Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze the diagnostic availability and to examine the co-relation between pedobaragraphy and radiography of pediatric flexible flatfoot.
Materials and Methods
Seventeen patients and ten normal children were studied. In radiographic evaluation, the talo-1st metatarsal angle was measured on anteroposterior radiographs; and the talo-1st metatarsal angle, the talo-horizontal angle, the calcaneal pitch, and the talocalcaneal angle were measured on lateral radiographs. In pedobarography, foot pressures were subdivided into eight areas for measurement of contact time, ratio of measured area and to investigate the relation between the degree of the medial deviation of the Center of pressure line and the radiographic measurements.
Results
Flat foot group and normal group showed statistically significant difference in every angle measured in lateral radiographs. The foot pressure ratios of the lateral sides in forefoot and the medial and lateral sides of midfoot and the medial side of hindfoot between the flexible flatfoot group and normal group showed statistically significant difference in pedobarography and ratio of contact area in forefoot and hindfoot showed significant change in statistics but no changes in contact time. The relation between pedobarography and radiography was investigated: foot pressure of the medial and lateral side of forefoot and the talocalcaneal angle showed significant relation in statistics and foot pressure of the medial and lateral side of mid foot and every angle measured in lateral radiographs showed significant relation in statistics. Contact time of midfoot and every radiographic value measured in lateral radiograph showed significant relation in statistics and contact area of forefoot and midfoot showed significant relation with every radiographic value measured in lateral radiographs. In addition, medial deviation of center of pressure line showed significant relation in statistics with talus-first metatarsal angle measured on anteroposterior radiographs and talo-horizontal angle and talus-first metatarsal angle measured on lateral radiographs.
Conclusion
The results of this study showed correlation between radiologic methods and pedobarography in diagnosis of pediatric flexible flatfoot and pedobarography is an useful tool in quantitative and qualitative analysis of the degree of foot deformity and medial deviation of center of pressure line.
Figures and Tables
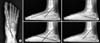 | Figure 1Radiographic indices in a flatfoot. (A) Anteroposterior view: talo-1st metatarsal angle. (B) Lateral view: talo-1st metatarsal angle. (C) Lateral view: calcaneal pitch. (D) Lateral view: talocalcaneal angle. (E) Lateral view: talo-horizontal angle. |
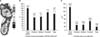 | Figure 2Pedobarographic result. (A) Foot pressure data. (B) Contact time data. (C) Contact area data. ROP, roll of process. |
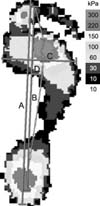 | Figure 3Anteroposterior index (B/A) and center of pressure excursion index (D/C). A, anteroposterior length of the foot; B, anteroposterior length of the path of the center of pressure; C, maximum width of the foot; D, lateral deviation of the center of pressure from the construction. |
References
1. Ananthakrisnan D, Ching R, Tencer A, Hansen ST Jr, Sangeorzan BJ. Subluxation of the talocalcaneal joint in adults who have symptomatic flatfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1147–1154.
3. Han SH, Jung M, Lee JW. Pedobarographic analysis in functional foot orthosis. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2006; 10:125–132.
4. Mickle KJ, Steele JR, Munro BJ. Is the foot structure of preschool children moderated by gender? J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28:593–596.

5. Jameson EG, Davids JR, Anderson JP, Davis RB 3rd, Blackhurst DW, Christopher LM. Dynamic pedobarography for children: use of the center of pressure progression. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28:254–258.
6. Harris EJ, Vanore JV, Thomas JL, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of pediatric flatfoot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:341–373.

7. Pauk J, Daunoraviciene K, Ihnatouski M, Griskevicius J, Raso JV. Analysis of the plantar pressure distribution in children with foot deformities. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2010; 12:29–34.
8. Park ES, Kim HW, Park CI, Rha DW, Park CW. Dynamic foot pressure measurements for assessing foot deformity in persons with spastic cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:703–709.

9. Alvarez C, De Vera M, Chhina H, Black A. Normative data for the dynamic pedobarographic profiles of children. Gait Posture. 2008; 28:309–315.

10. Oeffinger DJ, Pectol RW Jr, Tylkowski CM. Foot pressure and radiographic outcome measures of lateral column lengthening for pes planovalgus deformity. Gait Posture. 2000; 12:189–195.

11. Bae HS, Park CI, Shin JC, Park JW. The changes of plantar pressure and pathway of center of pressure in foot during the gait in normal preschool children with age. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:1041–1047.
12. Moon HW, Park SI, Rah UW, Lee IY, Yim SY, Kim JH. Foot pressure measurement using F-scan system in normal Korean adults. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1995; 19:289–295.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download