Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the position of the 10-mm-sized femur tunnel drilled aiming for the bifurcate ridge using anteromedial portal technique with 'Figure of 4 position' by 3-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) reconstruction images after anatomic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction and to evaluate it's propriety.
Materials and Methods
Out of 35 patients who underwent anatomic ACL reconstruction from March 2012 to February 2013, 32 patients who undergone postoperative 3D-CT scans were included in this study retrospectively. Medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle was reconstructed using Mimics, and then the position of the femoral tunnel was evaluated using the Bernard quadrant method and the results were compared with those of published literatures. The mean age of the patients was 32.6 years old. There were 25 cases of double-bundle ACL reconstruction with one femoral-two tibial tunnel. There were 7 cases of single bundle ACL reconstruction with one femoral-one tibial tunnel.
Results
The mean distance of the femoral tunnel center was 32.2%±2.9% (range, 27.4%-37.6%) along the line parallel to the Blumensaat's line from the posterior condylar surface and 46.7%±2.3% (range, 43.5%-51.1%) along the line perpendicular to the Blumensaat's line from the roof of the notch. In comparison with the results of published literature, although the center of the femoral tunnel was presented in the femoral footprint, it was located slightly more shallow and inferior than the center of the ACL footprints.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Fresh frozen allogenous Achilles tendon was split into 6-mm-diameter for posterolateral bundle, 8 mm diameter for anteromedial bundle with 20×10×10 mm bone block.

Figure 2
Operative technique during right knee anatomic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. (A) 'Figure of 4 position' which was knee flexion to 100° to 120° and varus state. (B) Micro-fracture awl tip marked the midpoint of the bifurcate ridge and 5 mm superior to the articular margin. (C) A guide pin was placed at the marked position and drilled out to the lateral cortex of the lateral condyle taking care to enclose the guide pin on the cartilage of the medial condyle but to avoid damaging it. (D) A 10-mm Sentinel drill bit was used to confirm the location of the tunnel without articular cartilage damage. (E) A 20-mm-depth bone tunnel was made in the anatomical position. (F) ACL graft was viewed through the central portal.
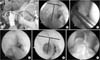
Figure 3
Three-dimensional reconstruction image using the Mimics program and tunnel measurement of the right knee using Bernard's quadrant method. (A) Medial-lateral view of the femoral condyle in the strictly lateral position where both condyles were superimposed. (B) In the distal view, the medial femoral condyle was removed at the highest point of the intercondylar notch (white arrow). (C) Leaving lateral femoral condyle was rotated back to the 'strictly lateral position' which was confirmed by superimposing onto (A). (D) Measurement of femoral tunnel location using the quadrant method described by Bernard et al.16)
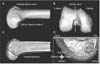
Figure 4
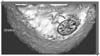
Distributed red dots of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) femoral tunnels according to our anteromedial portal technique using the quadrant method described by Bernard et al.16) Each marker represents the geographic mean distribution of ACL femoral tunnel location (☆, Current study; ★, Lertwanich et al.18); *, Bird et al.17); ¤, Zantop et al.20)).
References
1. Gabriel MT, Wong EK, Woo SL, Yagi M, Debski RE. Distribution of in situ forces in the anterior cruciate ligament in response to rotatory loads. J Orthop Res. 2004; 22:85–89.

2. Yagi M, Wong EK, Kanamori A, Debski RE, Fu FH, Woo SL. Biomechanical analysis of an anatomic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2002; 30:660–666.

3. Colombet P, Robinson J, Christel P, et al. Morphology of anterior cruciate ligament attachments for anatomic reconstruction: a cadaveric dissection and radiographic study. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:984–992.

4. Steckel H, Starman JS, Baums MH, Klinger HM, Schultz W, Fu FH. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament double bundle structure: a macroscopic evaluation. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2007; 17:387–392.

5. Tsukada H, Ishibashi Y, Tsuda E, Fukuda A, Toh S. Anatomical analysis of the anterior cruciate ligament femoral and tibial footprints. J Orthop Sci. 2008; 13:122–129.

6. Forsythe B, Kopf S, Wong AK, et al. The location of femoral and tibial tunnels in anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction analyzed by three-dimensional computed tomography models. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:1418–1426.

7. Loh JC, Fukuda Y, Tsuda E, Steadman RJ, Fu FH, Woo SL. Knee stability and graft function following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: comparison between 11 o'clock and 10 o'clock femoral tunnel placement. 2002 Richard O'Connor Award paper. Arthroscopy. 2003; 19:297–304.
8. Ferretti M, Ekdahl M, Shen W, Fu FH. Osseous landmarks of the femoral attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament: an anatomic study. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23:1218–1225.

9. Hussein M, van Eck CF, Cretnik A, Dinevski D, Fu FH. Prospective randomized clinical evaluation of conventional single-bundle, anatomic single-bundle, and anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: 281 cases with 3- to 5-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 40:512–520.
10. Steiner ME, Smart LR. Flexible instruments outperform rigid instruments to place anatomic anterior cruciate ligament femoral tunnels without hyperflexion. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:835–843.

11. Hensler D, Working ZM, Illingworth KD, Thorhauer ED, Tashman S, Fu FH. Medial portal drilling: effects on the femoral tunnel aperture morphology during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:2063–2071.

12. Araujo PH, van Eck CF, Macalena JA, Fu FH. Advances in the three-portal technique for anatomical single- or double-bundle ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1239–1242.

13. Kim DW, Lee K, Kim YW, Yang SJ, Seo JG, Kim JG. Comparative analysis of double bundle and single bundle ACL reconstruction with tibialis anterior allograft. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2008; 12:198–204.
14. Peterson RK, Shelton WR, Bomboy AL. Allograft versus autograft patellar tendon anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a 5-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2001; 17:9–13.
15. Linn RM, Fischer DA, Smith JP, Burstein DB, Quick DC. Achilles tendon allograft reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knee. Am J Sports Med. 1993; 21:825–831.

16. Bernard M, Hertel P, Hornung H, Cierpinski T. Femoral insertion of the ACL. Radiographic quadrant method. Am J Knee Surg. 1997; 10:14–21. discussion 21-2
17. Bird JH, Carmont MR, Dhillon M, et al. Validation of a new technique to determine midbundle femoral tunnel position in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using 3-dimensional computed tomography analysis. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:1259–1267.

18. Lertwanich P, Martins CA, Asai S, Ingham SJ, Smolinski P, Fu FH. Anterior cruciate ligament tunnel position measurement reliability on 3-dimensional reconstructed computed tomography. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:391–398.

19. Giron F, Cuomo P, Edwards A, Bull AM, Amis AA, Aglietti P. Double-bundle "anatomic" anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a cadaveric study of tunnel positioning with a transtibial technique. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23:7–13.

20. Zantop T, Diermann N, Schumacher T, Schanz S, Fu FH, Petersen W. Anatomical and nonanatomical double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: importance of femoral tunnel location on knee kinematics. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:678–685.
21. Bedi A, Raphael B, Maderazo A, Pavlov H, Williams RJ 3rd. Transtibial versus anteromedial portal drilling for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a cadaveric study of femoral tunnel length and obliquity. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:342–350.

22. Pombo MW, Shen W, Fu FH. Anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: where are we today? Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:1168–1177.

23. Nakagawa T, Takeda H, Nakajima K, et al. Intraoperative 3-dimensional imaging-based navigation-assisted anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:1161–1167.

24. Takeda Y, Iwame T, Takasago T, et al. Comparison of tunnel orientation between transtibial and anteromedial portal techniques for anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using 3-dimensional computed tomography. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:195–204.

25. Youm YS, Cho SD, Eo J, Lee KJ, Jung KH, Cha JR. 3D CT analysis of femoral and tibial tunnel positions after modified transtibial single bundle ACL reconstruction with varus and internal rotation of the tibia. Knee. 2013; 20:272–276.

26. Rue JP, Ghodadra N, Bach BR Jr. Femoral tunnel placement in single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a cadaveric study relating transtibial lateralized femoral tunnel position to the anteromedial and posterolateral bundle femoral origins of the anterior cruciate ligament. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:73–79.
27. Yagi M, Kuroda R, Nagamune K, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M. Double-bundle ACL reconstruction can improve rotational stability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 454:100–107.

28. Kato Y, Ingham SJ, Kramer S, Smolinski P, Saito A, Fu FH. Effect of tunnel position for anatomic single-bundle ACL reconstruction on knee biomechanics in a porcine model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18:2–10.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download