18. Ivey M, Clark R. Arthroscopic debridement of the knee for septic arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; 199:201–206.

19. Thiery JA. Arthroscopic drainage in septic arthritides of the knee: a multicenter study. Arthroscopy. 1989; 5:65–69.

20. Jeon IH, Choi CH, Seo JS, Seo KJ, Ko SH, Park JY. Arthroscopic management of septic arthritis of the shoulder joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:1802–1806.

21. Kim SJ, Choi NH, Ko SH, Linton JA, Park HW. Arthroscopic treatment of septic arthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 407:211–214.

22. Ladner B, Nester K, Cascio B. Abdominal fluid extravasation during hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:131–135.

23. Parisien JS, Shaffer B. Arthroscopic management of pyarthrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 275:243–247.

24. Nelson JD. Antibiotic concentrations in septic joint effusions. N Engl J Med. 1971; 284:349–353.

25. Jackson RW, Parsons CJ. Distension-irrigation treatment of major joint sepsis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973; 96:160–164.

26. Gainor BJ. Instillation of continuous tube irrigation in the
septic knee at arthroscopy. A technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; 183:96–98.
27. D'Angelo GL, Ogilvie-Harris DJ. Septic arthritis following arthroscopy, with cost/benefit analysis of antibiotic prophylaxis. Arthroscopy. 1988; 4:10–14.
28. Chung WK, Slater GL, Bates EH. Treatment of septic arthritis of the hip by arthroscopic lavage. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993; 13:444–446.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download