Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of our study was to assess the anomalous location and course of the superficial peroneal nerve (SPN), which were come across during exposure of distal fibula fracture.
Materials and Methods
We operated on 238 cases of ankle fractures, and examined the anomalous location and course of SPN around the distal part of the fibula. The study was performed prospectively.
Results
The mean length of surgical exposure was 9.8 cm. In 10 (4%) of 238 cases, the nerve was anomalous in its course, which was in parallel with the distal fibula and rapidly curved anteriorly at 3.5 cm proximal to the tip of the fibula. We found 3 cases of injury to the SPN; one was completely transected, the second was partially transected, and the third was stretched over the fracture site, at 2.5 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm proximal to the tip of distal fibula, respectively.
Figures and Tables
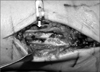
Figure 1
(A) Gross photograph of superficial peroneal nerve (white arrow) totally transected and sucked in fracture site. (B) Radiograph in same case with Danis-Weber type A fracture.

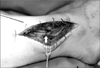
Figure 2
Gross photograph of partially transected superficial peroneal nerve (white arrow) over fracture site of lateral malleolus.
References
1. Standring S, Borley NR, Collins P. Gray's anatomy. 2008. 40th ed. London: Chruchill Livingstone;1411–1428.
2. Adkison DP, Bosse MJ, Gaccione DR, Gabriel KR. Anatomical variations in the course of the superficial peroneal nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:112–114.

3. Agthong S, Huanmanop T, Sasivongsbhakdi T, Ruenkhwan K, Piyawacharapun A, Chentanez V. Anatomy of the superficial peroneal nerve related to the harvesting for nerve graft. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008. 30:145–148.

4. Blair JM, Botte MJ. Surgical anatomy of the superficial peroneal nerve in the ankle and foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 305:229–238.

5. Huene DB, Bunnell WP. Operative anatomy of nerves encountered in the lateral approach to the distal part of the fibula. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:1021–1024.

6. Solomon LB, Ferris L, Tedman R, Henneberg M. Surgical anatomy of the sural and superficial fibular nerves with an emphasis on the approach to the lateral malleolus. J Anat. 2001. 199:717–723.

7. Hughes JL, Weber H, Willenegger H, Kuner EH. Evaluation of ankle fractures: non-operative and operative treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:111–119.
8. Canovas F, Bonnel F, Kouloumdjian P. The superficial peroneal nerve at the foot. Organisation, surgical applications. Surg Radiol Anat. 1996. 18:241–244.
9. Rosson GD, Dellon AL. Superficial peroneal nerve anatomic variability changes surgical technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 438:248–252.

10. O'Neill PJ, Parks BG, Walsh R, Simmons LM, Miller SD. Excursion and strain of the superficial peroneal nerve during inversion ankle sprain. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:979–986.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download