Abstract
There are no standard guidelines for treatment of massive rotator cuff tears. In this article, we reviewed the various modalities for treatment of massive rotator cuff tears, especially focusing on arthroscopic treatment. Selection of one of a variety of treatment modalities is essential for understanding pathogenesis, biomechanics and reparability of massive rotator cuff tears. The best clinical results have been reported with arthroscopic complete repair of massive rotator cuff tear. Satisfactory results have also been reported with other various arthroscopic treatment methods, including simple debridement, partial repair, biceps tenotomy or tendesis, and augmentation using a tissue substitution. However few long-term follow up results are available with these salvage options. Treatment of massive rotator cuff tears is difficult due to high incidence of irreparable tears and re-tear rate. Thus, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of various treatment modalities is thought to be helpful to improving the outcome of treatment of massive rotator cuff tears.
Figures and Tables
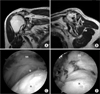 | Figure 1(A) Pre-operative magnetic resonance imaging shows a massive rotator cuff tear with severe tendon retraction and (B) fatty degeneration. (C) Arthroscopic finding of the same patient shows severe retraction of tendons. (D) Rotator cuff tendons could not be restored to the original footprint, despite of mobilization; therefore partial repair was performed. H, humeral head; G, Glenoid; SS, supraspinatus; SC, subscapularis; IS, infraspinatus; TM, teres minor. |
References
1. Denard PJ, Lädermann A, Jiwani AZ, Burkhart SS. Functional outcome after arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears in individuals with pseudoparalysis. Arthroscopy. 2012. 28:1214–1219.

3. Post M, Silver R, Singh M. Rotator cuff tear. Diagnosis and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983. 173:78–91.
4. Gerber C, Fuchs B, Hodler J. The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. 82:505–515.

5. Burkhart SS. Arthroscopic treatment of massive rotator cuff tears. Clinical results and biomechanical rationale. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 267:45–56.
6. Nobuhara K, Hata Y, Komai M. Surgical procedure and results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 304:54–59.

7. Tauro JC. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: analysis of technique and results at 2- and 3-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 1998. 14:45–51.

8. Inman VT, Saunders JB, Abbott LC. Observations of the function of the shoulder joint. 1944. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 330:3–12.
9. Lo IK, Burkhart SS. Arthroscopic repair of massive, contracted, immobile rotator cuff tears using single and double interval slides: technique and preliminary results. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:22–33.

10. Albritton MJ, Graham RD, Richards RS 2nd, Basamania CJ. An anatomic study of the effects on the suprascapular nerve due to retraction of the supraspinatus muscle after a rotator cuff tear. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003. 12:497–500.

11. Abrams JS. Arthroscopic approach to massive rotator cuff tears. Instr Course Lect. 2006. 55:59–66.
12. Gerber C, Meyer DC, Schneeberger AG, Hoppeler H, von Rechenberg B. Effect of tendon release and delayed repair on the structure of the muscles of the rotator cuff: an experimental study in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:1973–1982.
13. Gerber C, Galantay RV, Hersche O. The pattern of pain produced by irritation of the acromioclavicular joint and the subacromial space. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998. 7:352–355.

14. MacDonald PB, Altamimi S. Principles of arthroscopic repair of large and massive rotator cuff tears. Instr Course Lect. 2010. 59:269–280.
15. Walch G, Boulahia A, Calderone S, Robinson AH. The 'dropping' and 'hornblower's' signs in evaluation of rotator-cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:624–628.

16. Alqunaee M, Galvin R, Fahey T. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for subacromial impingement syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012. 93:229–236.

17. Rockwood CA Jr, Williams GR Jr, Burkhead WZ Jr. Débridement of degenerative, irreparable lesions of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:857–866.

18. Warner JJ, Parsons IM 4th. Latissimus dorsi tendon transfer: a comparative analysis of primary and salvage reconstruction of massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001. 10:514–521.

19. Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC. Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 304:78–83.
20. Thomazeau H, Boukobza E, Morcet N, Chaperon J, Langlais F. Prediction of rotator cuff repair results by magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 344:275–283.

21. Davidson JF, Burkhart SS, Richards DP, Campbell SE. Use of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging to predict rotator cuff tear pattern and method of repair. Arthroscopy. 2005. 21:1428.
22. Sugihara T, Nakagawa T, Tsuchiya M, Ishizuki M. Prediction of primary reparability of massive tears of the rotator cuff on preoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003. 12:222–225.

23. Zanetti M, Gerber C, Hodler J. Quantitative assessment of the muscles of the rotator cuff with magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 1998. 33:163–170.

24. Yoo JC, Ahn JH, Yang JH, Koh KH, Choi SH, Yoon YC. Correlation of arthroscopic repairability of large to massive rotator cuff tears with preoperative magnetic resonance imaging scans. Arthroscopy. 2009. 25:573–582.

25. Burkhead WZ Jr, Scheinberg RR, Box G. Surgical anatomy of the axillary nerve. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1992. 1:31–36.

27. Bigliani LU, Cordasco FA, McLlveen SJ, Musso ES. Operative repair of massive rotator cuff tears: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1992. 1:120–130.

28. Cofield RH, Parvizi J, Hoffmeyer PJ, Lanzer WL, Ilstrup DM, Rowland CM. Surgical repair of chronic rotator cuff tears. A prospective long-term study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83:71–77.
29. Musil D, Sadovský P, Stehlík J. Massive tears of rotator cuff - comparison of mini-open and arthroscopic techniques. Part 1. Mini-open technique. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2006. 73:387–393.
30. Bartl C, Kouloumentas P, Holzapfel K, et al. Long-term outcome and structural integrity following open repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2012. 6:1–8.

31. Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C. The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90:2423–2431.

32. Vastamäki M, Lohman M, Borgmästars N. Rotator cuff integrity correlates with clinical and functional results at a minimum 16 years after open repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. 471:554–561.

33. Kim DH, Elattrache NS, Tibone JE, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a single-row versus double-row suture anchor technique for rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34:407–414.

34. Mazzocca AD, Millett PJ, Guanche CA, Santangelo SA, Arciero RA. Arthroscopic single-row versus double-row suture anchor rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:1861–1868.

35. Charousset C, Grimberg J, Duranthon LD, Bellaiche L, Petrover D. Can a double-row anchorage technique improve tendon healing in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair?: a prospective, nonrandomized, comparative study of double-row and single-row anchorage techniques with computed tomographic arthrography tendon healing assessment. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:1247–1253.
36. Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J. Functional and structural outcome after arthroscopic full-thickness rotator cuff repair: single-row versus dual-row fixation. Arthroscopy. 2005. 21:1307–1316.

37. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:219–224.

38. Tauro JC. Arthroscopic repair of large rotator cuff tears using the interval slide technique. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:13–21.

39. Debeyre J, Patie D, Elmelik E. Repair of ruptures of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965. 47:36–42.

40. Warner JJ. Management of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: the role of tendon transfer. Instr Course Lect. 2001. 50:63–71.
41. Zanotti RM, Carpenter JE, Blasier RB, Greenfield ML, Adler RS, Bromberg MB. The low incidence of suprascapular nerve injury after primary repair of massive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997. 6:258–264.

42. Cho NS, Yi JW, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic biceps augmentation for avoiding undue tension in repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2009. 25:183–191.

43. Bond JL, Dopirak RM, Higgins J, Burns J, Snyder SJ. Arthroscopic replacement of massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears using a GraftJacket allograft: technique and preliminary results. Arthroscopy. 2008. 24:403–409.e1.

44. Berth A, Neumann W, Awiszus F, Pap G. Massive rotator cuff tears: functional outcome after debridement or arthroscopic partial repair. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010. 11:13–20.

45. Burkhart SS, Nottage WM, Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Kohn HS, Pachelli A. Partial repair of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 1994. 10:363–370.

46. Burkhart SS, Barth JR, Richards DP, Zlatkin MB, Larsen M. Arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears with stage 3 and 4 fatty degeneration. Arthroscopy. 2007. 23:347–354.

47. Duralde XA, Bair B. Massive rotator cuff tears: the result of partial rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005. 14:121–127.

48. Moser M, Jablonski MV, Horodyski M, Wright TW. Functional outcome of surgically treated massive rotator cuff tears: a comparison of complete repair, partial repair, and debridement. Orthopedics. 2007. 30:479–482.

49. Porcellini G, Castagna A, Cesari E, Merolla G, Pellegrini A, Paladini P. Partial repair of irreparable supraspinatus tendon tears: clinical and radiographic evaluations at long-term follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011. 20:1170–1177.

50. Gartsman GM. Massive, irreparable tears of the rotator cuff. Results of operative debridement and subacromial decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997. 79:715–721.

51. Liem D, Lengers N, Dedy N, Poetzl W, Steinbeck J, Marquardt B. Arthroscopic debridement of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2008. 24:743–748.

52. Fenlin JM Jr, Chase JM, Rushton SA, Frieman BG. Tuberoplasty: creation of an acromiohumeral articulation-a treatment option for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002. 11:136–142.

53. Scheibel M, Lichtenberg S, Habermeyer P. Reversed arthroscopic subacromial decompression for massive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004. 13:272–278.

54. Lee BG, Cho NS, Rhee YG. Results of arthroscopic decompression and tuberoplasty for irreparable massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy. 2011. 27:1341–1350.

55. Verhelst L, Vandekerckhove PJ, Sergeant G, Liekens K, Van Hoonacker P, Berghs B. Reversed arthroscopic subacromial decompression for symptomatic irreparable rotator cuff tears: mid-term follow-up results in 34 shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010. 19:601–608.

56. Rodosky MW, Harner CD, Fu FH. The role of the long head of the biceps muscle and superior glenoid labrum in anterior stability of the shoulder. Am J Sports Med. 1994. 22:121–130.

57. Warner JJ, McMahon PJ. The role of the long head of the biceps brachii in superior stability of the glenohumeral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:366–372.

58. Yamaguchi K, Riew KD, Galatz LM, Syme JA, Neviaser RJ. Biceps activity during shoulder motion: an electromyographic analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 336:122–129.

59. Walch G, Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Nové-Josserand L, Neyton L, Szabo I. Arthroscopic tenotomy of the long head of the biceps in the treatment of rotator cuff tears: clinical and radiographic results of 307 cases. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005. 14:238–246.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download