Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and radiological outcomes following reduction of displaced medial humeral epicondyle fracture with a K-wire cross-fixation.
Materials and Methods
Seventeen patients (mean age, 12.7 years; 12 boys and 5 girls) who underwent cross-fixation using K-wires in displaced medial epicondyle fracture, regardless of dislocation, were included. Surgical outcomes were estimated using the Elbow Assessment Score of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association. Statistical significance between the elbow assessment score and age, fracture type, dislocation, displacement width, and size difference between bilateral medial epicondyles was estimated 6 weeks after surgery.
Results
The mean elbow assessment score among the patients was 98 points (range, 94-100 points). Displaced medial epicondyle fractures were radiologically classified according to 3 groups: minimally displaced (2 cases), entrapped (9 cases), and associated with dislocation (6 cases). The mean displacement width of the fracture fragment was 11.6 mm. At 6 weeks postoperatively, the medial length of the distal humerus (28.6 mm) was greater compared to that of the contralateral side (28.1 mm). Displacement of the fracture fragment was statistically related to the elbow assessment score (p=0.011). The other assessed values did not show statistical meaning.
Figures and Tables
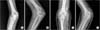 | Figure 1A 17-year-old male with a fracture in which bone fragment is positioned in the articular space. (A, B) Bone fragment positioned in the articular space, anteroposterior (AP) and lateral view. (C, D) Elbow was not reduced because of a bone fragment seen in AP and oblique view. |
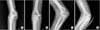 | Figure 2Pre- and postoperative state of a 17-year-old male. (A, C) Bone fragment positioned in the articular space, anteroposterior (AP) and oblique view. (B, D) Bone fragment was fixed by 4 K-wires seen in AP and oblique view. |
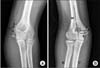 | Figure 3Method for measurement of displacement degree of bone fragment and medial epicondyle width. (A) Displacement degree was defined as distance of between proximal point of the fractured site and the same point of bone fragment (a, proximal point of the fractured site in the humerus; b, same point in a fractured bone fragment; D, distance between a and b). (B) Medial width was measured like (m, midline of the humerus which was the longitudinal axis; p, apex of the medial epicondyle; L, length; U, ulna side; R, radial side). |
References
1. Louahem DM, Bourelle S, Buscayret F, et al. Displaced medial epicondyle fractures of the humerus: surgical treatment and results A report of 139 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130:649–655.

2. Fowles JV, Slimane N, Kassab MT. Elbow dislocation with avulsion of the medial humeral epicondyle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:102–104.

3. Case SL, Hennrikus WL. Surgical treatment of displaced medial epicondyle fractures in adolescent athletes. Am J Sports Med. 1997; 25:682–686.

4. Woods GW, Tullos HS. Elbow instability and medial epicondyle fractures. Am J Sports Med. 1977; 5:23–30.

5. Park KB, Kwak YH. Treatment of medial epicondyle fracture without associated elbow dislocation in older children and adolescents. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:1190–1196.

6. Dias JJ, Johnson GV, Hoskinson J, Sulaiman K. Management of severely displaced medial epicondyle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1987; 1:59–62.

7. Kim SJ, Whang KS, Park YB. Medial epicondylar fracture in children. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1993; 28:234–239.

8. Cho HO, Kwak KD, Cho SD, Lee SI. Elbow dislocation with fracture of the medial humeral epicondyle. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1991; 26:1140–1144.
9. Fowles JV, Kassab MT, Moula T. Untreated intra-articular entrapment of the medial humeral epicondyle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:562–565.

10. Lee HH, Shen HC, Chang JH, Lee CH, Wu SS. Operative treatment of displaced medial epicondyle fractures in children and adolescents. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005; 14:178–185.

11. Oh JH, Kim YH. The current concepts in the treatment of proximal humerus fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2012; 25:94–104.

12. Cho DY, Song SJ, Yoon HK, Han SH, Chang JH, Yoon BH. Usefulness of the oblique radiographic view in ankle fractures. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2005; 9:94–98.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download